Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Intracranial hemorrhage due to hyperperfusion syndrome is a severe carotid artery stent placement complication of extremely high-grade stenosis, causing hemodynamic insufficiency. To prevent hyperperfusion syndrome, we attempted intentional residual stent stenosis and implemented “gentle” carotid artery stent placement, defined as carotid artery stent placement using a closed-cell stent coupled with slight balloon predilation, without balloon postdilation. Gradual stent expansion was expected. We investigated the incidence of hyperperfusion syndrome and long-term outcomes after gentle carotid artery stent placement.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We included patients who underwent carotid artery stent placement for extremely high-grade stenosis from January 2015 to March 2019. We defined extremely high-grade stenosis as carotid stenosis with conventional angiographic “slow flow” and a reduced MCA signal intensity on MRA. A reduced MCA signal intensity was defined as MCA with a relative signal intensity of <0.9 in the ipsilateral compared with the contralateral MCA. We evaluated the stent diameter, CBF on SPECT, hyperperfusion syndrome, and intracranial hemorrhage. We defined hyperperfusion syndrome as a triad of ipsilateral headache, seizure, and hemiparesis.
RESULTS: Twenty-eight of the 191 patients met our inclusion criteria. After carotid artery stent placement, their median minimal stent diameter was 2.9 mm, which expanded to 3.9 mm at 4 months. Neither cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome nor intracranial hemorrhage occurred.
CONCLUSIONS: The gentle carotid artery stent placement strategy for intentional residual stent stenosis may prevent hyperperfusion syndrome in high-risk patients. Stents spontaneously dilated in 4 months.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- AI
- asymmetric index
- AVDO2
- arteriovenous difference of oxygen
- CAS
- carotid artery stent placement
- HI
- hemodynamic insufficiency
- ex-HS
- extremely high-grade carotid artery stenosis
- HPP
- hyperperfusion phenomenon
- HPS
- hyperperfusion syndrome
- ICH
- intracerebral hemorrhage
- MLD
- minimal luminal diameter
- OEF
- oxygen extraction fraction
- PSV
- peak systolic velocity
- rCBF
- regional CBF
- SI
- signal intensity
Hyperperfusion syndrome (HPS) is a critical complication of carotid revascularization.1-4 HPS occurs after revascularization of extremely high-grade carotid artery stenosis (ex-HS) causing cerebral hemodynamic insufficiency.1,5 SPECT was used in Japan to assess hemodynamic insufficiency before carotid artery stent placement (CAS) in 127 (82.5%) of 154 institutions;6 however, the risk of HPS was evaluated routinely by only 102 (15.5%) of 664 anesthesiologists in a US survey about carotid endarterectomy,7 and SPECT was not included in the survey. Thus, a simple index to identify high-risk patients is required. Classic angiographic “slow flow” in the MCA4 or reduced MCA signal intensity (SI) on MRA8 is a feasible index in most facilities. We, therefore, defined an ex-HS with a carotid artery stenosis rate of > 80% or a minimal luminal diameter (MLD) of <1 mm, coupled with angiographic slow flow and reduced SI in the ipsilateral MCA, as hemodynamic insufficiency (HI) criteria.
The prevention of HPS has not been established,9,10 though staged revascularization is a treatment option.11,12 Therefore, we attempted to perform intentional residual stent stenosis to prevent marked hyperperfusion after CAS. To retain stent stenosis intentionally, we implemented “gentle” CAS, defined as CAS using a closed-cell stent coupled with slight balloon predilation, without poststenting balloon dilation. Compared with open-cell stents, the closed-cell stents may slowly self-expand and decrease embolic complications by avoiding dislodgement of the plaque while the stent expands, because the radial force in closed-cell stents is weaker than that in open-cell stents.13 Gradual and gentle self-expansion of the stent was the expected outcome.
We investigated the incidences of hyperperfusion phenomenon (HPP), HPS, and intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and the long-term clinical and angiographic outcomes after gentle CAS for ex-HS identified by the HI criteria.8 Furthermore, we evaluated the validity of the HI criteria.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For this retrospective observational cohort study, we included patients who underwent elective gentle CAS for ex-HS from January 2015 to March 2019 and MRA and DWI before and after CAS. We measured the carotid artery stenosis rate according to the NASCET criteria.14 We defined elective CAS as scheduled CAS in asymptomatic patients or in those who had experienced their latest ischemic attack ≥30 days prior. We excluded patients under the following circumstances: 1) They underwent CAS within 29 days of the last ischemic attack, 2) had an ipsilateral CAS history, 3) had a contraindication to MR imaging, 4) experienced unsuccessful introduction of a stent, 5) underwent CAS for lesions without ex-HS, or 6) underwent CAS with an open-cell stent for ex-HS.
Evaluation
We evaluated the patients’ baseline characteristics; the relative SI of the M1 segment on MRA; carotid lesions with high signal in T1-weighted black-blood MR imaging;15 the MLD before CAS; the carotid artery stenosis rate (NASCET method) before and after CAS;14 the minimal stent diameter immediately after and at 4 months after CAS; additional balloon angioplasty for severe stenosis at 4 months; HPP, ICH, and HPS after CAS; number of patients with new ischemic lesions and the number of lesions as observed on DWI after CAS; any symptomatic stroke or myocardial infarction within 30 days after CAS; and any symptomatic stroke within 4 months after CAS. To estimate the HI degree, we accessed the ultrasonographic peak systolic velocity (PSV), SPECT,16 blood-sampling arteriovenous differences of oxygen (AVDO2), and the oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) before and after CAS.17,18 Furthermore, we investigated the minimal stent diameter immediately after additional balloon angioplasty in patients who underwent additional balloon angioplasty at 4 months.
Slow Flow in the MCA
Evidence of slow flow in the MCA was defined as external carotid circulation delineation earlier than that of the corresponding internal carotid circulation.4
Reduced MCA Signal Intensity
We measured the SI on the bilateral MCA M1 segments on MRA and defined MCA relative SI as follows: (SI on the Affected-Side M1) / (SI on the Contralateral M1).
We defined the reduced MCA SI as an MCA relative SI of < 0.9.
MRA and DWI
We performed MRA and DWI using a 3T MR imaging machine equipped with an 8-channel sensitivity encoding head coil. 3D TOF-MRA was performed using a 3D fast-field echo sequence. The DWI protocol was echo-planar imaging. The parameters are summarized in Online Table 1. The baseline MRA and DWI values were obtained the day before CAS. A second MRA and DWI were performed between 24 and 48 hours after CAS, and only new lesions, with reference to the baseline DWI, were regarded as new ischemic lesions due to CAS.
Gentle CAS for Intentional Residual Stent Stenosis
Patients provided written informed consent to undergo CAS. We performed CAS through transbrachial catheterization with the patient under local anesthesia. A 6F (0.088-inch internal diameter) guiding sheath, 90-cm long, designed for transbrachial access, was positioned in the affected common carotid artery proximal to the stenosis.19 All patients received 5000 U of heparin intravenously immediately after the 6F guiding sheath was introduced into the brachial artery. A 5F temporary bipolar pacing (J-Tip) catheter was positioned in the right ventricle through the femoral vein to prevent bradycardia or cardiac arrest during CAS. We coaxially introduced a 0.010-inch flexible microguidewire and a microcatheter through the ex-HS. We replaced the flexible microguidewire with a 0.014-inch hard guidewire and replaced the microcatheter coaxially with a filter as the embolic distal protection device. We performed balloon predilation with a semicompliant balloon catheter and subsequently deployed a closed-cell stent over the residual stenosis. We did not perform poststenting balloon dilation of the residual stent stenosis (Online Table 2).
For balloon predilation, we used 3.0- and 4.0-mm-diameter balloon catheters for lesions with and without hyperintensity on T1-weighted black-blood MR imaging, respectively.15,20 Lesions with hyperintensity on T1 black-blood MR imaging have been reported to be vulnerable,15, and we used a 3.0-mm balloon for these lesions to facilitate a gentler procedure. We inflated the balloons at 8 atm of nominal pressure and did not inflate balloons to diameters greater than the nominal.
Conventional Angiographic Investigation after CAS and Repeat Treatment of Significant Stenosis
We expected the stent to self-expand during a few months, as reported previously.21 Some stents, however, can fail to expand and in-stent restenosis may occur; therefore, we performed conventional angiography at 4 months (within the range of 3–6 months after CAS) to accurately assess the in-stent carotid artery stenosis rate and measure the stent diameter, as reported in previous studies,22,23 in addition to ultrasonographic investigation. We defined an in-stent stenosis rate of >70% as significant stenosis. When the MLD was significantly stenotic at 4 months, we performed additional balloon angioplasty of the in-stent stenosis with a semicompliant 5.0-mm-diameter balloon and inflated it at 14 atm of the rated burst pressure. The diameter of the balloon was increased to 5.17 mm. We obtained fluoroscopic images of the stent using digital angiography and measured the minimal stent diameter on the lateral-view image immediately after CAS and after 4 months. When additional balloon angioplasty was performed at 4 months, the minimal stent diameter was measured after the procedure.
AVDO2 and OEF
Before positioning a temporary pacing catheter, we introduced a 4F catheter into the dominant-sided jugular bulb via transfemoral venous access.17 We measured the arterial oxygen content (CtaO2) and the venous oxygen content (CtvO2) with a blood gas analyzer.17,18 The AVDO2 was calculated as follows: AVDO2 = CtaO2–CtvO2. The OEF was calculated as follows: OEF = (CtaO2–CtvO2) / CtaO2.
SPECT
We performed SPECT and measured the CBF at 1 week before and 3 or 4 hours after CAS. We measured the CBF with iodine 123 N-isopropyl-p-iodoamphetamine (123I-IMP) combined with a graph plot method. A dose of 185 MBq of 123I-IMP was infused rapidly into the right cubital vein. ROIs were automatically set with the CBF analyzing software (NeuroFlexor; Aggero MedTech).
The asymmetric index percentage (AI%) was defined as follows: (CBF in the Affected MCA Territory/CBF in the Contralateral MCA Territory) × 100 (%).
The regional CBF percentage (rCBF%) was defined as follows: (CBF in the Affected MCA Territory/CBF in the Ipsilateral Cerebellum) × 100 (%).
HPP
We assessed the HPP according to 4 SPECT definitions: 1) AI% before and after CAS, <100% and >100%, respectively; 24 2) AI% before and after CAS , <100% and >120%, respectively;10 3) rCBF% after CAS–rCBF% before CAS, >10%;16 and 4) rCBF% increase, defined as follows: [(rCBF% after CAS–rCBF% before CAS)/rCBF% before CAS] × 100, > 100% (doubling).4
HPS
In 1981, HPS was defined as a clinical triad of ipsilateral headache, seizures, and neurologic deficits in the absence of cerebral ischemia after a successful carotid endarterectomy.3
Management before and after CAS
Patients began receiving dual-antiplatelet therapy, comprising clopidogrel (75 mg/day) and pletal (Cilostazol) (100 mg/day) administration25,26 for at least 7 days before CAS, and they continued to receive this therapy for 3–6 months of angiographic investigation. On the day before CAS, the patients received the following sedative drugs via the oral route: 2.5 g of TSUMURA Yokukansan (TJ-54; Kampo, a Japanese herbal medicine), 3 times a day,27 and 2.0 g of etizolam, twice a day. TJ-54 and etizolam were administered until 7 and 2 days after CAS, respectively. When blood pressure was elevated after CAS, antihypertensive drugs were administered until 7 days after CAS to reduce the systolic and diastolic blood pressures to below 150 and 90 mm Hg, respectively.
Ethics Approval
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the study was performed and the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. The relevant ethics committee approved our retrospective analysis (TGE01011-024). Written informed consent for participation and publication was not required. The study was based on an opt-out model of enrollment, which was permitted by the ethics committee.
Statistical Analysis
Non-normally distributed continuous variables are expressed as medians and interquartile ranges. For nonparametric data, the Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to compare paired variables. A P value < .05 was considered statistically significant. We used the JMP software (Version 15.1; SAS Institute) for all statistical analyses.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight (14.7%) of the 191 patients who were scheduled to undergo CAS during the study period met our inclusion criteria (Online Fig 1). Their age (median, interquartile range) was 78 years (72–81 years). Twenty-five patients (89%) were men, 16 (57%) were symptomatic, and vascular risk factors were controlled (Online Table 3). They did not have a contralateral ex-HS or occlusion of the carotid artery.
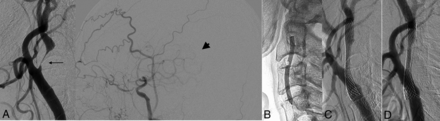
Nine patients (32.1%) with hyperintensity on T1-weighted black-blood MR imaging underwent balloon predilation with a semicompliant 3.0-mm balloon catheter. The median NASCET% decreased after CAS (P < .001). The median MLD values before and after CAS were 0.63 and 2.9 mm, respectively (P < .001). Gentle CAS successfully provided intentional residual stent stenosis (Fig 1). The MCA relative SI increased after CAS (P < .001), and the PSV decreased after CAS (P < .001). The AI% and rCBF% increased after CAS (P < .001). The AVDO2 decreased (P = .02), and the OEF remained unchanged after CAS (Table). The HI criteria successfully identified patients with HI.
Angiograms before and during gentle CAS and at 4 months. A, Angiograms before CAS reveal extremely high-grade stenosis (arrow) and a “reduced MCA perfusion territory” in the middle cerebral artery (arrowhead). B, An inflated balloon with a 3.0-mm diameter. C, Angiography after CAS shows a residual stent stenosis. D, Angiography at 4 months shows self-expansion of the stent.
Changes in luminal diameters and hemodynamic factors before and after CAS
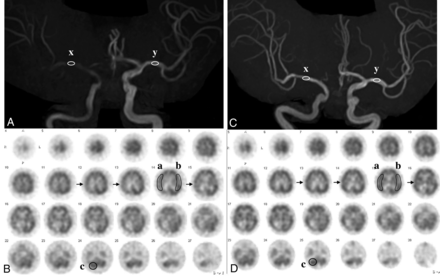
Blood pressure after CAS was controlled (Table). The incidence of HPP was dependent on the definition. HPP occurred in 11 patients according to definition 1, in 1 patient according to definition 2, and in 8 patients according to definition 3 (Figs 1 and 2). HPP did not occur according to definition 4, and CBF was not doubled. The patient with HPP of definition 2 was included in those of definitions 1 and 3. In patients with HPP, the stents were stenotic after CAS. AI% and rCBF% slightly increased after CAS, and AVDO2 and OEF reciprocally decreased (Online Table 4).
MRA and SPECT in the same case as in Fig 1. A, MRA before CAS reveals an MCA rSI value of 0.44: [(x: 784) divided by (y: 1775)]. B, SPECT before CAS demonstrates a CBF decrease in the right MCA territory (arrows). AI was 80.3%% [(a: 31.94) divided by (b: 39.78)], and rCBF% was 83.9% [(a: 31.94) divided by (c: 38.07)]. C, MRA after CAS reveals an MCA rSI of 1.16: [(x: 2967) divided by (y: 2667)]. D, SPECT after CAS demonstrates a CBF increase in the right MCA territory (arrows). AI% was 92.7% [(a: 37.95) divided by (b: 40.93)] and rCBF% was 99.9% [(a: 37.95) divided by (c: 37.99)]. rSI indicates relative signal intensity.
Neither HPS nor ICH occurred, and no patient experienced symptomatic cerebral infarction immediately after CAS. Neither stroke nor myocardial infarction occurred within 30 days, though 1 patient died due to heart failure 26 days after CAS.
Twenty-five (92.6%) of 27 surviving patients underwent conventional angiography at 4 months. The stent spontaneously and sufficiently expanded, and the median minimal stent diameter increased from 2.9 to 3.9 mm at 4 months (P < .001) (Online Fig 2). Three patients (3/25; 12.0%) had severe in-stent stenosis and underwent additional balloon angioplasty with the 5.0-mm balloon at 14 atm. Their stents were sufficiently dilated from 3.2- to 4.4-mm median minimal stent diameter. No HPS or ICH occurred after additional balloon angioplasty. One of 2 patients who withdrew from angiographic investigation underwent ultrasonography at 4 months, which revealed a PSV of 52.7 cm/s, no stenosis, and no turbulent flow inside the stent. No strokes occurred in the 27 patients within 4 months after CAS.
DISCUSSION
Our results suggested that the HI criteria were effective as a simple, valid tool to identify high-risk patients and that the gentle CAS strategy successfully provided intentional stent stenosis and prevented HPS and ICH in high-risk patients with ex-HS. Stents spontaneously dilated at 4 months, and 12.0% of them achieved sufficient dilation without HPS or ICH after long-term additional balloon angioplasty.
Ex-HS, defined by the HI criteria, identified high-risk patients with HI. High-risk patients can be identified without SPECT or OEF when the HI criteria are used hereafter. The AI% and rCBF% of these patients slightly increased, and the AVDO2 decreased reciprocally after CAS. HPP was dependent on the definition and occurred in 0–11 patients after CAS. In 8 patients with HPP of definition 3, rCBF% slightly increased from 80.2% to 94.9%. This rCBF% increase is similar to that of a previous report in which the average AI% increased from 70.3% to 87.6% in 9 patients after stage 1 angioplasty, before stage 2 stent placement.12 A previous study reported that inadequate dilation or extensive dissection occurred in 4 of 44 patients after stage 1 angioplasty. The 4 patients underwent regular CAS immediately, and HPP occurred in all of them.28 Inadequate dilation or extensive dissection, however, was not considered in our patients because they underwent CAS immediately after slight balloon predilation. Residual stent stenosis might contribute to the prevention of a marked increase in CBF and the maintenance of cerebral autoregulation. The stent stenosis resulted in a slight increase in CBF and a reciprocal decrease in AVDO2 and OEF immediately after CAS. Therefore, neither HPS nor ICH occurred after CAS.
Strict control of postoperative blood pressure is defined as the maintenance of blood pressure at least below the preoperative value immediately after surgical procedures;9 thus, blood pressure in the present study was strictly controlled. Strict control of postoperative blood pressure prevents ICH after carotid endarterectomy (CEA); however, it is unsuccessful in preventing ICH after CAS.9 Residual stent stenosis successfully prevented ICH after CAS in the present high-risk patients.
Previous studies have been reported on CAS without post-CAS balloon dilation29 and CAS without any balloon dilation.30 Primary CAS without any balloon dilation was performed with 2 types of open-cell stents. Transient ischemic attacks occurred in 4.3% of patients within 24 hours; 1 patient died at 11 days due to stent thrombosis.30 In our series, no transient ischemic attacks occurred within 24 hours, and no stent thrombosis occurred within 30 days. These results may be associated with the closed-cell stent and slight balloon predilation in our series. Primary CAS may be a treatment option for ex-HS when a closed-cell stent is selected, though high restenosis (12.8%) and repeat angioplasty (14.8%) rates have been reported.21,30 In our series, 12.0% of patients underwent long-term staged balloon angiography.
Gentle CAS for intentional residual stent stenosis can be performed in 1 session because its strategy is simpler and more feasible than staged angioplasty, which requires invasive procedures in 2 sessions.12,28 Staged angioplasty has been attempted in only 27.1% of Japanese institutions.6 Gentle CAS could become the first-line treatment for high-risk patients with ex-HS when combined with long-term staged angioplasty.
Limitations
Our study had several limitations. A small number of patients were included, and the study was a retrospective and observational cohort study without a control group. Standardization of how to evaluate the MRA relative SI is required. The sensitivity and specificity of the HI criteria have not been assessed. We used the same types of balloon catheters, filter devices, and the same closed-cell stents in all 28 patients. Our results cannot be generalized to other types of balloon catheters, filter devices, or closed-cell stents. Therefore, an appropriate balloon catheter and balloon size for predilation and an appropriate stent must be determined.
A prospective study with a large sample size is required to assess intentional residual stent stenosis of high-risk ex-HS.
CONCLUSIONS
The gentle CAS strategy of intentionally leaving a stent stenosis was feasible and prevented HPS in high-risk patients with ex-HS. Stents spontaneously dilated within 4 months, and 12.0% of patients achieved sufficient dilation without HPS or ICH after long-term staged balloon angioplasty. Intentional residual stent stenosis could become the first-line treatment for high-risk ex-HS.
Footnotes
Disclosures: Takahisa Mori—UNRELATED: Board Membership: one of the Editorial Board members of the American Journal of Neuroradiology; Royalties: Medikit, Comments: less than US $2500/year.
Paper previously presented, in part, at: International Stroke Conference, February 6–8, 2019; Honolulu, Hawaii (ATP156).
References
- Received June 25, 2020.
- Accepted after revision August 14, 2020.
- © 2021 by American Journal of Neuroradiology