Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Quantitative bone densitometry on multidetector CT of the temporal bone is a diagnostic adjunct for otosclerosis in its active (spongiotic) phase, but translating this technique to conebeam CT is limited by the technical variability of conebeam CT pixel values. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the performance of internally calibrated conebeam CT pixel value measurements that can enable the determination of active fenestral otosclerosis (otospongiosis).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This study included 37 ears in 22 patients with a clinical diagnosis of otospongiosis in those ears and 35 ears in 22 control patients without the diagnosis. Temporal bone conebeam CT was performed. ROIs were set anterior to the oval window, in the lateral semicircular canal bone island, and in a nearby aerated space. Mean conebeam CT pixel values in these regions determined the relative attenuation ratio of the area anterior to the oval window normalized to normal otic capsule bone and air.
RESULTS: The relative attenuation ratio for cases of otospongiosis was significantly lower than that for controls (P < .001). Based on receiver operating characteristic analysis, the optimal cutoff relative attenuation ratio was 0.876, which had an accuracy of 97.2% for the diagnosis of otospongiosis.
CONCLUSIONS: Internally calibrated pixel value ratios in temporal bone conebeam CT can feasibly help diagnose active/spongiotic-phase fenestral otosclerosis in an objective manner.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- CBCT
- conebeam CT
- MDCT
- multidetector CT
- RAR
- relative attenuation ratio
Imaging diagnosis of the active or spongiotic/lucent phase of otosclerosis (otospongiosis) relies primarily on the detection of abnormal hypodensity involving the otic capsule on multidetector CT (MDCT). The preferential site of involvement for fenestral otospongiosis is the region anterior to the oval window. Prior studies support quantitative bone densitometry on MDCT as a diagnostic aid for fenestral otospongiosis.1⇓⇓⇓-5
Conebeam CT (CBCT) has gained interest in temporal bone imaging for its ability to produce high-spatial-resolution images, but a barrier to assessing bone density on CBCT is the technical variability of CBCT pixel values. Compared with MDCT, CBCT is more susceptible to regional artifacts due to off-axis x-ray beam projections, beam hardening, and scatter radiation, particularly involving high-density material within the beam path but outside the reconstructed FOV (exomass).6 These artifacts can vary among patients, acquisition parameters, and reconstruction methods. Recognizing these limitations, current CBCT manufacturers often do not scale pixel (gray) values to Hounsfield units, as that would misleadingly imply accurate and standardized density representations. However, some authors have suggested correcting for some of these effects by calibrating CBCT pixel values using internal references.6,7
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the performance of internally calibrated CBCT pixel value measurements/ratios that can enable objective determination of fenestral otospongiosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
A retrospective case-control study was approved by the institutional review board of Massachusetts Eye and Ear. The cases were 22 consecutive patients with a clinical diagnosis of otospongiosis who underwent CBCT of the temporal bones between January 2016 and June 2017. The clinical diagnosis was established on the basis of history, otologic examination, and audiogram findings. Of the 44 ears in 22 patients, 7 ears were not included in the study because they either did not have clinical evidence of otosclerosis (the patients had unilateral signs and symptoms) or the scan showed postoperative findings (eg, stapes implant) that could suggest the diagnosis of otospongiosis and thereby unblind the reviewer. The controls were an equal number of patients without clinical evidence of otospongiosis, including normal audiogram findings, who were matched within a decade of age and scanned on the same CBCT unit between May 2018 and July 2018 for other indications (eg, dizziness, vertigo, facial palsy). Of the 44 ears in 22 controls, 35 ears were imaged (9 patients underwent unilateral CBCT).
Image Acquisition
All patients underwent dedicated temporal bone CBCT without intravenous contrast. Patients were imaged on a sitting CBCT unit, 3D Accuitomo (Morita), with a small FOV of 6 × 6 cm, tube potential = 90 kV(peak), tube current = 8 mA, high-resolution mode with rotation time = 30.8 seconds, pixel size = 125 × 125 μm, and section thickness = 0.5 mm. Patients had one or both temporal bones imaged separately in 1 session. Axial reformats of the temporal bones were created in a plane parallel to the that of the lateral semicircular canal. Images were exported to a PACS for viewing and analysis.
Image Analysis
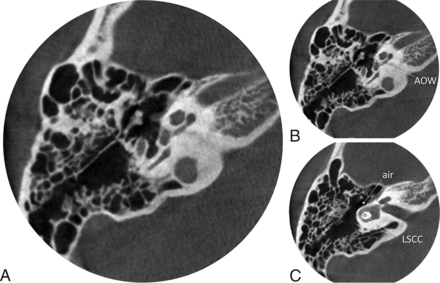
Blinded to the clinical diagnoses, 2 radiologists (A.F.J. with 10 years of head and neck radiology experience; and either P.T. or K.L.R. with 4 years and 2 years of head and neck radiology experience, respectively) independently measured CBCT pixel values on axial reformatted images for each CBCT examination. Round or oval ROIs of 0.5 mm2 were placed in 3 areas in each case (Fig 1), anterior to the oval window, in the lateral semicircular canal bone island, and in an aerated space within the middle ear cleft nearest the lateral otic capsule (air). The area anterior to the oval window was selected as the area of interest for assessment of otospongiosis because that is most often involved initially by otospongiosis.8⇓-10 The lateral semicircular canal bone island was chosen as an internal reference, as others have done,11 because it is not an area described as involved by otospongiosis12 and has a predictably large enough area for placing a 0.5-mm2 ROI. Occasionally, a central hypodensity has been noted in the lateral semicircular canal bone island as an anatomic variant,13 so we deliberately placed the ROI off-center to avoid such variants.
Temporal bone conebeam CT in a representative patient with otospongiosis. An image at the level of the oval window is shown without (A) and with (B) ROIs drawn anterior to the oval window (AOW). Additional ROIs at a separate level (C) are shown off-center within the lateral semicircular canal bone island (LSCC) and adjacent aerated cavity (air). The RAR in this patient was 0.756.
The mean CBCT pixel value for each of the 3 ROIs was calculated using values obtained from the 2 readers for each temporal bone. A relative attenuation ratio (RAR) was then calculated for each CBCT examination: (anterior to the oval window − air) / (lateral semicircular canal bone island − air).
Statistical Analysis
The interrater correlation for the RAR was determined; then, the RAR was averaged between raters. Differences among groups were evaluated using the unpaired, 2-tailed Student t test. Diagnostic performance in predicting otospongiosis was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic analysis. An optimal operating point was identified by maximizing the Youden J statistic (sensitivity + specificity – 1). These statistics were computed using XLSTAT (Version 2016.2; Addinsoft) on Excel (Version 2011; Microsoft 365) and depicted using GraphPad Prism software (Version 9.0; GraphPad Software).
RESULTS
Patient Characteristics
Twenty-two individuals (4 men and 18 women; age range, 24–65 years; mean age, 46 [SD, 11] years) for a total of 37 ears were included in the otospongiosis group. Twenty-two individuals (14 men and 8 women; age range, 17–67 years; mean age 47 [SD, 14] years) for a total of 35 ears were included in the control group.
Relative Attenuation Ratio
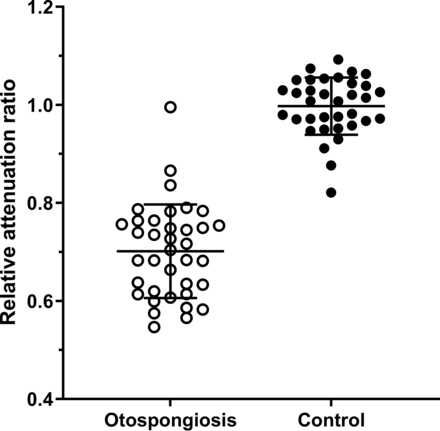
The interrater reliability for the RAR was high (Pearson r = 0.93). The mean RAR for cases of otospongiosis was 0.701 (SD, 0.095), compared with 0.997 (SD, 0.058) for controls, a statistically significant difference (P < .001; Fig 2).
RAR. Individual ears with otospongiosis (open circle; n = 37) and controls (solid circle; n = 35) are shown with group means and SDs (bars). The RAR in otospongiotic ears was significantly less than that in control ears (P < .001).
Performance
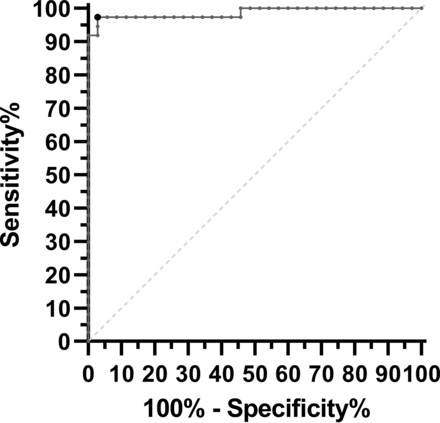
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.986 (95% CI, 0.981–1.000; P < .001 for difference from 0.5; Fig 3). The optimal RAR cutoff was 0.876. Below this cutoff, otospongiosis was correctly predicted with a sensitivity of 97.3% (95% CI, 86.2%–99.5%), specificity of 97.1% (95% CI, 85.5%–99.5%), and accuracy of 97.2%.
Receiver operating characteristic curve. The area under the curve (solid line) was 0.986, which was significantly different from the area under the line of identity (dashed line; P < .001). The operating point at which the Youden J statistic is maximized is shown as a larger black dot (RAR threshold = 0.876, sensitivity = 97.3%, specificity = 97.1%).
DISCUSSION
Otosclerosis is a primary osteodystrophy involving the otic capsule in adults. The earlier, histologically active phase of otosclerosis is also referred to as otospongiosis in reference to the appearance of spongy bone that has abundant vascular spaces within it.14 In combination with clinical and audiologic evaluations, imaging plays a role in the diagnosis of otospongiosis. Specifically, MDCT demonstrates hypodensity in the otic capsule, most commonly located in the region anterior to the oval window in so-called fenestral otospongiosis. In the later inactive/sclerotic phase, the bone becomes denser and can appear thickened.15
The CT appearance of early-phase active fenestral otospongiosis can be subtle. Prior studies support quantitative bone densitometry on MDCT as a diagnostic aid.1⇓⇓⇓-5 These studies measured the Hounsfield units within regions anterior to the oval window in patients with and without otospongiosis. Depending on the study, the mean bone density in otospongiosis fell in the range of 1008–1649 HU, whereas the means in control ears were significantly higher in the range of 1396–2416 HU.1⇓⇓⇓-5
While MDCT has been the reference standard for otospongiosis imaging, CBCT has gained interest in temporal bone imaging for its ability to produce high-spatial-resolution images potentially by using less radiation than MDCT.16,17 However, a barrier to assessing bone density on CBCT is the variability of CBCT pixel values (gray levels).18 CBCT output is not expressed in Hounsfield units and may differ across units, protocols, and patients due to technical factors arising from the conebeam geometry and limited FOVs. Assessment of material density on CBCT images relies on relative values, rather than absolute values as is the case with Hounsfield units in MDCT. However, many groups have found strong linear correlations between actual Hounsfield units on MDCT and CBCT pixel values in most devices.18⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-27
In this study, we calibrated CBCT pixel values using 3 internal references to obtain an RAR that allows quantitative assessment of bone density.7 We selected the lateral semicircular canal bone island away from the edges bordering on the canal lumen as a reference standard because that area is rarely if ever described as a region affected by otospongiosis/otosclerosis.12 Uncommonly, the bone island may contain anatomic variant radiolucencies that would need to be excluded from measurement, but these variants did not occur in our study cohort. We further normalized the pixel values for bone by subtracting the pixel values of nearby air from them. Using this method, we found that the mean RAR for cases of fenestral otospongiosis was about 0.7 (ie, the mean normalized pixel value in diseased bone anterior to the oval window was 70% that of unaffected bone), compared with 1.0 for controls. We suggest an RAR cutoff value of 0.876, below which fenestral otospongiosis can be predicted with high sensitivity and specificity.
Our study has limitations. We used a single CBCT unit and imaging protocol, and measurements may differ under other technical parameters. There was no histologic confirmation of disease, but all cases fulfilled clinical criteria that were confirmatory of fenestral otospongiosis. The study cohort did not include children or older adults. Otospongiosis is primarily an entity seen in young and middle-aged adults, and otic capsule density should not be age-dependent, especially once past the neonatal or infancy period when the cochlear cleft may be prominent. The density of diseased bone changes with time, so densitometry would not be expected to help diagnose cases presenting in the later, inactive/sclerotic phase, when alternative features at CT like otic capsule contour and thickness may be informative.15 Our study did not evaluate less common diseases that can decrease otic capsule density such as osteogenesis imperfecta and Paget disease of the temporal bone, which may mimic the densitometric findings in otospongiosis.
Several areas of future research are suggested. First, replication is required with different CBCT scanners and settings to ensure generalizability of our quantitative findings. Second, future studies may corroborate the relative attenuation evaluation on CBCT with audiometry, as has been shown with MDCT densitometry in fenestral otospongiosis.3 Finally, a CT grading system of otospongiosis based on location (fenestral, localized cochlear, and diffuse cochlear disease) was proposed in 2005;28 the use of relative attenuation analysis on CBCT can, therefore, also be investigated in retrofenestral locations.
CONCLUSIONS
Change in bone density is an imaging feature of fenestral otospongiosis. Internally calibrated pixel value ratios in temporal bone CBCT can feasibly help diagnose active/spongiotic-phase fenestral otosclerosis in an objective manner.
Footnotes
Paper previously presented, in part, at: Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology, May 30 to June 4, 2020; Virtual.
References
- Received January 15, 2021.
- Accepted after revision April 16, 2021.
- © 2021 by American Journal of Neuroradiology