Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Nearly 20% of patients with spontaneous SAH have no definitive source on initial DSA. The purpose of this study was to investigate the timing and yield of repeat DSA, to clarify the influence of initial CT bleed pattern, and to characterize sources of diagnostic error in this scenario.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We evaluated the yield of repeat DSA and clinical outcomes stratified by hemorrhage pattern on CT in consecutive patients with nontraumatic SAH with negative initial DSA findings at a referral center. Cases in which the culprit lesion was subsequently diagnosed were classified as physiologically occult (ie, undetectable) on the initial DSA, despite adequate technique and interpretation or misdiagnosed due to operator-dependent error.
RESULTS: Two hundred forty-two of 1163 (20.8%) patients with spontaneous SAH had negative initial DSA findings between 2009 and 2018. The SAH CT pattern was nonperimesencephalic (41%), perimesencephalic (36%), sulcal (18%), and CT-negative (5%). Repeat DSA in 135/242 patients (55.8%) revealed a source in 10 patients (7.4%): 4 saccular aneurysms, 4 atypical aneurysms, and 2 arteriovenous shunts. The overall yield of repeat DSA was 11.3% with nonperimesencephalic and 2.2% for perimesencephalic patterns. The yield of the second and third DSAs with a nonperimesencephalic pattern was 7.7% and 12%, respectively. Physiologically occult lesions accounted for 6/242 (2.5%) and operator-dependent errors accounted for 7/242 (2.9%) of all angiographically occult lesions on the first DSA.
CONCLUSIONS: Atypical aneurysms and small arteriovenous shunts are important causes of SAH negative on angiography. Improving DSAs technique can modestly reduce the need for repeat DSA; however, a small fraction of SAH sources remain occult despite adequate technique. These findings support the practice of repeating DSA in patients with a nonperimesencephalic SAH pattern.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- NPM
- nonperimesencephalic
- PM
- perimesencephalic
DSA is the criterion standard for detecting cerebral aneurysms and other sources of spontaneous SAH. However, approximately 15%–20% of patients with spontaneous (atraumatic) SAH have negative findings on the initial angiogram.1,2 In these cases, second and sometimes third catheter angiograms may be necessary to guide management. Previous studies estimated that source lesions are identified in 2%–17% of these cases when DSA is repeated.3⇓-5 This yield may be influenced by the blood distribution on CT, which can be categorized as perimesencephalic (PM), diffuse nonperimesencephalic (NPM), sulcal, or radiologically negative (eg, diagnosed by CSF examination).6 To date, the predictive value of the CT SAH pattern on the diagnostic yield of repeat DSA is uncertain, but this information could refine and simplify algorithms for repeating DSA in this population.
The initial DSA can yield false-negative results for a variety of reasons, which can be broadly categorized as physiologic (ie, obscuration due to vasospasm, thrombosis, or hematoma) or operator-dependent (eg, inadequate projections, magnification, or patient motion). Several schemata exist for framing and contextualizing operator-dependent error in diagnostic imaging.7⇓-9 For example, Bruno et al10 proposed 2 principal error subtypes: perceptual and interpretive (cognitive). However, a systematic approach to error has not been applied to DSA in the context of occult, spontaneous SAH.
The purpose of this study was, therefore, 2-fold: First, we aimed to quantify the diagnostic yield of repeat DSA in patients with spontaneous SAH, accounting for differences in the CT blood distribution pattern. Second, we estimated the fraction of these cases that are attributable to physiologic versus operator-dependent factors and presented a framework for classifying diagnostic error in this setting.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed a retrospective cohort study at a single, tertiary, academic medical center of consecutive adults (older than 18 years of age) admitted with SAH between January 1, 2009, and December 31, 2018. This study was approved by the local institutional review board with a waiver of informed consent. Patients were excluded if there was evidence of trauma or primarily intraparenchymal or intraventricular hemorrhage.
Clinical data were abstracted from the electronic health record, including demographics and risk factors for SAH (Online Supplemental Data). In addition to the CT hemorrhage pattern, the initial Hunt & Hess scores, modified Fisher grade, external ventricular drain placement, ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement, vasospasm, delayed cerebral ischemia, and rebleed events were documented.
DSA was performed in each case by an experienced neurointerventionalist in 1 of 3 biplane angiography suites (Artis Q or zee; Siemens). MRA of the brain and cervical spine was performed after initial negative findings on DSA. The decision to perform repeat DSA was determined by multidisciplinary consensus. The yield of identifying a vascular source was assessed for repeat DSA and MR imaging.
Neuroradiologic Review and Classification of Diagnostic Error on Initial DSA
Baseline head CT images were reviewed and categorized into 4 groups by a neuroradiologist on the basis of the SAH pattern: 1) diffuse NPM, 2) PM, 3) sulcal, or 4) CT-negative but confirmed by CSF examination. PM SAH was defined as hemorrhage limited to the prepontine, suprasellar, ambient, crural, and/or quadrigeminal cisterns without significant extension into the Sylvian or interhemispheric fissures according to the criteria of van Gijn et al.6
In each case in which a diagnosis was revealed only with repeat DSA or surgical exploration, the initial DSA (reported as having negative findings) was scrutinized independently by 2 neurointerventionalists. Lesions that were retrospectively evident were classified as operator-dependent errors and subclassified as technical or cognitive errors. The cognitive error categories were further subdivided into specific error classes according to the framework of Bruno et al.10 When no diagnostic error was detected, the lesion was considered physiologically occult, meaning that the lesion could truly not be detected despite optimal technique and interpretation.
Statistical comparison of continuous variables between groups was assessed with the Student t test, the Mann-Whitney U test, or ANOVA. Frequency data were compared using the Fisher exact test, and P < .05 was considered significant. Statistical analyses were performed using R statistical and computing software (Version 3.6.2; http://www.r-project.org/).
RESULTS
Patient Cohort Clinical Characteristics
During the 10-year study period, 242/1163 (20.8%) patients with spontaneous SAH had negative initial DSA findings. A visual summary of the characteristics and diagnostic results of these selected 242 patients is provided in the Online Supplemental Data. One hundred twenty-two were women (50.4%), and the mean age was 56 years (range, 18–91 years). The Hunt & Hess scores were grade 1 in 53 patients (22%), grade 2 in 143 patients (59%), grade 3 in 26 patients (11%), grade 4 in 8 patients (3%), and grade 5 in 8 patients (3%). The SAH pattern on the initial head CT was NPM in 41%, PM in 36%, sulcal in 18%, and CT-negative in 5% (Online Supplemental Data). Most patients were transferred from an outside hospital (214/242, 88%). Patients with high Hunt & Hess scores (3–5) included 3 patients (8.6%) with PM SAH and 32 patients (91.4%) with NPM SAH. Patients with NPM SAH had a higher incidence of moderate/severe vasospasm (19% versus 8%, P = .03), a need for an external ventricular drain (30% versus 6%, P <.01), persistent hydrocephalus requiring a ventriculoperitoneal shunt (11% versus 0%, P <.01), and a lower rate of discharge home (55% versus 92%, P <.01) than patients with PM SAH.
The rebleed rate was significantly higher in NPM SAH compared with PM SAH (8% versus 1%, P = .04), with 4 aneurysms identified after rebleed. In 8 patients who had a rebleed event and a high suspicion of an occult vascular source, the median time from the index SAH event and rebleed was 17 days (range, 1–49 days). The remaining rebleed events were attributed to vasculitis (n = 1), hypertension versus cerebral amyloid angiopathy (n = 1), and unknown etiology (n = 3).
Diagnostic Yield of Repeat DSA by CT Blood Distribution Pattern
Repeat DSA was performed in 135/242 patients (55.8%) and revealed a source of hemorrhage in 10 patients (7.4%; 8 aneurysms and 2 cervicomedullary AVFs). Of the 100 patients in the NPM group, 80 (80%) underwent repeat DSA, and a vascular source was identified in 9/80 (11.3%; Figs 1 and 2 and the Table). Of the 87 patients in the PM group, 46 (52.9%) underwent repeat DSA and a cervicomedullary AVF was identified in 1/46 (2.2%). The difference in yield between NPM and PM was not statistically significant (P = .09). Repeat DSA was infrequently performed in patients with sulcal SAH (6/43, 13.9%) or CT-negative SAH (3/12, 25%) and did not identify a vascular source in any case for these SAH distribution patterns.
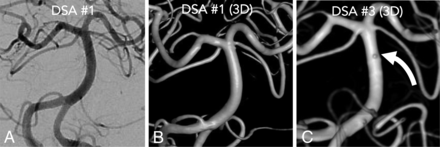
A 78-year-old woman with an example of a physiologically occult aneurysm on the initial DSA on the postbleed day 1. A frontal projection (A) with 3D reconstruction shows no source lesion (B). A second DSA on postbleed day 6 had normal findings. The patient was discharged and re-presented with worsening headache on postbleed day 12. A third DSA on postbleed day 12 (C) demonstrated a submillimeter basilar artery perforator blister aneurysm (curved white arrow) that was clipped.
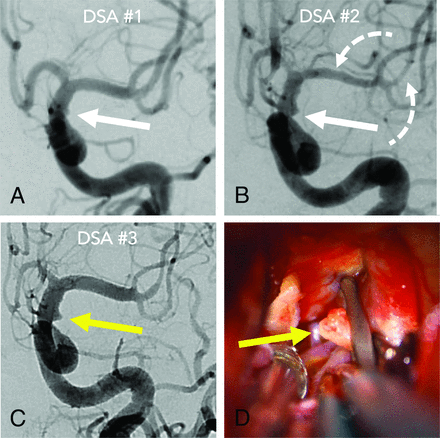
A 36-year-old woman admitted with an internal carotid artery blister aneurysm, misdiagnosed due to 2 forms of operator-dependent error. The initial DSA (A) shows a perceptual-type interpretive error in that a laterally projecting blister (white arrow) was not recognized. The blister was more evident on the second DSA (B) and perceived but misinterpreted as vasospasm due to developing vasospasm elsewhere (dashed arrows). Finally, the lesion (yellow arrow) was recognized on the third DSA (C) as vasospasm abated. Intraoperative photographs (D) confirm the rupture site (yellow arrow) secured with clipping.
| Patient | Positive DSA Findings (No.) | Timing of Diagnosis (PBD) | Rebleed | SAH Pattern | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 5 | No | NPM | A1 blister aneurysm |
| 2 | 2 | 3 | Day 2 | NPM | PICA dissecting aneurysm |
| 3 | 2 | 5 | No | NPM | A1 blister aneurysm |
| 4 | 2 | 7 | No | NPM | Cervicomedullary AVF |
| 5 | 2 | 8 | No | NPM | Distal MCA mycotic aneurysm |
| 6 | 2 | 39 | Day 37 | NPM | AcomA saccular aneurysm |
| 7 | 3 | 5 | No | NPM | A1 dissecting aneurysm |
| 8 | 3 | 12 | No | NPM | Basilar blister aneurysm |
| 9 | 3 | 8 | No | NPM | AcomA saccular aneurysm |
| 10 | 3 | 7 | No | PM | Cervicomedullary AVF |
| 11a | NA | 17 | Day 17 | NPM | AcomA saccular aneurysm |
| 12a | NA | 2 | No | NPM | AcomA blister aneurysm |
| 13a | NA | 16 | Day 16 | NPM | Thrombosed R MCA aneurysm |
Note:—AcomA indicates anterior communicating artery; PBD, postbleed day; NA, not applicable; R, right.
↵a Aneurysm identified at craniotomy.
Summary of data in patients with vascular source identified
In total, 6/135 patients (4.4%) had a vascular source identified on a second DSA, and 4 of 34 patients (11.8%) were diagnosed on a third DSA (Table). The diagnostic yield of the second and third DSAs in patients with NPM SAH was 7.7% and 12%, respectively. The median time from the index SAH event until identification of a vascular source on DSA was 7 days (range, 3–39 days). MRA of the brain and neck was performed in 182 of 242 patients (75.2%) and did not reveal an SAH source in any case.
Sources and Classification of Diagnostic Error in Initial DSA
In total, 13/242 patients (5.4%) with initially angiographically occult SAH were subsequently diagnosed with a vascular source: 2/13 (15.4%) at craniotomy, 10/13 (76.9%) by repeat DSA, and 1/13 (7.7%) by delayed CTA (Table). Of 9 patients in whom an aneurysm was identified on repeat DSA, most were <3-mm nonsaccular aneurysms, including blister aneurysms (n = 4), dissecting aneurysms (n = 2), and a mycotic aneurysm (n = 1). Two saccular aneurysms were thrombosed during the initial DSA. The anterior cerebral artery and anterior communicating artery were the most frequent locations (n = 6). A cervicomedullary AVF was the source of SAH in 2/13 (15.4%) patients.
Of this subset of 13 patients with initially angiographically occult SAH, 6/13 (46.1%) had lesions that were undetectable on detailed review by 2 neurointerventionalists despite a technically adequate DSA and were, therefore, classified as physiologically occult rather than missed due to operator-dependent error. Two (33.3%) of these were diagnosed only at exploratory craniotomy performed urgently for declining clinical status. All (4/4, 100%) of the remaining cases diagnosed by repeat DSA showed a change in the angiographic appearance (recanalization or growth), leading to the final diagnosis.
Seven of 13 (53.8%) cases were classified as operator-dependent errors. Four of 7 (57.1%) cases were subclassified as technical errors. These errors included the following: 1) lack of 3D rotational DSA of the relevant vessel (n = 2, 50%), 2) insufficient planar projections (lack of skull base and cervical vertebral artery views; n = 1, 25%), and 3) missed diagnosis of a cervicomedullary AVF due to failure to selectively inject the external carotid artery (n = 1, 25%). The remaining 3/7 (42.8%) operator-dependent errors were classified as cognitive errors. These were further subclassified as perceptual (n = 1, 14.3%) or interpretive (n = 2, 28.6%) errors. These included the following: 1) a subtle-but-present blister aneurysm of the A1 segment (error of perception), 2) a small fusiform PICA aneurysm in which an abnormal contour was recognized but misinterpreted, and 3) a small, dissecting aneurysm of the A1, which was recognized but not interpreted as a pathologic until it subsequently enlarged.
DISCUSSION
In this retrospective study of 242 consecutive patients with spontaneous SAH and negative initial DSA findings, a vascular source was ultimately identified in 13/242 (5.4%). The combined diagnostic yield of repeat DSA was 11.3% for the NPM pattern (9/80), 2.2% for the PM pattern (1/46), and 0% in the sulcal and CT-negative groups. Given the significantly higher rebleed rate, the risks of repeat DSA (including a third DSA) in the acute interval appear justified in the angiographically occult NPM SAH subgroup. This study also presents a new framework for diagnostic error analysis in angiographically occult SAH and found that technical and cognitive errors together occurred in 2.9% (7/242) of cases.
The rate of negative initial DSA findings in this 10-year cohort was 20.8% of all patients with SAH, consistent with previous studies.1,2,11 Also similar to prior studies, patients with negative SAH on angiography had lower complication rates and better functional outcomes than patients with aneurysmal SAH.12 When stratified by CT pattern, patients with NPM SAH had more severe clinical presentations and complications and poorer outcomes (rebleeding, symptomatic vasospasm, external ventricular drain ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement, discharge home) compared with patients with PM SAH.4,13,14 These findings highlight an increased risk of NPM in patients with SAH compared with those with PM SAH.
Sources of Angiographically Occult SAH
Atypical lesions such as blisterlike and dissecting aneurysms were an important source of occult hemorrhage in patients with NPM SAH. Blister aneurysms are thought to account for 0.5%–2% of all aneurysmal SAHs but were estimated to comprise up to 25.2% of angiographically occult aneurysms.14,15 Blister aneurysms, which typically occur in the supraclinoid ICA, are exceedingly rare in other vessels.16 In this cohort, blister aneurysms were found in the anterior cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, and a basilar perforator artery; blister aneurysms in such unusual locations, therefore, represent an important source of SAH that may be easily missed despite a good technique because they evade the standard neuroangiographic search pattern. Dissecting aneurysms are also difficult to detect because they often manifest subtle angiographic features that mimic intracranial atherosclerosis.17
Imaging Strategies in Angiographically Occult SAH
Rebleed events occurred in 3.7% of patients in this study and represent the leading rationale for repeat DSA in the acute setting. These findings are generally consistent with prior estimates of rebleed but are higher for patients with NPM SAH (8%) than previously reported.4 Most important, most rebleed events occurred >2 weeks after the index SAH and after hospital discharge. The median delay in detecting a vascular source was 7 days, while the median delay of rebleed events was 17 days. Together these findings support previous recommendations for routine DSA during this window.6 For patients with negative findings on 2 DSAs during hospitalization, the utility of a third DSA is less certain; in our study, 4 of 34 patients (11.8%) had a vascular source identified on the third angiogram, though patients with a high suspicion of an occult source were likely selected for repeat DSA. The incidence of positive findings on a third long-term follow-up DSA has been reported to be between 7% and 10%,3,18 though these studies are also limited by small sample sizes, inconsistent imaging protocols, and selection bias. One study had a standardized protocol of obtaining a third angiogram at 6 weeks postictus and reported a yield of 4% for the third DSA (0% in PM SAH, 7.8% in NPM SAH).6 Therefore, it may be reasonable to obtain a delayed third angiogram, especially for patients with NPM-pattern SAH.
Notably, these data indicate that MR imaging of the brain and cervical spine has a relatively low diagnostic yield. 3,19⇓-21 However, there have been reports of an MR imaging diagnosis of an occult aneurysm, a cervical arteriovenous vascular malformation, or a cavernous malformation in patients with initial negative findings on DSA.19,22 Therefore, MR imaging may be useful in selected patients with atypical clinical presentations or patterns of hemorrhage.
The Role of Operator-Dependent Error in Angiographically Occult SAH
The present study found that operator-dependent error occurred in 7/242 (2.9%) cases of angiographically occult SAH and accounted for more than half (53.8%) of cases subsequently diagnosed by repeat DSA or craniotomy. Such operator-dependent errors (ie, sum of technical and cognitive errors) are underreported and underinvestigated in neuroangiography relative to noninvasive radiology. Technical error, believed to account for only 2% of errors in diagnostic radiology, represented 57.1% of errors in the current study.23 A meticulous technique, including high-magnification planar projections, is essential to unmask common aneurysm “blind spots.”24 3D rotational DSA also increases the overall sensitivity of cerebral angiography, and our findings support prior recommendations that 3D DSA be performed routinely in each vascular territory for all patients with SAH of uncertain source. Finally, cervicomedullary/foramen magnum AVFs comprised 15.4% (2/13) of lesions in this series.25 The frequency of these lesions emphasizes the importance of adequate projections of the skull base and the need for high-quality external carotid artery DSA.
The other major category of operator-dependent error in DSA is cognitive error. Cognitive-type errors accounted for 42.8% of missed diagnoses in the current study, whereas they are estimated to explain 60%–80% of errors in diagnostic radiology.7,10 Cognitive errors include errors of perception and interpretation.10 Perception errors including “scanning error” (incomplete review of acquired data), and “satisfaction of search” (a premature conclusion after an overt finding is noted) are influenced by human factors such as fatigue, inexperience, and distractors. Interpretation errors include the heuristic biases of framing (misleading contextual information), anchoring (failure to adjust the impression with new information), confirmation (commitment to pretest hypothesis), and availability (overweighted influence of recent experiences). One instructive case (Fig 2) highlights a perceptual error on initial DSA, an interpretive error on the second DSA, and the effect of anchoring bias because the interpreting physician was influenced by a concurrent vasospasm and failed to consider the possibility of an aneurysm.
Last, although DSA remains the criterion standard of diagnostic neurovascular imaging, our results clarify its physiologic limitations because 2.5% (6/242) of all angiographically occult SAH-source lesions were undetectable despite excellent technique and critical retrospective review. These findings reiterate the concept that DSA is inherently a luminal technique; thus, thrombosed or nonopacifying lesions are undetectable. This finding suggests an upper bound on the sensitivity of DSA. Emerging extraluminal imaging techniques, including vessel wall imaging, endoluminal optical coherence tomography, high-field MR imaging, and cinematic 3D rendering may serve as complementary tools to DSA to improve the diagnostic yield and avoid delays in care.26,27
This study has several important limitations. Although large and inclusive, the cohort is retrospective and therefore influenced by selection bias and referral patterns. In our cohort of 242 patients, only 135 (56%) had a second angiogram. Although there were no rebleed events or delayed complications in the remaining 107 patients, diagnostic follow-up for those patients was incomplete. The variation in the practice of repeat DSA and the lack of a standardized protocol also limit the generalizability of the findings. These limitations can be addressed with prospective, multi-institution registries.
CONCLUSIONS
The relatively high diagnostic yield of repeat DSA and the high rebleed rates in patients with the NPM SAH pattern and negative initial DSA support the practice of repeat DSA in this CT hemorrhage pattern subgroup. More than half (53.8%) of angiographically occult lesions were missed due to operator-dependent errors, and the remaining (46.2%) were undetectable by DSA, highlighting the limits of the sensitivity of DSA as a diagnostic technique.
Footnotes
I. Nguyen and M.T. Caton contributed equally to the manuscript.
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text and PDF of this article at www.ajnr.org.
References
- Received December 13, 2021.
- Accepted after revision February 9, 2022.
- © 2022 by American Journal of Neuroradiology