Abstract
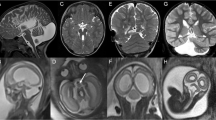
Cerebellar hypoplasia may present with a wide variety of neurological and systemic features, ranging from aplasia causing neonatal death to mild hypoplasia in an asymptomatic adult. MRI clearly documents the size of the cerebellum and any associated abnormalities. We describe 7 cases of cerebellar hypoplasia of varying aetiology-3 inherited, 2 associated with spinal dysraphism, 1 with Joubert's syndrome and 1 with pontine agenesis, probably as a result of basilar artery infarction in utero. T1- and T2-weighted images were obtained in each case and gadolinium-DTPA was administered in one. Associated features such as a Chiari malformation (2 cases), brain stem hypoplasia (2 cases), Dandy-Walker cyst and pachygyria (3 cases) and spinal dysraphism (2 cases) were clearly identified. Accurate documentation of these appearances assists in genetic counselling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKusick VA (1988) Mendelian inheritance in man, 8th edn. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, p 854
Sarnat HB, Alcala H (1980) Human cerebellar hypoplasia: a syndrome of diverse causes. Arch Neurol 37: 300–305
Altman NR, Naidich TP, Braffman BH (1992) Posterior fossa malformations. AJNR 13: 691–724
Norman RM (1940) Primary degeneration of the granular cell layer of the cerebellum: an unusual form of familial cerebellar atrophy occurring in early life. Brain 63: 365–379
Jervis GA (1954) Concordant primary atrophy of the cerebellar granules in monozygotis twins. Acta Genet Med Gemellol 3: 153–162
Wichman A, Frank LM, Kelly TE (1985) Autosomal recessive congenital cerebellar hypoplasia. Clin Genet 27: 373–382
Kvistadt PH, Dahl A, Skre H (1985) Autosomal recessive nonprogressive ataxia with an early childhood debut. Acta Neurol Scand 71: 295–302
Mathews KD, Afifi AK, Hanson JW (1989) Autosomal recessive cerebellar hypoplasia. J Child Neurol 4: 189–194
Byrd SE (1989) Magnetic resonance imaging of infratentorial congenital brain malformations. J Natl Med Assoc 81: 961–966
Young ID, Moore JR, Tripp JH (1987) Sex-linked recessive congenital ataxia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50: 1230–1232
Lesney I (1985) Symmetrical hypogenesis of the cerebellum. Acta Neurol Scand 71: 295–302
Paine RS (1960) Evaluation of familial biochemically determined mental retardation in children with special reference to aminoaciduria. New Eng J Med 262: 658–665
Boltshauser E, Isler W (1977) Joubert syndrome: episodic hyperpnoea, abnormal eye movements, retardation and ataxia associated with dysplasia of the cerebellar vermis. Neuropediatrie 8: 57–66
King MD, Dudgeon J, Stephenson JBP (1984) Joubert's syndrome with retinal dysplasia; neonatal tachypnoe as the clue to the genetic brain-eye malformation. Arch Dis Child 59: 709–718
Friede RL, Boltshauser E (1978) Uncommon syndromes of cerebellar vermis hypoplasia 1. Joubert's syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 20: 362–366
Kendall BK, Kingsley D, Lambert SR, Taylor D, Finn P (1990) Joubert's syndrome: a clinico-radiological study. Neuroradiology 31: 502–506
Wang PJ, Maeda Y, Izumi T, Yajima K, Hara M, Kubayashi N, Fukuyama Y (1983) An association of sub-total cerebellar agenesis with organoid naevus—a possible new variety of neurocutaneous syndrome. Brain Dev 5: 503–508
Mizuno Y, Kurokawa T, Numaguchi Y, Goya N (1982) Facial haemangioma with cerebrovascular anomalies and cerebellarhypoplasia. Brain Dev 4: 375–378
Reiner WO, Gabreels FJM, Hustinx TWJ (1983) Cerebellar hypoplasia, communicating hydrocephalus and mental retardation in two brothers and a maternal uncle. Brain Dev 5: 41–45
Norman RM, Urich H (1958) Cerebellar hypoplasia associated with systemic degeneration in early life. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 21: 159–166
Gessaga EC, Herrich MK, Urich H (1986) Necrosis of fetal brainstem with cerebellar hypoplasia. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 69: 326–331
DeLeon GA, Grover WD, D'Cruz CA (1984) Amyotrophic cerebellar hypoplasia: a specific form of infantile spinal atrophy. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 63: 282–286
Williams RS, Marshall PC, Lott IT (1977) Dendritic abnormalities in steely hair syndrome: a Golgi microscopic analysis. Neurology 27: 369
Vaizey MH, Sandero MD, Mybar KC, Wilson J (1977) Neurological abnormalities in congenital amaurosis of Leber. Arch Dis Child 52: 399–402
Stagno S, Pass RF, Dworsky ME, Henderson RE, Moore EG, Walton PD, Alford C (1982) Congenital CMV infection, the relative importance of primary and recurrent maternal infection. New Eng J Med 306: 945–949
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
deSouza, N., Chaudhuri, R., Bingham, J. et al. MRI in cerebellar hypoplasia. Neuroradiology 36, 148–151 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588085
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588085