Summary
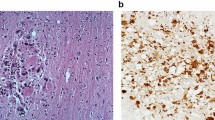
Significant contributions from many different groups during the last 2 or 3 years have characterized relatively uniform neuropathological changes of the CNS in AIDS patients. They feature human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-induced multinucleated giant cells as a histopathological hallmark and HIV demonstrable by electron microscopy, immunocytochemistry, and in situ hyridization. Unfortunately, a varying and confusing terminology is used to designate these changes which have been reported in surprisingly different incidences. Focal lesions have a microgranulomatous appearance and were designated as multifocal giant cell encephalitis or subacute encephalitis, which may be confused with the nodular encephalitis caused by cytomegalovirus. For some authors, the latter designation also covers characteristic diffuse white matter changes which have been termed progressive diffuse leukoencephalopathy by others, and which may overlap with focal lesions. Pathological features of these HIV-induced syndromes and other data do not support a major cytopathic effect of HIV on neural cells; rather, they suggest secondary pathogenetic events involving the predominant cell type in the lesion, the monocyte/macrophage/microglia. However, low-level, latent, and persisting HIV infections of neural cells cannot be excluded at present; the CNS may then serve as an early infected virus reservoir. A detailed correlation of clinical symptoms and stage of the infection to neuropathological changes is currently lacking but urgently needed. The presence of the HIV-receptor (CD4) molecule on brain cells is controversial; similarly, a putative cross-reaction of HIV proteins with trophic substances and transmitters needs to be substantiated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann R, Nekic M, Jürgens R (1986) Locally synthesized antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Neurol 233:140–141
Anand R, Reed C, Forlenza S, Siegal F, Cheung T, Moore J (1987) Non-cytocidal natural variants of human immunodeficiency virus isolated from AIDS patients with neurological disorders. Lancet II:234–238
Anders KH, Guerra WF, Tomiyasu U, Verity MA, Vinters HV (1986) The neuropathology of AIDS. UCLA experience and review. Am J Pathol 124:537–558
Anders KH, Steinsapir KD, Iverson DJ, Glasgow BJ, Layfield LJ, Brown WJ, Cancilla PA, Verity MA, Vinters HV (1986) Neuropathologic findings in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clin Neuropathol 5:1–20
Anzil AP, Kozlowski PB, Wrzolek M, Sher JH, Rao C, Sersen EA (1988) The central nervous system in AIDS: sex differences in an autopsy study of 144 adult cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol [Abstr] 47:387
Barnes DM (1987) Brain damage by AIDS under active study. Science 235:1574–1577
Berger JR, Resnick L (1987) HTLV-III/LAV-related neurological disease. In: Broder S (ed) AIDS. Modern concepts and therapeutic challenges. Marcel Dekker, New York Basel, pp 263–283
Bridge TP, Mirsky AF, Goodwin FK (eds) (1988) Psychological neuropsychiatric, and substance abuse aspects of AIDS. Raven Press, New York
Brunet P, Bolgert F, Pierrot-Deseilligny C (1988) L'infection dy système nerveux par le virus du deficit immunitaire humain acquis. Rev Neurol (Paris) 144:317–326
Budka H (1986) Multinucleated giant cells in brain: a hallmark of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 69:253–258
Budka H (1987) Das morphologische Korrelat der HIV-Infektion des Gehirns. In: Fische P-A, Schlote W (eds) AIDS und Nervensystem. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 117–132
Budka H (1987) Pathogenesis of HIV-associated brain lesions: a neuropathological evaluation. J Neuroimmunol [Abstr] 16:24–25
Budka H (1988) Pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated brain lesions: a neuropathological evaluation. Ann NY Acad Sci (in press)
Budka H, Lassmann H (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in glia? J Infect Dis 157:203 [Lett]
Budka H, Jellinger K, Wolf A, Zazgornik J, Stummvoll HK, Schmidt P, Pinggera WF, Kopsa H (1976) Neuropathologische Befunde nach Nierentransplantation. Wien Klin Wochenschr 88:175–179
Budka H, Costanzi G, Cristina S, Lechi A, Parravicini C, Trabattoni R, Vago L (1987) Brain pathology induced by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A histological, immunocytochemical, and electron microscopical study of 100 autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:185–198
Budka H, Costanzi G, Cristina S, Lechi A, Trabattoni G (1988) Morphological correlates of cerebral HIV infection. In: Kubicki St, Henkes H, Bienzle U, Pohle HD (eds) HIV and the nervous system. Fischer, Stuttgart New York, pp 27–40
Budka H, Maier H, Pohl P (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus in vacuolar myelopathy of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med (in press)
Carne CA, Tedder RS, Smith A (1985) Acute encephalopathy coincident with seroconversion for anti-HTLV-III. Lancet II:1206–1208
Centers for disease control (1987) Revision of the CDC surveillance case definition for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Am Med Assoc 258:1143–1154
Cheng-Mayer C, Rutka JT, rosenblum ML, McHugh T, Stites DP, Levy JA (1987) Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3526–3530
Cheng-Mayer C, Seto D, Tateno M, Levy JA (1988) Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science 240:80–82
Chiodi F, Asjö B, Fenyö E-M, Norkrans G, Hagberg L, Albert J (1986) Isolation of human immunodeficiency virus from cerebrospinal fluid of antibody-positive virus carriers without neurological symptoms. Lancet II:1276–1277
Clague CPT, Ostrowski MA, Deck JHN, Harnish DG, Colley EA, Stead RH (1988) Severe diffuse necrotizing cortical encephalopathy in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): an immunocytochemical and ultrastructural study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol [Abstr] 47:346
Dalgleish AG, Beverley PCL, Clapham PR, Crawfold DH, Greaves MF, Weiss RA (1984) The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature 312:763–767
Denning DW, Anderson J, Rudge P, Smith H (1987) Acute myelopathy associated with primary infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Br Med J 294:143–144
Dickson DW (1986) Multinucleated giant cells in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome encephalopathy: origin from endogenous microglia? Arch Pathol Lab Med 110:967–968
Dewhurst S, Sakai K, Bresser J, Stevenson M, Evinger-Hodges MJ Volsky DJ (1987) Persistent productive infection of human glial cells by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and by infectious molecular clones of HIV. J Virol 61:3774–3782
Dewhurst S, Sakai K, Zhang XH, Wasiak A, Volsky DJ (1988) Establishment of human glial cell lines chronically infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Virology 162:151–159
Dolman CL (1985) Microglia. In: Davis RL, Robertson DM (eds) Textbook of neuropathology. Williams & Wilkins. Baltimore London Sydney, pp 117–135
Dorfman LJ (1973) Cytomegalovirus encephalitis in adults. Neurology 23:136–144
Elder GA, Sever JL (1988) Neurologic disorders associated with AIDS retroviral infection. Rev Infect Dis 10:286–302
Epstein LG, Sharer LR (1988) Neurology of human immunodeficiency virus infection in children. In: Rosenblum ML, Levy RM, Bredesen DE (eds) AIDS and the nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 79–101
Epstein LG, Sharer LR, Joshi VV, Fojas MM, Koenigsberger MR, Oleske JM (1985) Progressive encephalopathy in children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol 17:488–496
Epstein LG, Sharer LR, Cho E-S, Myenhofer M, Navia BA, Price RW (1985) HTLV-III/LAV-like retrovirus particles in the brains of patients with AIDS encephalopathy. AIDS Res 1:447–454
Fauci AS (1987) AIDS: immunopathogenic mechanisms and research strategies. Clin Res 35:503–510
Fauci AS (1988) The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science 239:617–622
Felgenhauer K (1987) Another venereal disease with frequent nervous system involvement: neuro-AIDS. J Neurol 234:65–66
Fischer P-A, Enzenberger W (1987) Neurological complications in AIDS. J Neurol 234:269–279
Fischer P-A, Schlote W (eds) (1987) AIDS und Nervensystem. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Funke I, Hahn A, Rieber EP, Weiss E Riethmüller G (1987) The cellular receptor (CD4) of the human immunodeficiency virus is expressed on neurons and glial cells in human brain. J Exp Med 165:1230–1235
Gabuzda DH, Hirsch MS (1987) Neurologic manifestations of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Clinical features and pathogenesis. Ann Int Med 107:383–391
Gabuzda DH, Ho DD, de la Monte SM, Hirsch MS, Rota TR, Sobel RA (1986) Immunohistochemical identification of HTLV-III antigen in brains of patients with AIDS. Ann Neurol 20:289–295
Gartner S, Markovits P, Markovitz DM, Betts RF, Popovic M (1986) Virus isolation from and identification of HTLV-III/LAV-producing cells in brain tissue from a patients with AIDS. J Am Med Assoc 256:2365–2371
Georgsson G, Houwers DJ, Stefansson K, Palsson PA, Petursson G (1987) Immunohistochemical staining of cells in the brain of a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) with a monoclonal antibody to visna virus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:406–408
Goldstick L, Mandybur TI, Bode R (1985) Spinal cord degeneration in AIDS. Neurology 35:103–106
Gonda MA, Wong-Staal F, Gallo RC, Clements JE, Narayan O, Gilden RV (1985) Sequence homology and morphologic similarity of HTLV-III and visna virus, a pathogenic lentivirus. Science 227:173–177
Gosztonyi G, Lamperth L, Webster HdeF (1988) In situ hybridization study of HIV DNA and RNA distribution in AIDS encephalopathy lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:346 [abstr]
Grant I, Atkinson JH Hesselink JR, Kennedy CJ, Richman DD, Spectro SA, McCutchan JA (1987) Evidence for early central nervous system involvement in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and other human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections. Ann Int Med 107:828–836
Gray F, Gherardi R, Baudrimont M, Gaulard P, Meyrignac C, Vedrenne C, Poirier J (1987) Leucoencephalopathy with multinucleated giant cells containing human immune deficiency virus-like particles and multiple opportunistic cerebral infections in one patient with AIDS. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:99–104
Gray F, Gherardi R, Scaravilli F (1988) The neuropathology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). A review. Brain 11:245–266
Gullotta F, Kuchelmeister K, Vollmer E (1988) Multinucleated cells in AIDS encephalopathy. In: Kubicki St, Henkes H, Bienzle U, Pohle HD (eds) HIV and the nervous system. Fischer, Stuttgart New York, pp 49–52
Gurney ME, Heinrich SP, Lee MR, Yin, HS (1986) Molecular cloning and expression of neuroleukin, a neurotrophic factor for spinal and sensory neurons. Science 234:566–574
Györkey F, Melnick JL, Györkey P (1987) Human immunodeficiency virus in brain biopsies of patients with AIDS and progressive encephalopathy. J Infect Dis 155:870–876
Haug H, Budka H, Knebel G (1987) Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen an den Cortexgefäßen bei AIDS-Erkrankungen. Zentralbl Allg Pathol [Abstr] (in press)
Hauser SL, Bhan AK, Gilles FH, Hoban CJ, Reinherz EL, Schlossman SF, Weiner HL (1983) Immunohistochemical staining of human brain with monoclonal antibodies that identify lymphocytes, monocytes, and the Ia antigen. J Neuroimmunol 5:197–205
Hénin D, Duyckaerts C, Chaunu M-P, Vazeux R, Brousse N, Rozenbaum W, Hauw J-J (1987) Etude neuropathologique de 31 cas de syndrome d'immuno-dépression acquise. Rev Neurol (Paris) 143:631–642
Hickey WF, Kimura H (1988) Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science 239:290–292
Ho DD, Rota TR, Schooley RT, Kaplan JC, Allan JD, Groopman JE, Resnick L, Felsenstein D, Andrews CA, Hirsch MS (1985) Isolation of HTLV-III from cerebrospinal fluid and neural tissues of patients with neurologic syndromes related to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 313:1493–1497
Ho DD, Pomerantz RJ, Kaplan JC (1987) Pathogenesis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med 317:278–286
Hollander H, Stringari S (1987) Human immunodeficiency virus-associated meningitis. Clinical course and correlation. Am J Med 83:813–816
Janssen RS, Saykin AJ, Kaplan JE, Spira TJ, Pinsky PF, Sprehn GC, Hoffman JC, Mayer B jr, Schonberger LB (1988) Neurological complications of human immunodeficiency virus infection in patients with lymphadenopathy syndrome. Ann Neurol 23:49–55
Johnson RT (1982) Viral infections of the nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 237–241
Kannagi M, Kiyotaki M, King NW, Lord CI, Letvin NL (1987) Simian immunodeficiency virus induces expression of class II major histocompatibility complex structures on infected target cells in vitro. J. Virol 61:1421–1426
Kato T, Hirano A, Llena JF, Dembitzer HM (1987) Neuropathology of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) in 53 autopsy cases with particular emphasis on microglial nodules and multinucleated giant cells. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:287–294
Kato T, Dembitzer HM, Hirano A, Llena JF (1987) HTLV III-like particles within a cell process surrounded by a myelin sheath in an AIDS brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:306–308
Ketzler S, Knebel G, Budka H, Haug H (1988) Messungen von Zellgröße, Zelldichte und Synapsendichte am Cortex cerebri AIDS-dementer Männer. Verh Dtsch Ges Anat (in press)
Klatzmann D, Champagne E, Chamaret S, Gruest J, Guetard D, Hercend T, Gluckman J-C, Montagnier L (1984) T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retroviral LAV. Nature 312:767–768
Kleihues P, Lang W, Burger PC, Budka H, Vogt M, Maurer R, Lüthy R, Siegenthaler W (1985) Progressive diffuse leukoencephalopathy in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:333–339
Koenig S, Gendelman HE, Orenstein JM, Dal Canto MC, Pezeshkpour GH, Yungbluth M, Janotta F, Aksamit A, Martin MA, Fauci AS (1986) Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science 233:1089–1093
Koyanagi Y, Miles S, Mitsuyasu RT, Merrill JE, Vinters HV, Chen ISY (1987) Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science 236:819–822
Kubicki S, Henkes H, Bienzle U, Pohle HD (eds) (1988) HIV and the nervous system. Fischer, Stuttgart New York
Lang W, Miklossy J, Deruaz JP, Pizzolato GP, Probst A, Schaffner T, Gessaga E, Kleihues P (1989) Neuropathology of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): a report of 135 consecutive autopsy cases from Switzerland. Acta Neuropathol (in press)
Lee S, Harris C, Hirschfeld A, Dickson DW (1988) Cytomembranous inclusions in the brain of a patient with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Acta Neuropathol 76:101–106
Letvin NL, Daniel MD, Sehgal PK, Desrosiers RC, Hunt RD, Waldron LM, MacKey JJ, Schmidt DK, Chalifoux LV, King NW (1985) Induction of AIDS-like disease in macaque monkeys with T cell tropic retrovirus STLV-III. Science 230:71–73
Levy JA, Shimabukuro J, Hollander H, Mills J, Kaminsky L (1985) Isolation of AIDS-associated retroviruses from cerebrospinal fluid and brain of patients with neurological symptoms. Lancet II:586–588
Lifson JD, Reyes GR, McGrath MS, Stein BS, Engleman EG (1986) AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of the CD4 antigen. Science 232:1123–1127
Lynn WS, Tweedale A, Cloyd MW (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) cytotoxicity: pertubation of the cell membrane and depression of phospholipid synthesis. Virology 163:43–51
Maddon P, Dalgleish AG, McDougal JS, Clapham PR, Weiss RA, Axel R (1986) The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and in the brain Cell 47:333–348
Maier H, Budka H, Lassman H, Pohl P (1989) Vacuolar myelopathy with multinucleated giant cells in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Light and electron microscopic distribution of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antigens (submitted)
Meyenhofer MF, Epstein LG, Cho E-S, Sharer LR (1987) Ultrastructural morphology and intracellular production of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:474–484
Michaels J, Price RW, Rosenblum MK (1988) Microglia in the giant cell encephalitis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: proliferation, infection and fusion. Acta Neuropathol 76:373–379
Miles JM, Chou SM (1988) Multinucleated giant cells in AIDS encephalopathy are not derived from microglia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol [Abstr] 47:302
Mizusawa H, Hirano A, Llena JF, Kato T (1987) Nuclear bridges in multinucleated giant cells associated with primary lymphoma of the brain in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:23–26
Mizusawa H, Hirano A, Llena F (1988) Nuclear bridges within multinucleated giant cells in subacute encephalitis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol 76:166–169
Mizusawa H, Hirano A, Llena JF, Shintaku M (1986) Cerebrovascular lesions in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Acta Neuropathol 76:451–457
Monte SM de la, Moore T, Hedley-Whyte ET (1986) Vacuolar encephalopathy of AIDS (letter). N Engl J Med 315:1549–1550
Monte SM de la, Ho DD, Schooley RT, Hirsch MS, Richardson EP Jr (1987) Subacute encephalomyelitis of AIDS and its relation to HTLV-III infection. Neurology 37:562–569
Navia BA, Price RW (1987) The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex as the presenting or sol manifestation of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Neurol 44:65–69
Navia BA, Jordan BD, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex. I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol 19:517–524
Navia BA, Cho E-S, Petito CK, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex. II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol 19:525–535
Nielsen SL, Davis RL (1988) Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. In: Rosenblum ML, Levy RM, Bredesen DE (eds) AIDS and the nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 155–181
Nielsen SL, Petito CK, Urmacher CD, Posner JB (1984) Subacute encephalitis in acquired immune deficiency syndrome: a postmortem study. Am J Clin Pathol 82:678–682
Perry VH, Gordon S (1987) Modulation of CD4 antigen on macrophages and microglia in rat brain. J Exp Med 166:1138–1143
Pert CB, Hill JM, Ruff MR, Berman RM, Robey WG, Arthur LO, Ruscetti FW, Farrar WL (1986) Octapeptides deduced from the neuropeptide receptor-like pattern of antigen T4 in brain potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus-receptor binding and T cell infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9254–9258
Petito CK, Navia BA, Cho ES, Jordan BD, George DC, Price RW (1985) Vacuolar myelopathy pathologically resembling subacute combined degeneration in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 312:874–879
Petito CK, Cho E-S, Lemann W, Navia BA, Price RW (1986) Neuropathology of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): an autopsy review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:635–646
Popovic M, Sarngadharan MG, Read E, Gallo RC (1984) Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science 224:497–500
Price RW, Brew B, Sidtis J, Rosenblum M, Scheck AC, Cleary P (1988) The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science 239:586–592
Pumarola-Sune T, Navia BA, Cordon-Cardo C, Cho E-S, Price RW (1987) HIV antigen in the brains of patients with the AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol 21:490–496
Rance NE, McArthur JC, Cornblath DR, Landstrom DL, Griffin JW, Price DL (1988) Gracile tract degeneration in patients with sensory neuropathy and AIDS. Neurology 38:265–271
Resnick L, di Marzo-Veronese F, Schüpbach J, Tourtelotte WW, Ho DD, Müller F, Shapshak P, Vogt M, Groopman JE, Markham PD, Gallo RC (1985) Intra-blood-brain barier synthesis of HTLV-III-specific IgG in patients with neurologic symptoms associated with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. N Engl J Med 313:1498–1504
Resnick L, Berger JR, Shapshak P, Tourtellotte WW (1988) Early penetration of the blood-brain barrier by HIV. Neurology 38:9–14
Rhodes RH (1987) Histopathology of the central nervous system in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol 18:636–643
Rosenblum ML, Levy RM, Bredesen DE (eds) (1988) AIDS and the nervous system. Raven Press, New York
Rosenblum ML, Levy RM, Bredesen DE (1988) Overview of AIDS and the nervous system. In: Rosenblum ML, Levy RM, Bredesen DE (eds) AIDS and the nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–12
Roy S, Wainberg MA (1988) Role of the mononuclear phagocyte system in the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Leukocyte Biol 43:91–97
Ruff MR, Martin BM, Ginns EI, Farrar WL, Pert CB (1987) CD4 receptor binding peptides that block HIV infectivity cause human monocyte chemotaxis. Relationship to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. FEBS Lett 211:17–22
Schlote W, Gräfin Vitzthum H, Thomas E, Hübner K, Stutte HJ, Woelki U, Kauss J (1987) Neuropathologische Beobachtungen in 28 Fällen von erworbenem Immundefektsyndrom (AIDS). In: Fischer P-A, Schlote W (eds) AIDS und Nervensystem. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 85–116
Schmidbauer M, Budka H, Ambros P, Ulrich W (1988) In situ diagnosis of human herpes simplex virus (HSV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) encephalitis by DNA hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Clin Neuropathol 7:207 [Abstr]
Schmidbauer M, Budka H, Ambros P (1989) Herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA in microglial nodular brainstem encephalitis (submitted)
Schober R, Herman MM (1973) Neuropathology of cardiac transplantation. Survey of 31 cases. Lancet I:962–967
Schwenk, J, Cruz-Sanchez F, Gosztonyi G, Cervos-Navarro J (1987) Spongiform encephalopathy in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrom (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:389–392
Seitelberger F (1975) General neuropathology of the degenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Handb Clin Neurol 21:43–71
Sever JL, Gibbs CJ jr (Suppl eds) (1988) Retroviruses in the nervous system. Ann Neurol [Suppl] 23
Sharer LR, Prineas JW (1988) Human immunodeficiency virus in glial cells, continued. J Infect Dis 157:204 [Lett]
Sharer LR, Cho E-S, Epstein LG (1985) Multinucleated giant cells and HTLV-III in AIDS encephalopathy. Hum Pathol 16:760
Sharer LR, Epstein LG, Cho E-S, Joshi VV, Meyenhofer MF, Rankin LF, Petito CK (1986) Pathologic features of AIDS encephalopathy in children: evidence for LAV/HTLV-III infection of brain. Hum Pathol 17:271–284
Sharer LR, Epstein LG, Cho E-S, Petito CK (1986) HTLV-III and vacuolar myelopathy. N Engl J Med 315:62–63
Shaw GM, Harper ME, Hahn BH, Epstein LG, Gajdusek DC, Price RW, Navia BA, Petito CK, O'Hara CJ, Groopman JE, Cho E-S, Oleske JM, Wong-Staal F, Gallo RC (1985) HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Sciece 227:177–182
Skolnik PR, Kosloff BR, Hirsch MS (1988) Bidirectional interaction between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis 157:508–514
Snider WD, Simpson DM, Nielsen S, Gold JWM, Metroka CE, Posner JB (1983) Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol 14:403–418
Stehr-Green JK, Jason JM, Evatt BL (1988) Potential effect of revising the CDC surveillance case definition for AIDS. Lancet I:520–521
Stoler MH, Eskin TA, Benn S, Angerer RC Angerer LM (1986) Human T cell lymphotropic virus type III infection of the central nervous system. A preliminary in situ analysis. J Am Med Assoc 256:2360–2364
Stoltenburg-Didinger G (1988) Are pathomorphological patterns in HIV-infected brains different? In: Kubicki S, Henkes H, Bienzle U, Pohle, HD (eds) HIV and the nervous system. Fischer, Stuttgart New York, pp 41–48
Vazeux R, Brousse N, Jarry A, Henin D, Marche C, Vedrenne C, Mikol J, Wolff M, Michon C, Rozenbaum W, Bureau J-F, Montagnier L, Brahic M (1987) AIDS subacute encephalitis. Identification of HIV-infected cells. Am J Pathol 126: 403–410
Vinters HV (1987) The AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol 21:612 (letter)
Ward JM, O'Leary TJ, Baskin GB, Benveniste R, Harris CA, Nara PL, Rhodes RH (1987) Immunohistochemical localization of human and simian immunodeficiency viral antigens in fixed tissue sections. Am J Pathol 127:199–205
Wigdahl B, Guyton RA, Sarin PS (1987) Human immunodeficiency virus infection of the developing human nervous system. Virology 159:440–445
Wiley CA, Schrier RD, Nelson JA, Lampert PW, Oldstone MBA (1986) Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7089–7093
Wisniewski HM, Bloom BR (1975) Primary demyelination as a nonspecific consequence of a cell-mediated immune response. J Exp Med 141:346–359
Yankner BA, Skolnik PR, Shoukimas GM, Gabuzda DH, Sobel RA, Ho DD (1986) Cerebral granulomatous angiitis associated with isolation of human T lymphotropic virus type III from the central nervous system. Ann Neurol 20:362–364
Yoffe B, Lewis DE, Petrie BL, Noonan CA, Melnick JL, Hollinger FB (1987) Fusion as a mediator of cytolysis in mixtures of uninfected CD4+ lymphocytes and cells infected by human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1429–1433
Zuniga JL, Mansell PW (1986) AIDS: from immunity to infection to autoimmunity. A comprehensive hypothesis of the pathogenesis of the disease. AIDS Res 2:363–368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the Medical-Scientific Fund of the Lord Mayor of the Federal Capital of Vienna, Austria
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budka, H. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-induced disease of the central nervous system: pathology and implications for pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol 77, 225–236 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687573
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687573