Abstract
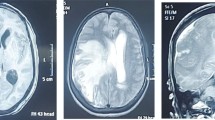
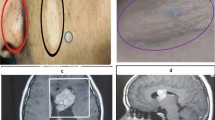
Intracranial tumors are rare in the neonatal period, and generally the most common histological types are astrocytoma, medulloblastoma, choroid plexus papilloma and neuroectodermal tumors. The early diagnosis of these tumors is often very difficult. The authors report a case of a full-term newborn who presented with opisthotonus. A subependymal mass was detected by cerebral ultrasonography, and when the child was 1 month of age depigmentations appeared on the trunk and on the right leg, confirming the suspicion of tuberous sclerosis. At 3 months of age the child suffered infantile spasm with hypsarrhythmia. The developmental delay, the marked progressive neurological deterioration and the daily seizures suggested surgical resection. Histologic studies showed a subependymal giant cell astrocytoma such as typically occurs in tuberous sclerosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curatolo P, Brinchi V (1993) Antenatal diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis. Lancet 341:176–177
Di Rocco C, Ceddia A, Iannelli A (1993) Intracranial tumours in the first year of life. A report on 51 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 123:14–24
Di Rocco C, Iannelli A, Ceddia A (1991) Intracranial tumors of the first year of life. A cooperative survey of the 1986–1987 Education Committee of the ISPN. Child's Nerv Syst 7:150–153
Di Rocco C, Iannelli A, Marchese E (1994) Implicazioni neurochirurgiche nci pazienti affetti da sclerosi tuberosa. Min Ped (in press)
Fujiwara S, Takaki T, Hikita T, Nishio S (1989) Subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis. Do subependymal nodules grow? Child's Nerv Syst 5:43–44
Groenendaal F, Meiners LC, Gooskens R, Vries LS de (1994) Cerebral proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in a neonate with tuberous sclerosis. Neuropediatrics 25:154–157
Hahn JS, Bejar R, Gladson CL (1991) Neonatal subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis: MRI, CT, and ultrasound correlation. Neurology 41:124–128
Jellinger K, Sunder-Plossmann M (1973) Connatal intracranial tumours. Neuropediatrie 4:46–49
Kapp JP, Paulson GW, Odom GL (1967) Brain tumors with tuberous sclerosis. J Neurosurg 26:191–194
Menkes JH, Till K (1990) Tumors of the nervous system. In: Menkes JH (ed) Textbook of child neurology. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 526–582
Morimoto K, Mogami H (1986) Sequential CT study of subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis. J Neurosurg 65:874–877
Painter MJ, Pang D, Ahdad-Barmada M, Bergman I (1984) Connatal brain tumors in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Neurosurgery 14:570–573
Radkowski MA, Naidich TP, Tomita T (1988) Neonatal brain tumours: CT and MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 11:10–12
Roach ES, Smith M, Huttenlocher P (1992) Diagnostic Criteria Committee of the National Tuberous Sclerosis Association. J Child Neurol 7:221–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramenghi, L.A., Verrotti, A., Domizio, S. et al. Neonatal diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis. Child's Nerv Syst 12, 121–123 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00819512
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00819512