Summary
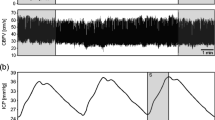
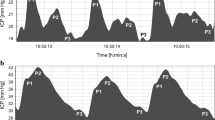
A method is described for monitoring the relationship between CSF pulse pressure and ICP in clinical patients. Highly significant linear relationships were found during 65 continuous ICP recordings in 58 patients. The slope value of this relationship showed a positive correlation with the elastance coefficient, a volume-pressure parameter assessed by bolus injection. However, the correlation was too weak to allow for a confident prediction of the elastance coefficient on the basis of CSF pulse pressure in the individual patient. This was attributed to the variable magnitude of the volume change underlying the CSF pulse pressure: the pulsatile variation in cerebral blood volume. This quantity was calculated on the basis of a mathematical model from the slope value and the elastance coefficient and was found to vary between 0.36 and 4.38ml. During plateau waves a disproportionate increase in pulse pressure with the ICP was observed in contrast with a relative decrease in intracranial elastance. This phenomenon was ascribed to an increase in the pulsatile variation in cerebral blood volume. It is concluded that, under certain conditions, the intracranial volume-pressure relationship can be continuously monitored by means of CSF pulse pressure analysis. The findings during plateau waves suggest that the pulse pressure also reflects the state of the cerebral vasomotor tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avezaat, C. J. J., Eijndhoven, J. H. M. van, Jong, D. A. de, Moolenaar, W. C. J., A new method of monitoring intracranial volume-pressure relationships. In: Intracranial Pressure III (Beks, J. W. F., Bosch, D. A., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 308–313. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1976.
Avezaat, C. J. J., Eijndhoven, J. H. M. van, Wyper, D. J., Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and intracranial volume-pressure relationships. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.42 (1979), 687–700.
Avezaat, C. J. J., Eijndhoven, J. H. M. van, Wyper, D. J., Effects of hypercapnia and arterial hypotension and hypertension on cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and intracranial volume-pressure relationships. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.43 (1980), 222–234.
Barnes, R. W., McGraw, C. P., A new on-line portable ICP data processor. In: Intracranial Pressure II (Lundberg, N., Pontén, U., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 389–390. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1975.
Brock, M., Diefenthaler, K., Zywietz, C., Pöll, W., Mock, P., Dietz, H., Amplitude analysis of intracranial pressure recordings. In: Intracranial Pressure II (Lundberg, N., Pontén, U., Brock, M., eds.), p. 391. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1975.
Brock, M., Zywietz, C., Mock, P., Wiegand, H., Zillig, C., Tamburus, W. M., Reliability and reproduceability of ICP frequence analysis. In: Intracranial Pressure III (Beks, J. W. F., Bosch, D. A., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 288–294. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1976.
Cohadon, F., Castel, J. P., Nouillant, A., Vandendriessche, M., Volume pressure relationship in clinical and experimental conditions of raised ICP. In: Intracranial Pressure II (Lundberg, N., Pontén, U., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 107–112. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1975.
Corbin, S. D., Schmidt, E. V., Silverberg, G. D., Fryer, T. B., Data display for intracranial pressure monitoring. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 426–428. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Crockard, H. A., Hanlon, K., Ganz, E., Duda, E. E., Intracranial pressure gradients in a patient with a thalamic tumor. Surg. Neurol.5 (1976), 151–154.
Eijndhoven, J. H. M. van, Avezaat, C. J. J., Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and craniospinal dynamics. A theoretical, clinical and experimental study. Thesis, Erasmus University Rotterdam. The Hague: A. Jongbloed en Zoon. 1984.
Eijndhoven, J. H. M. van, Avezaat, C. J. J., An experimental study on the pulsatile variations in cerebral blood volume. In press.
Fridén, H., Ekstedt, J., CSF pressure-volume relation and pulse related CSF pressure variations in man. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 93–96. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Godin, D., Stevenaert, A., Lhommel, R., Study of the CSF pulsation transfer: Application to the frequency analysis. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 191–194. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Graham, S. H., Hackenberry, L. E., Rea, G., Miner, M. E., A microcomputer system for ICP analysis. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 409–412. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Guillaume, J., Janny, P., Manométrie intracrânienne continue. Intérêt de la méthode et premier résultats. Rev. Neurol.84 (1951), 131–142.
Guinane, J. E., Cerebrospinal fluid pressure and brain compliance in adult cats. Neurology25 (1975), 559–564.
Hartmann, A., Continuous monitoring of CSF pressure in acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, eds.), pp. 220–228. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Hulme, A., Cooper, R., Multi-channel data acquisition and analysis in clinical practice. In: Intracranial Pressure II (Lundberg, N., Pontén, U., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 387–388. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1975.
Janny, P., La pression intra-crânienne chez l'homme. Méthode d'enregistrement, étude de ses variations et des rapports avec des signes cliniques et ophtalmologiques. Thèse. Paris: Clermont-Ferrand reproduction. 1950.
Janny, P., La surveillance de la pression intra-crânienne en neurochirurgie. Neurochir.20 (1974), 521–554.
Janny, P., Jouan, J. P., Janny, L., Gourgand, M., Gueit, U. M., A statistical approach to long-term monitoring of intracranial pressure. In: Intracranial Pressure (Brock, M., Dietz, H., eds.), pp. 59–64. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1972.
Kullberg, G., A method for statistical analysis of intracranial pressure recordings. In: Intracranial Pressure (Brock, M., Dietz, H., eds.), pp. 65–69. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1972.
Langfitt, T. W., Weinstein, J. D., Kassel, N. F., Cerebral vasomotor paralysis produced by intracranial hypertension. Neurology15 (1965), 622–641.
Löfgren, J., Essen, C. von, Zwetnow, N. N., The pressure-volume curve of the cerebrospinal fluid space in dogs. Acta Neurol. Scand.49 (1973), 557–574.
Lundberg, N., Continuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiat. Neurol. Scand.36, Suppl. 149 (1960).
Lundberg, N., Cronqvist, S., Kjällquist, A., Clinical investigations of interrelations between intracranial pressure and intracranial hemodynamics. Progr. Brain Res.30 (1968), 69–75.
Marmarou, A., Shulman, K., La Morgese, J., Compartmental analysis of compliance and outflow resistance of the cerebrospinal fluid system. J. Neurosurg.43 (1975), 523–534.
Mason, J., Price, D. J., Trimnell, S., The integration of ICP with other monitoring signals on a single computer data base. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 429–431. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Miller, J. D., Volume and pressure in the craniospinal axis. Clin. Neurosurg.22 (1975), 76–105.
Miller, J. D., Garibi, J., Intracranial volume-pressure relationship during continuous monitoring of ventricular fluid pressure. In: Intracranial Pressure (Brock, M., Dietz, H., eds.), pp. 270–274. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1972.
Miller, J. D., Garibi, J., Pickard, J. D., Induced changes of cerebrospinal fluid volume. Arch. Neurol.28 (1973), 265–269.
Miller, J. D., Leech, P. J., Assessing the effects of mannitol and steroid therapy on intracranial volume-pressure relationships. J. Neurosurg.42 (1975), 274–281.
Rickham, P. P., Penn, I. A., The place of the ventriculostomy reservoir in the treatment of myelomeningoceles and hydrocephalus. Develop. Med. Child Neurol.7 (1965), 296–301.
Risberg, J., Lundberg, N., Ingvar, D. H., Regional cerebral blood volume during acute transient rises of the intracranial pressure (plateau waves). J. Neurosurg.31 (1969), 303–310.
Shapiro, K., Marmarou, A., Shulman, K., Characterization of clinical CSF dynamics and neural axis compliance using the pressure-volume index. I. The normal pressure-volume index. Ann. Neurol.7 (1980), 508–514.
Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Pressure-volume considerations in infantile hydrocephalus. Develop. Med. Child Neurol.13, Suppl. 25 (1971), 90–95.
Sklar, F. H., Beyer, C. W., Hagler, H., Ramanathan, M., Clark, W. K., The pressure-volume function of brain elasticity and its relationship with ventricular size. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 81–84. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Stålhammer, D., Arkelsjö, P., Lindström, L., Örtengren, R., Intracranial pressure registration administrated by a microprocessor. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 404–408. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Szewczykowkski, J., Sliwka, S., Kunicki, A., Dytko, P., Korsak-Sliwka, J., A fast method of estimating the elastance of the intracranial system. A practical application in neurosurgery. J. Neurosurg.47 (1977), 19–26.
Takizawa, H., Chishiki, T., Muraoka, K., Sugiura, K., A combination of bed-side ICP recordings; histogram, trend-graph and digital print. In: Intracranial Pressure IV (Shulman, K., Marmarou, A., Miller, J. D., Becker, D. P., Hochwald, G. M., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 400–403. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1980.
Turner, J. M., McDowall, D. G., Gibson, R. M., Khalili, H., Computer analysis of intracranial pressure measurements: Clinical value and nursing response. In: Intracranial Pressure III (Beks, J. W. F., Bosch, D. A., Brock, M., eds.), pp. 283–287. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. 1976.
Wilkinson, H. A., Schuman, N., Ruggiero, J., Nonvolumetric methods of detecting impaired intracranial compliance or reactivity. Pulse width and wave from analysis. J. Neurosurg.50 (1979), 758–767.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avezaat, C.J.J., van Eijndhoven, J.H.M. Clinical observations on the relationship between cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and intracranial pressure. Acta neurochir 79, 13–29 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01403461
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01403461