Summary
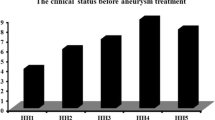
We evaluated the effect of intra-arterially infused papaverine solutions of various concentrations on cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid haemorrhage. A total of 90 vascular territories in 46 patients with symptomatic cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid haemorrhage were treated with intra-arterial infusions of papaverine. In all patients, papaverine was infused at the top of the internal carotid artery (ICA). Of the 90 vascular territories, 30 vascular territories in 14 patients were treated with an infusion of 0.1–0.2% (weight/volume) papaverine (Group 1), 30 vascular territories in 16 patients were treated with a 0.4% (w/v) papaverine infusion (Group 2), and 30 vascular territories in 16 patients were treated with an infusion of 0.8–2.0% (w/v) papaverine (Group 3). Among the three groups, we compared the vasodilatory effects of papaverine by assessing the angiographical and clinical improvements following the treatment. When 0.4% (w/v) papaverine was infused, 24 vascular territories (80%) were successfully dilated and 7 patients (44%) showed a marked reversal of neurological deficits due to vasospasm. Therefore, 80 mg/20 ml (0.4% (w/v)) papaverine infused over a 10-minute period proved to be a beneficial concentration. Transient focal neurological deficits due to the infusion of papaverine occurred in 1 Group 1 patient (7%), 1 Group 2 patient (6%), and 7 Group 3 patients (44%). Highly concentrated papaverine had a higher risk of temporary deterioration. In conclusion, the papaverine concentration of 0.4% (w/v) infused at the top of the ICA was a safe and adequate concentration for treating cerebral vasospasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr JD, Mathis JM, Horton JA (1994) Transient severe brain stem depression during intraarterial papaverine infusion for cerebral vasospasm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15: 719–723
Clouston JE, Numaguchi Y, Zoarski GH, Aldrich EF, Simard JM, Zitnay KM (1995) Intraarterial papaverine infusion for cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16: 27–38
Clyde BL, Firlik AD, Kaufmann AM, Spearman MP, Yonas H (1996) Paradoxical aggravation of vasospasm with papaverine infusion following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 84: 690–695
Cook P, James I (1981) Cerebral vasodilators. N Engl J Med 305: 1508–1513
Heilbrun MP, Olesen J, Lassen NA (1994) Regional cerebral blood flow studies in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 37: 36–44
Hendrix LE, Dion JE, Jensen ME, Phillips CD, Newman SA (1994) Papaverine-induced mydriasis. AJNR 15: 716–718
Jin Y, Sagher O, Thai Q, Kassell NF, Lee KS (1994) The effects of papaverine on phorbol dibutyrate-induced vasoconstriction in brain slice microvessels. J Neurosurg 81: 574–578
Kaku Y, Yonekawa Y, Tsukahara T (1992) Superselective intra-arterial infusion of papaverine for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 77: 842–847
Kassell NF, Heim G, Simmons N, Phillips CD, Cail WS (1992) Treatment of cerebral vasospasm with intra-arterial papaverine. J Neurosurg 77: 848–852
Kimberly L, Hopkins LN (1993) Intraarterial papaverine as an adjunct to transluminal angioplasty for vasospasm induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage. AJNR 14: 346–347
Marks MP, Steinberg GK, Lane B (1993) Intraarterial papaverine for the treatment of vasospasm. AJNR 14: 822–826
Mathis JM, DeNardo AJ, Thibault L, Jensen ME, Savory J, Dion JE (1994) In vitro evaluation of papaverine hydrochloride incompatibilities: a simulation of intraarterial infusion for cerebral vasospasm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15: 1665–1670
Mathis JM, De Nardo A, Jensen ME, Scott J, Dion JE (1994) Transient neurologic events associated with intraarterial papaverine infusion for subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced vasospasm. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15: 1671–1674
McAuliffe W, Townsend M, Eskridge JM, Newell DW, Grady MS, Winn HR (1995) Intracranial pressure changes induced during papaverine infusion for treatment of vasospasm. J Neurosurg 83: 430–434
Miller JA, Cross DT, Moran CJ, Dacey RG, McFarland JG, Diringer MN (1995) Severe thrombocytopenia following intracranial papaverine administration for treatment of vasospasm. J Neurosurg 83: 435–437
Poch G, KuKovetz WR (1971) Papaverine-induced inhibition of phosphodiesterase activity in various mammalian tissues. Life Sci 10: 133–144
Tsukahara T, Yonekawa Y, Yamamoto M,et al (1990) The endothelium-dependent response of human cerebral arteries and its changes after subarachnoid hemorrhage. In: Sano K, Tsukahara K, Kassell NF,et al (eds) Cerebral vasospasm. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp 227–230
Tsukahara T, Yoshimura S, Kazekawa K, Hashimoto N (1994) Intra-arterial papaverine for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Auton Nerv Syst 49: S163-S166
Yoshimura S, Tsukahara T, Hashimoto N, Kazekawa K, Kobayashi A (1995) Intra-arterial infusion of papaverine combined with intravenous administration of high-dose nicardipine for cerebral vasospasm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 135: 186–190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, M., Hashimoto, N., Tsukahara, T. et al. Effectiveness of intra-arterially infused papaverine solutions of various concentrations for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm. Acta neurochir 139, 706–711 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01420042
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01420042