Summary
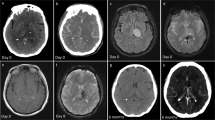
Eleven patients with venous angiomas, 6 males and 5 females ranging in age from 4 to 58, are presented. Four patients presented with intracerebral haematoma and 3 patients had associated cavernous angioma, respectively. Patients with intracerebral haematoma had signs and symptoms due to the localication of the haematoma. The other patients presented with headache, seizures, vertigo, ataxia and mental disturbances. Pre-operative diagnosis was based on computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and cerebral angiography. In 9 surgical cases it was confirmed by histopathological examination of operative specimens.
After establishing the type, size and location of the lesion decision for operative treatment was made in nine cases, in four of them because of the presence of an intracerebral haematoma and in 5 of them due to severe disability. Eight of these 9 patients recovered completely and one improved. No severe cerebral oedema was encountered after converging medullary veins were excised and main draining veins partially coagulated.
In this small series we encountered an unexpectedly large percentage of venous angiomas causing intracerebral haemorrhage which are commonly considered more benign than other vascular malformations. After reviewing previously reported cases of venous angiomas causing intracerebral haemorrhage and severe neurological deficit we think that the term “benign” is worth reconsidering. We propose a thorough examination of each case of venous angioma and the operative treatment when appropriate taking into account patients state and location of angioma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnoli Al, Hildebrandt G (1985) Cerebral venous angiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 78: 4–12
Dandy WE (1969) The brain, 2nd Ed. Hoeber Medical Division, Harper and Row, New York, pp 389–391
Forster DMC, Steiner L, Hakanson S (1972) Arteriovenous malformations of the brain: a long-term clinical study. J Neurosurg 37: 562–570
Garretson HD (1985) Intracranial arterivenous malformations. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds) Neurosurgery, Vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1448–1458
Imakita S, Nishimura T, Yamada N, Naito H, Takamiya M, Yamada Y, Kikuchi H, Yonekawa Y, Sawada T, Yamaguchi T (1989) Cerebral vascular malformations: application of magnetic resonance imaging to differential diagnosis. Neuroradiology 31: 320–325
Kumabe T, Kayama T, Sakurai Y, Ogasawara K, Niizuma H, Wada T, Namiki T (1990) Encapsulated chronic intracerebral haematoma caused by venous angioma of the basal ganglia: a case report. No Shinkei Geka 18: 735–739
Little JR, Awad IA, Jones SC, Ebrahim ZY (1990) Vascular pressures and cortical blood flow in cavernous angioma of the brain. J Neurosurg 73: 555–559
Lobato RD, Perez C, Rivas JJ, Cordobes F (1988) Clinical, radiological and pathological spectrum of angiographically occult intracranial vascular malformations. J Neurosurg 68: 518–531
Malik GM, Morgan JK, Boulos RS, Ausman JI (1988) Venous angiomas: an underestimated cause of intracranial haemorrhage. Surg Neurol 30: 350–358
Moritake K, Handa H, Mori K, Ishikawa M, Mozimoto M, Takebe Y (1980) Venous angiomas of the brain. Surg Neurol 14: 95–105
Pak H, Patel SC, Malik GM, Ausman JI (1981) Successful evacuation of a pontine haematoma secondary to rupture of a venous angioma. Surg Neurol 15: 164–167
Rengachary SS, Kalyan-Raman UP (1985) Other cranial intradural angiomas. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds) Neurosurgery, Vol 2. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1465–1473
Rigamonti D, Spetzler RF, Drayer BP, Bojanowski WM, Hodak J, Rigamonti KH, Plence K, Powers M, Rekate H (1988) Appearance of venous malformations on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 69: 535–539
Rigamonti D, Spetzler RF (1988) The association of venous and cavernous malformations. Report of four cases and discussion of the pathophysiological, diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 92: 100–105
Rigamonti D, Spetzler RF, Medina M, Rigamonti K, Geckle DS, Pappas C (1990) Cerebral venous malformations. J Neurosurg 73: 560–564
Rothfus WE, Albright LA, Casey KF, Latchaw RE, Rappolo HMN (1984) Cerebellar venous angioma: “Benign” entity?. AJNR 5: 61–66
Russel DS, Rubinstein LJ (1989) Pathology of tumours of the nervous system, 5 th Ed. Arnold, London, pp 744–746
Saito Y, Kobayashi N (1981) Cerebral venous angiomas: clinical evaluation and possible etiology. Radiology 139: 87–94
Sarwar M, McCormick WF (1978) Intracerebral venous angioma: case reprot and review. Arch Neurol 35: 323–325
Senegor M, Dohrmann GJ, Wollman RL (1983) Venous angiomas of the posterior fossa should be considered as anomalous venous drainage. Surg Neurol 19: 26–32
Toro VE, Geyer CA, Sherman JL, Parisi JE, Brantley MJ (1988) Cerebral venous angiomas: MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12: 935–940
Valavanis A, Wellenauer J, Yaşargil GM (1983) The radiological diangosis of cerebral venous angioma: cerebral angiography and computed tomography. Neuroradiology 24: 193–199
Wilkins RH (1985) Natural history of intracranial vascular malformations: a review. Neurosurgery 16: 421–430
Wilms G, Marchal G, Van Hecke P, Van Fraeyenhoven L, Decrop E, Baert AL (1990) Cerebral venous angiomas. MR imaging at 1.5 tesla. Neuroradiology 32: 81–85
Yaşargil MG (eds) (1987) Microneurosurgery, Vol 3 A. Thieme, New York, pp 49–57
Yaşargil MG (eds) (1987) Microneurosurgery, Vol 3 B. Thieme, New York, pp 406–438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lupret, V., Negovetic, L., Smiljanic, D. et al. Cerebral venous angiomas: Surgery as a mode of treatment for selected cases. Acta neurochir 120, 33–39 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02001466
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02001466