Abstract
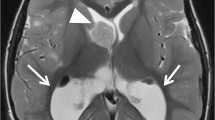
CT and MRI were used in a prospective study of the central nervous system (CNS) manifestations in 41 consecutive children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1). Gadolinium-DTPA was used in 15 patients. MRI was more effective than CT in delimiting the extension of the optic pathway glioma and in evaluating associated cerebral malformations. MRI visualized lesions generally undetected by CT, in the form of iso- or hyperintense foci with respect to the cerebral cortex in T2-weighted sequences. Well-delimited lesions of high signal intensity were observed in the globus pallidus (22 cases), the internal capsule (6 cases), corpus callosum (2 cases), anterior commissure (1 case) and semioval center (2 cases). Poorly defined hyper- or isointense areas were also observed affecting the cerebellar white matter (21 cases) and brain stem (17 cases). None of these lesions showed Gadolinium-DTPA enhancement, and were of no clinical significance. MRI has displaced CT in the initial diagnosis of patients with NF-1. Periodic annual MRI controls are only justified in patients with MRI changes to evaluate the progression or stabilization of the lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riccardi VM (1987) Neurofibromatosis. Neurol Clin 5: 337
Conference Statement Neurofibromatosis (1988) National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference. Arch Neurol 45: 575
Barker D, Wright E, Nguyen K, Kannon L, Fain P, Goldgar D, Bishop DT, Carey J, Baty B, Kivlin J, Willard H, Waye JS, Greig G, Leinwand L, Nakamura Y, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lalouel JM, White R, Skolnick M (1987) Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science 236: 1100
Huson SM (1987) The different forms of neurofibromatosis. Br Med J 294: 1113
Aoki S, Barkovich AJ, Nishimura K, Kjos BO, Machida T, Cogen P, Edwards M, Nomrian D (1989) Neurofibromatosis Types 1 and 2: cranial MR findings. Radiology 172: 527
Rubenstein AE (1986) Neurofibromatosis: a review of the clinical problem. Ann NY Acad Sci 486: 1
Diebler C, Dulac O (1987) Neurocutaneous syndromes. In: Pediatric Neurology and Neuroradiology, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 85
Lalande G, Sellier N, Kalifa G (1987) Phakomatoses: syndromes neurocutanés. In: Montagne J-PH, Couture A (eds) Tomodenitométrie Pédiatrique. Vigot, Paris, p 145
Jacoby CG, Go RT, Beren RA (1980) Cranial CT of neurofibromatosis. AJR 135: 553
Gardeur D, Palmieri A, Mashaly R (1983) Cranial computed tomography in the phakomatoses. Neuroradiology 25: 293
Bilaniuk LT (1985) MR imaging of the phakomatosis. Presented at the 71st Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting of the Radiologic Society of North America, Chicago
Kuhn JP, Cohen ML, Duffner PK (1986) MR imaging of the brain in neurofibromatosis. Presented at the 72nd Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting of the Radiologic Society of North America, Chicago
Brown EW, Riccardi VM, Mawad M, Handel S, Goldman A, Bryan RN (1987) MR imaging of optic pathways in patients with neurofibromatosis. AJNR 8: 1031
Crawford SC, Boyer RS, Harnsberger H, Polley SR, Smoker WRK, Osborn AG (1988) Disorders of histogenesis: the neurocutaneous syndromes. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 9: 247
Braffman BH, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmemrian RA (1990) MR of central nervous system neoplasia of the phacomatoses. Semin Roentgenol 25: 198
Bognanno JR, Edwars MK, Lee TA, Dunn DW, Roos KL, Klatte EC (1988) Cranial MR in neurofibromatosis. AJR 151: 381
Barkovich AJ (1990) Phakomatosis. In: Pediatric Neuroimaging. Raven, New York, p 123
Mirowitz SA, Sartor K, Gado M (1990) High-intensity basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted MR images in neurofibromatosis. AJR 154: 369
Harwood-Nash DC (1972) Optic gliomas and pediatric neuroradiology. Radiol Clin North Am 10: 83
Lee Y, Tassel PV, Bruner JM, Moser RP, Share JC (1989) Juvenile pilocytic astrocytomas: CT and MR characteristics. AJNR 10: 363
Hendrix LE, Kneeland JB, Haughton VM, Daniels DL, Szumowski J, Williams AL, Mark LP, Czervionke LF (1990) MRI of optic nerve lesions: value of Gadopentetate Dimeglumine and fat-suppression technique. AJR 155: 849
Atlas SW, Zimmerman RA, Bruce D, Schut L, Bilaniuk LT, Hackney DB, Goldberg HI, Grossman RI (1988) Neurofibromatosis and agenesis of the corpus callosum in identical twins: MR diagnosis. AJNR 9: 598
Bolande RP (1981) Neurofibromatosis — the quintessentiel neurocristopathy: pathogenetic concepts and relationships. Adv Neurol 29: 67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menor, F., Martí-Bonmatí, L., Mulas, F. et al. Imaging considerations of central nervous system manifestations in pediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatr Radiol 21, 389–394 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026665
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026665