Abstract
Purpose
It has been reported that the extent of intravascular thrombi and the quality of collateral filling in computed tomography (CT) angiography are predictive for the clinical outcome in patients with acute stroke. We hypothesized that multi-phase four-dimensional CTA (4D-CTA) allows better assessment of clot burden and collateral flow compared with arterial single-phase CTA (CTA).
Methods
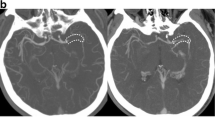
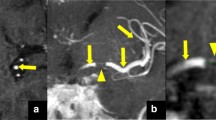
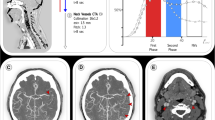
In 49 patients (33 female; age: 77 ± 12 years) with acute anterior circulation stroke, CTA and 4D-CTA reconstructed from dynamic perfusion CT data were analyzed for absolute thrombus length (TL), clot burden score (CBS), and collateral score (CS). The length of the filling defect was also defined on thin-slice nonenhanced CT as corresponding hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign (HMCAS) when present.
Results
There was good correlation (r = 0.62, p < 0.01) between the length of HMCAS (1.29 ± 0.62 cm) and TL in 4D-CTA (1.22 ± 0.51 cm). 4D-CTA and CTA significantly varied (p < 0.01) in TL (1.42 ± 0.73 cm (CTA) versus 1.11 ± 0.62 cm (4D-CTA)), CBS (median: 5, interquartile range: 4–7 (CTA) versus median: 6, interquartile range: 5–8 (4D-CTA); p < 0.001), and CS (median: 2, interquartile range: 1–2 (CTA) versus median: 3, interquartile range: 2–3 (4D-CTA); p < 0.001). Accordingly, CTA significantly overrated clot burden and underestimated collateral flow.
Conclusions
4D-CTA more closely defines clot burden and collateral supply in anterior circulation stroke than CTA, implicating an additional diagnostic benefit.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frölich AMJ, Psychogios MN, Klotz E, Schramm R, Knauth M, Schramm P. Angiographic reconstructions from whole-brain perfusion CT for the Detection of large vessel occlusion in acute stroke. Stroke. 2012;43:97–102.
Smit EJ, Vonken EJ, van Seeters T, Dankbaar JW, van der Schaaf IC, Kappelle LJ, van Ginneken B, Velthuis BK, Prokop M. Timing-invariant imaging of collateral vessels in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2013;44(8):2194–9. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000675.
Menon BK, O’Brien B, Bivard A, Spratt NJ, Demchuk AM, Miteff F, Lu X, Levi C, Parsons MW. Assessment of leptomeningeal collaterals using dynamic CT angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:365–71.
Riedel CH, Zimmermann P, Jensen-Kondering U, Stingele R, Deuschl G, Jansen O. The importance of size: successful recanalization by intravenous thrombolysis in acute anterior stroke depends on thrombus length. Stroke. 2011;42:1775–7.
Shobha N, Bal S, Boyko M, Kroshus E, Menon BK, Bhatia R, Sohn SI, Kumarpillai G, Kosior J, Hill MD, Demchuk AM. Measurement of length of hyperdense MCA sign in acute ischemic stroke predicts disappearance after IV tPA. J Neuroimaging. 2014;24(1):7–10. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2012.00761.x.
Paliwal PR, Ahmed A, Shen L, Yeo LLL, Loh PK, Ng KWP, Chong VF, Ong BKC, Venketasubramanian N, Sinha AK, Teoh HL, Bathla G, Chan BPL, Sharma VK. Persistence of hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign on follow-up CT scan after intravenous thrombolysis is associated with poor outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;33:446–52.
Maas MB, Lev MH, Ay H, Singhal AB, Greer DM, Smith WS, Harris GJ, Halpern E, Kemmling A, Koroshetz WJ, Furie KL. Collateral vessels on CT angiography predict outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2009;40:3001–5.
Grech R, Galvin PL, Power S, O’Hare A, Looby S, Brennan P, Thornton J. Outcome prediction in acute stroke patients considered for endovascular treatment: a novel tool. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014;20(3):312–24. doi:10.15274/NRJ-2014-10029.
Puetz V, Dzialowski I, Hill MD, Steffenhagen N, Coutts SB, O’Reilly C, Demchuk AM. Malignant Profile detected by CT angiographic information predicts poor prognosis despite thrombolyses within three hours from symptom onset. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;29:584–91.
Puetz V, Dzialowski I, Hill MD, Subramaniam S, Sylaja PN, Krol A, O’Reilly C, Hudon ME, Hu WY, Coutts SB, Barber PA, Watson T, Roy J, Demchuk AM. Intracranial thrombus extent predicts clinical outcome, final infarct size and hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke: the clot burden score. Int J Stroke. 2008;3:230–6.
Tan IYL, Demchuk AM, Hopyan J, Zhang L, Gladstone D, Wong K, Martin M, Symons SP, Fox AJ, Aviv RI. CT angiography clot burden score and collateral score: correlation with clinical and radiologic outcomes in acute middle cerebral artery infarct. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30:525–31.
Sillanpaa N, Saarinen JT, Rusanen H, Hakomaki J, Lahteela A, Numminen H, Elovaara I, Dastidar P, Soimakallio S. The clot burden score, the Boston Acute Stroke Imaging Scale, the cerebral blood volume ASPECTS, and two novel imaging parameters in the prediction of clinical outcome of ischemic stroke patients receiving intravenous thrombolytic therapy. Neuroradiology. 2012;54:663–72.
Baxa J, Rohan V, Tupy R, Cerna L, Flohr T, Polivka J, Ferda J. Determination of the middle cerebral artery occlusion length in acute stroke: contribution of 4D CT angiography and importance for thrombolytic efficacy prediction. Clin Neuroradiol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s00062-014-0302-x.
Frölich AMJ, Schrader D, Klotz E, Schramm R, Wasser K, Knauth M, Schramm P. 4D CT angiography more closely defines intracranial thrombus burden than single-phase ct angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3533.
Frölich AMJ, Psychogios MN, Klotz E, Schramm R, Knauth M, Schramm P. Antegrade flow across incomplete vessel occlusions can be distinguished from retrograde collateral flow using 4-dimensional computed tomographic angiography. Stroke. 2012;43:2974–9.
Willems PWA, Taeshineetanakul P, Schenk B, Brouwer PA, Terbrugge KG, Krings T. The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology. 2012;54:123–31.
Saake M, Goelitz P, Struffert T, Breuer L, Volbers B, Doerfler A, Kloska S. Comparison of conventional CTA and volume perfusion CTA in evaluation of cerebral arterial vasculature in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:2068–73.
Zhu G, Michel P, Jovin T, Patrie JT, Xin W, Eskandari A, Zhang W, Wintermark M. Prediction of recanalization in acute stroke patients receiving intravenous and endovascular revascularization therapy. Int J Stroke. 2014. doi:10.1111/ijs.12312.
Gralla J, Burkhardt M, Schroth G, El-Koussy M, Reinert M, Nedeltchev K. Occlusion length is a crucial determinant of efficiency and complication rate in thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:247–52.
Acknowledgements
None.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Iris N. Kaschka and Stephan P. Kloska contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaschka, I., Kloska, S., Struffert, T. et al. Clot Burden and Collaterals in Anterior Circulation Stroke: Differences Between Single-Phase CTA and Multi-phase 4D-CTA. Clin Neuroradiol 26, 309–315 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0359-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0359-6