Abstract
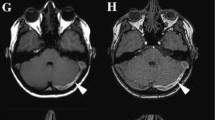
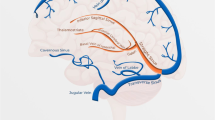
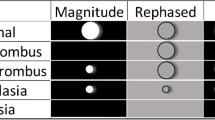
The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash and 2D time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) sequences in the visualization and evaluation of the intracranial venous system. A prospective study was carried out on 41 patients referred to our Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) unit with clinical findings suggestive of dural sinus thrombosis. Contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash and 2D TOF MRA sequences were performed, and the dural sinuses and cerebral veins were classified into five grades according to the quality of visualization and presence of thrombosis. We found the dural sinuses and cerebral veins to be normal in all sequences in 31 patients. Thrombosis of dural sinuses was detected in ten patients, with four of these ten cases found only in the contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash sequence. In general, complete visualization of cerebral veins and dural sinuses was significantly better accomplished with contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash MRA than with 2D TOF in either coronal or sagittal/oblique planes. Although 2D TOF MRA may be superior in detecting chronic dural sinus thrombosis, contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash MRA sequences may offer advantages for the early diagnosis and management of acute and subacute dural sinus thrombosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousser M-G (1999) Cerebral venous thrombosis, nothing, heparin, or local thrombolysis?. Stroke 30:481–483
Daif A, Awada A, Al-Rajeh S, et al. (1995) Cerebral venous thrombosis in adults. A study of 40 cases from Saudi Arabia. Stroke 26:1193–1195
Liauw L, Van Buchem MA, Split A, et al. (2000) MR angiography of the intracranial venous system. Radiology 214:678–682
Ozsvath RR, Casey SO, Lustrin ES, et al. (1997) Cerebral venography: comparison of CT and MR projection venography. Am J Roentgenol 169:1699–1707
Vogl TJ, Bergman C, Villringer A, et al. (1994) Dural sinus thrombosis: value of venous MR angiography for diagnosis and follow up. Am J Roentgenol 162:1191–1198
Allroggen H, Abbott RJ (2000) Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Postgrad Med J 76:12–15
Liang L, Korogi Y, Sugahara T, et al. (2001) Evaluation of the intracranial dural sinuses with a 3D contrast-enhanced MP-RAGE sequence: prospective comparison with 2D-TOF MR venography and digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 22:481–492
Keller E, Flacke S, Urbach H, et al. (1999) Diffusion and perfusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging in deep cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke 30:1144–1146
Chu K, Kang D-W, Yoon B-W, et al. (2001) Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance in cerebral venous thrombosis. Arch Neurol 58:1569–1576
Provenzale JM, Joseph GJ, Barboriak DP (1998) Dural sinus thrombosis: findings on CT and MR imaging and diagnostic pitfalls. Am J Roentgenol 170:777–783
Isensee C, Reul J, Thron A (1994) Magnetic resonance imaging of thrombosed dural sinuses. Stroke 25:29–34
Ayanzen RH, Bird CR, Keller PJ, et al. (2000) Cerebral MR venography: normal anatomy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. Am J Neuroradiol 21:74–78
Yang JJ, Hill MD, Morrish WF, et al. (2002) Comparison of pre- and postcontrast 3D time-of-flight MR angiography for the evaluation of distal intracranial branch occlusion in acute ischemic stroke. Am J Neuroradiol 23:557–567
Yucel EK, Anderson CM, Edelman RR, et al. (1999) Magnetic resonance angiography. Circulation 100:2284–2301
Kirchhof K, Welzel T, Jansen O, et al. (2002) More reliable noninvasive visualization of the cerebral veins and dural sinuses: comparison of three MR angiographic techniques. Radiology 224:804–810
Chakeres DW, Schmalbrock P, Brogan M, et al. (1991) Normal venous anatomy of the brain: demonstration with gadopentate dimeglumine in enhanced 3 D MR angiography. Am J Roentgenol 156:161–172
Liang L, Korogi Y, Sugahara T, et al. (2002) Normal structures in the intracranial dural sinuses: delineation with 3D contrast enhanced magnetization prepared rapid acquisition gradient-echo imaging sequence. Am J Neuroradiol 23:1739–1746
Dormont D, Sag K, Biondi A, et al. (1995) Gadolinium-enhanced MR of chronic dural sinus thrombosis. Am J Neuroradiol 16:1347–1352
Lafitte F, Boukobza M, Guichard J-P, et al. (1999) Deep cerebral venous thrombosis: imaging in 8 cases. Neuroradiology 41:410–418
Lacour J-C, Ducrocq X, Anxionnat R, et al. (2000) Thrombosis of deep cerebral veins in adults: clinical features and diagnostic approach. Rev Neurol (Paris) 156:739–745
Gladstone J-F, Silver F-L, Willinsky R-A, et al. (2001) Deep cerebral venous thrombosis: an illustrative case with irreversible diencephalic dysfunction. Can J Neurol Sci 28:159–162
Wakamoto H, Miyazaki H, Inaba M, et al. (1999) Recanalization of cerebral cortical venous thrombosis: a case report. No Shinkei Geka 27:469–473
Acknowledgments
I would like to express my sincere thanks to Professor M. Shennak for his valuable review of the manuscript. I would also like to thank the technical staff of our MRI Unit; without their help, this study would not have been accomplished.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haroun, A. Utility of contrast-enhanced 3D turbo-flash MR angiography in evaluating the intracranial venous system. Neuroradiology 47, 322–327 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-004-1311-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-004-1311-2