Abstract
Introduction
Diffusion weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) give information about the amount and directionality of water diffusion occurring in a given tissue. Here we study the role of diffusion tensor metrics including fractional anisotropy (FA) and spherical anisotropy (CS) in preoperative grading of diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas.
Methods
We performed DTI in 38 patients with pathologically proven diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas, who were classified into two groups, i.e., 15 patients with high-grade astrocytoma (HGAs, WHO grade III and IV) and 23 patients with low-grade astrocytoma (LGAs, WHO grade II). We measured maximum FA and minimum CS values in all cases from tumor. Histopathological diagnosis was established in all cases.
Results
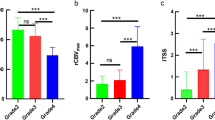
The mean maximum FA values were higher in HGA (0.583 ± 0.104) than LGA (0.295 ± 0.058), while mean minimum CS values were lower in HGA (0.42 ± 0.121) than LGA (0.722 ± 0.061). The difference in the diffusion tensor indices between HGA and LGA was found to be statistically significant with P value of <0.001. Keeping cutoff FA value of 0.4, all HGAs showed higher maximum FA values, and all LGAs showed lower maximum FA values. Also, all HGAs showed minimum CS values less than a cutoff value of 0.6, and all LGAs showed minimum CS values higher than 0.6.
Conclusion
Diffusion tensor metrics such as maximum FA and minimum CS can help to differentiate HGA from LGA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lantos PL, Louis DN, Rosenblum MK, Kleihues P (2002) Tumors of nervous system. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s neuropathology, vol II, 7th edn. Arnold, London, pp 767–1052
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) (2007) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC, Lyon
Kayama T, Kumabe T, Tominaga T, Yoshimoto T (1996) Prognostic value of complete response after the initial treatment for malignant astrocytoma. Neurol Res 18:321–324
Black PM (1991) Brain tumors. Part 1. N Engl J Med 324:1471–1476
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M et al (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60
Dean BL, Drayer BP, Bird CR et al (1990) Gliomas: classification with MR imaging. Radiology 174:411–415
Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas. Neuroradiology 34:463–469
Law M, Yang S, Wang H et al (2003) Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1989–1998
Law M, Yang S, Babb JS et al (2004) Comparison of cerebral blood volume and vascular permeability from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging with glioma grade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:746–755
Tamiya T, Kinoshita K, Ono Y, Matsumoto K, Furuta T, Ohmoto T (2000) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy reflects cellular proliferative activity in astrocytomas. Neuroradiology 42:333–338
Shimizu H, Kumabe T, Shirane R, Yoshimoto T (2000) Correlation between choline level measured by proton MR spectroscopy and Ki-67 labeling index in gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:659–665
Castillo M, Smith JK, Kwock L (2000) Correlation of myo-inositol levels and grading of cerebral astrocytomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645–1649
Kim J, Chang K, Na DG et al (2006) 3T 1H-MR spectroscopy in grading of cerebral gliomas: comparison of short and intermediate echo time sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1412–1418
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Martinez AJ (1993) Unreliability of contemporary neurodiagnostic imaging in evaluating suspected adult supratentorial (low-grade) astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 79:533–536
Sundgren PC, Dong Q, Gómez-Hassan D, Mukherji SK, Maly P, Welsh R (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain: review of clinical applications. Neuroradiology 46:339–350
Toh CH, Castillo M, Wong AMC et al (2008) Differentiation between classic and atypical meningiomas with use of diffusion tensor imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 29:1630–1635
Beppu T, Inoue T, Shibata Y et al (2003) Measurement of fractional anisotropy using diffusion tensor MRI in supratentorial astrocytic tumors. J Neurooncol 63:109–116
Inoue T, Ogasawara K, Beppu T, Oqawa A, Kabasawa H (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging for preoperative evaluation of tumor grade in gliomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 107:174–180
Beppu T, Inoue T, Shibata Y, PhDb YN et al (2005) Fractional anisotropy value by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of cell density and proliferation activity of glioblastomas. Surgical Neurology 63:56–61
Sinha S, Bastin ME, Whittle IR, Wardlaw JM (2002) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23(4):520–527
Jolapara M, Kesavadas C, Radhakrishnan VV et al (2009) Diffusion tensor mode in imaging of intracranial epidermoid cysts: one step ahead of fractional anisotropy. Neuroradiology 51(2):123–129
Hagmann P, Jonasson L, Maeder P, Thiran JP, Wedeen VJ, Meuli R (2006) Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: from scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. RadioGraphics 26:S205–S223
Le Bihan D, Mangain JF, Poupon C et al (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(4):534–546
Thomas B, Sunaert S (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging: technique, clinical and research applications. Rivista de Neuroradiologia 18:419–435
Chenevert TL, Sundgren PC, Ross BD (2006) Diffusion imaging: insight to cell status and cytoarchitecture. Neuroimag Clin N Am 16:619–632
Bahn MM (1999) Invariant and orthonormal scalar measures derived from magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson 141:68–77
Ennis DB, Kindlmann G (2006) Orthogonal tensor invariants and the analysis of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 55:136–146
Peled S, Gudbjartsson H, Westin CF, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging shows orientation and asymmetry of white matter fiber tracts. Brain Res 780:27–33
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111(3):209–219
Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K et al (2001) The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1081–1088
Castillo M, Smith JK, Kwock L, Wilber K (2001) Apparent diffusion coefficients in the evaluation of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22(1):60–64
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Sankara Sarma, Additional Professor of Biostatistics, for his advice on statistics.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jolapara, M., Patro, S.N., Kesavadas, C. et al. Can diffusion tensor metrics help in preoperative grading of diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas? A retrospective study of 36 cases. Neuroradiology 53, 63–68 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0761-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0761-y