Abstract
Introduction
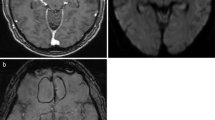
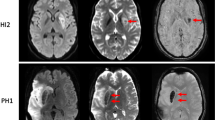
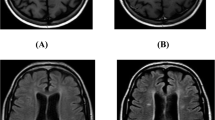
The purpose of the present study was to identify the true prevalence of hemorrhage in the abscess using T2*-weighted angiography (SWAN) imaging and to study its influence on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics.
Methods
Fifteen patients of brain abscess underwent conventional, SWAN, and DT imaging on a 3-T MRI followed by its confirmation with histology. DTI metrics were quantified by region-of-interest analysis on hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic regions of the abscess wall. Prussian blue staining was performed on excised abscess walls to confirm hemorrhage on histology.
Results
Eleven of 15 patients showed evidence of hemorrhage on both Prussian blue staining as well as SWAN imaging. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and linear anisotropy (CL) values were significantly higher, while spherical anisotropy was significantly lower in hemorrhagic compared to non-hemorrhagic regions of the abscess wall.
Conclusion
Hemorrhage in the abscess wall is a common feature and may not always indicate neoplasm. The presence of intracellular iron in addition to concentrically laid collagen fibers may have synergistic effect on FA and CL values in the abscess wall. Inclusion of SWAN to MRI protocol will define the true prevalence of hemorrhage in brain abscess.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathisen GE, Johnson JP (1997) Brain abscess. Clin Infect Dis 25:763–779
Townsend GC, Scheld WM (1998) Infections of the central nervous system. Adv Intern Med 43:403–447
Takeshita M, Kagawa M, Izawa M, Takakura K (1998) Current treatment strategies and factors influencing outcome in patients with bacterial brain abscess. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140:1263–1270
Seydoux C, Francioli P (1992) Bacterial brain abscesses: factors influencing mortality and sequelae. Clin Infect Dis 15:394–401
Yang SY, Zhao CS (1993) Review of 140 patients with brain abscess. Surg Neurol 39:290–296
Kao PT, Tseng HK, Liu CP, Su SC, Lee CM (2003) Brain abscess: clinical analysis of 53 cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 36:129–136
Lu CH, Chang WN, Lin YC et al (2002) Bacterial brain abscess: microbiological features, epidemiological trends and therapeutic outcomes. QJM 95:501–509
Qureshi HU, Habib AA, Siddiqui AA, Mozaffar T, Sarwari AR (2002) Predictors of mortality in brain abscess. J Pak Med Assoc 52:111–116
Orita T, Fujii M, Hayashi M, Fudaba H, Aoki H (1987) Brain abscess with hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 29:576–577
Kaplan M, Topsakal C, Cihangiroglu M (2006) Hemorrhage into the brain abscess cavity with Fallot's tetralogy. Pediatr Neurosurg 42:65–66
Terakawa Y, Takami T, Yamagata T, Saito T, Nakanishi N (2007) MRI of brain abscess with hemorrhage: implications of mechanism of hemorrhage. Neurol Med Chir Tokyo 47:516–518
Devi BI, Bhatia S, Kak VK, Bantwal S (1993) Spontaneous hemorrhage associated with a brain abscess. Childs Nerv Syst 9:481–482
Haris M, Gupta RK, Singh A et al (2008) Differentiation of infective from neoplastic brain lesions by dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Neuroradiology 50(6):531–540
Haris M, Gupta RK, Husain N, Hasan KM, Husain M, Narayana PA (2006) Measurement of DTI metrics in hemorrhagic brain lesions: possible implication in MRI interpretation. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1259–1268
Gupta RK, Hasan KM, Mishra AM et al (2005) High fractional anisotropy in brain abscesses versus other cystic intracranial lesions. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1107–1114
Gupta RK, Srivastava S, Saksena S et al (2010) Correlation of DTI metrics in the wall and cavity of brain abscess with histology and immunohistochemistry. NMR Biomed 23(3):262–269
Gupta RK, Hasan KM, Trivedi R et al (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging of the developing human cerebrum. J Neurosci Res 81:172–178
Miller JH, McKinstry RC, Philip JV, Mukherjee P, Neil JJ (2003) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of normal brain maturation: a guide to structural development and myelination. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:851–859
Trivedi R, Malik GK, Gupta RK et al (2007) Increased anisotropy in neonatal meningitis: an indicator of meningeal inflammation. Neuroradiology 49:767–775
Yadav A, Malik GK, Trivedi R et al (2009) Correlation of CSF neuroinflammatory molecules with leptomeningeal cortical subcortical white matter fractional anisotropy in neonatal meningitis. Magn Reson Imaging 27(2):214–221
Koot RW, Jagtap AP, Akkerman EM, Den Heeten GJ, Majoie CB (2003) Epidermoid of the lateral ventricle: evaluation with diffusion weighted and diffusion tensor imaging. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 105:270–273
Kumar M, Gupta RK, Nath K et al (2008) Can we differentiate true white matter fibers from pseudofibers inside a brain abscess cavity using geometrical diffusion tensor imaging metrics? NMR Biomed 21(6):581–588
Tanenbaum L, Vu T (2008) Susceptibility enhanced imaging of brain vasculature with SWAN. Neuroimaging Signa PULSE, 24–26
Bradley WG Jr (1993) MR appearance of hemorrhage in the brain. Radiology 189:15–26
Kraemer JL, Worm PV, de Barros FM, Maulaz A (2008) Brain abscess following ischemic stroke with secondary hemorrhage. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66(1):104–106
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Obenaus A, Nickerson JP, Kido D, Haacke EM (2008) Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: a review of clinical applications in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:9–17
Essig M, Reichenbach JR, Schad L, Debus J, Kaiser WA (2001) High resolution MR-venography of cerebral arteriovenous malformations [in German]. Radiologe 41:288–295
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA et al (2004) Diffuse axonal injury in children: clinical correlation with hemorrhagic lesions. Ann Neurol 56:36–50
Tan IL, van Schijndel RA, Pouwels PJ et al (2000) MR venography of multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1039–1042
Sehgal V, Delproposto Z, Haacke EM et al (2005) Clinical applications of neuroimaging with susceptibility-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:439–450
Awasthi R, Verma SK, Haris M et al (2010) Comparative evaluation of dynamic contrast-enhanced perfusion with diffusion tensor imaging metrics in assessment of corticospinal tract infiltration in malignant glioma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34(1):82–88
Prasad KN, Mishra AM, Gupta D, Husain N, Husain M, Gupta RK (2006) Analysis of microbial etiology and mortality in patients with brain abscess. J Infect 53(4):221–227
Eisen HN (1980) Cell mediated hypersensitivity and immunity. In: Davis BD, Dulbecco R, Eisen HN, Ginsberg HS (eds) Microbiology, including immunology and molecular genetics, 3rd edn. Harper & Row, Hagerstown, pp 494–521
Johnston RB Jr (1978) Oxygen metabolism and the microbicidal activity of macrophages. Fed Proc 37:2759–2764
Adams DO, Hamilton TA (1984) The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol 2:283–318
Sudhakar KV, Agrawal S, Rashid MR, Hussain N, Hussain M, Gupta RK (2001) MRI demonstration of haemorrhage in the wall of brain abscess: possible implications for diagnosis and management. Neuroradiology 43:218–222
Nandigam RN, Viswanathan A, Delgado P et al (2009) MR imaging detection of cerebral microbleeds: effect of susceptibility-weighted imaging, section thickness, and field strength. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(2):338–343
Haacke EM, DelProposto ZS, Chaturvedi S et al (2007) Imaging cerebral amyloid angiopathy with susceptibility-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:316–317
Sheline GE, Wara WM, Smith V (1980) Therapeutic irradiation and brain injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 6:1215–1228
Xia Z, Nguyen BD, La Mar GN (2000) The use of chemical shift temperature gradients to establish the paramagnetic susceptibility tensor orientation: implication for structure determination/refinement in paramagnetic metalloproteins. J Biomol NMR 17:167–174
Awasthi R, Gupta RK, Trivedi R, Singh JK, Paliwal VK, Rathore RK (2010) Diffusion tensor MR imaging in children with pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation and their siblings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(3):442–447
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Rohlfing T, Sullivan EV (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging of deep gray matter brain structures: effects of age and iron concentration. Neurobiol Aging 31(3):482–493
Pal D, Trivedi R, Saksena S et al (2011) Quantification of age- and gender-related changes in diffusion tensor imaging indices in deep grey matter of the normal human brain. J Clin Neurosci 18(2):193–196
Acknowledgments
RA received financial assistance from the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R.K., Tomar, V., Awasthi, R. et al. T2*-weighted MR angiography substantially increases the detection of hemorrhage in the wall of brain abscess: implications in clinical interpretation. Neuroradiology 54, 565–572 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0952-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0952-1