Abstract
Introduction
Endovascular coil embolization of posterior circulation aneurysms has advantages over a surgical approach. However, the application of coil embolization is sometimes limited in wide-necked posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) aneurysms, which are incorporating the origin of the branch. Presented here is a series of patients who were subjected to stent-supported coil embolization of PICA aneurysms.
Methods
From a prospective data repository, we retrieved records of seven consecutive patients with PICA aneurysms, all of whom were treated by stent-assisted coil embolization between January 2010 and November 2012. Outcomes were analyzed in terms of aneurysm morphology and clinical status.
Results
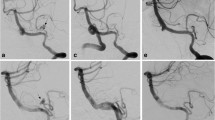
In all seven instances, the stents were placed from proximal PICA to vertebral artery (VA). A retrograde approach, via contralateral VA, was performed in five patients, where the origin of PICA from VA assumed an acute angle. In the other two patients, where the angles were obtuse, the stenting was done antegrade, via ipsilateral VA. Out of five patients with retrograde approach, single puncture and a single guiding catheter sufficed in three patients, whereas the remaining two patients required dual puncture and two guiding catheters. Endovascular treatments, as performed, resulted in excellent outcomes for all seven patients, although an asymptomatic thrombus developed in one patient with a ruptured aneurysm.
Conclusion
For coil embolization of PICA aneurysm requiring stent protection, either ipsilateral or contralateral VA access routes may be used, depending on the angle of PICA origin and the configuration of the aneurysm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tokimura H, Yamahata H, Kamezawa T et al (2011) Clinical presentation and treatment of distal posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev 34:57–67
ISUIA investigators (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110
Peluso JP, van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M et al (2008) A new self-expandable nitinol stent for the treatment of wide-neck aneurysms: initial clinical experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1405–1408
Weber W, Bendszus M, Kis B et al (2007) A new self-expanding nitinol stent (Enterprise) for the treatment of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms: initial clinical and angiographic results in 31 aneurysms. Neuroradiology 49:555–561
Biondi A, Janardhan V, Katz JM et al (2007) Neuroform stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms: strategies in stent deployment and midterm follow-up. Neurosurgery 61:460–468
Piotin M, Blanc R, Spelle L et al (2010) Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms: clinical and angiographic results in 216 consecutive aneurysms. Stroke 41:110–115
Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Dowd CF et al (2005) Initial clinical experience with a new self-expanding nitinol stent for the treatment of intracranial cerebral aneurysms: the Cordis Enterprise stent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1751–1756
Benitez RP, Silva MT, Klem J et al (2004) Endovascular occlusion of wide-necked aneurysms with a new intracranial microstent (Neuroform) and detachable coils. Neurosurgery 54:1359–1367
Lozen A, Manjila S, Rhiew R et al (2009) Y-stent-assisted coil embolization for the management of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: report of six cases. Acta Neurochir 151:1663–1672
Sedat J, Chau Y, Mondot L et al (2009) Endovascular occlusion of intracranial wide-necked aneurysms with stenting (Neuroform) and coiling: mid-term and long-term results. Neuroradiology 51:401–409
Lubicz B, Bandeira A, Bruneau M et al (2009) Stenting is improving and stabilizing anatomical results of coiled intracranial aneurysms. Neuroradiology 51:419–425
Kang HS, Kwon BJ, Kim JE et al (2010) Preinterventional clopidogrel response variability for coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms: clinical implications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1206–1210
Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A et al (2003) Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke 34:1398–1403
Roh HG, Chun YI, Choi JW et al (2012) Retrograde stent placement for coil embolization of a wide-necked posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm. Korean J Radiol 13:510–514
Song HH, Won YD, Kim YJ et al (2008) The endovascular management of saccular posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Korean J Radiol 9:396–400
Mukonoweshuro W, Laitt RD, Hughes DG (2003) Endovascular treatment of PICA aneurysms. Neuroradiology 45:188–192
Huynh-Le P, Matsushima T, Miyazono M et al (2004) Three-dimensional CT angiography for the surgical management of the vertebral artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:329–335
Peluso JP, van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M et al (2008) Posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms: incidence, clinical presentation, and outcome of endovascular treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:86–90
Kim MJ, Chung J, Kim SL et al (2012) Stenting from the vertebral artery to the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:348–352
Chung J, Kim BS, Lee D et al (2010) Vertebral artery occlusion with vertebral artery-to-posterior inferior cerebellar artery stenting for preservation of the PICA in treating ruptured vertebral artery dissection. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:1489–1492
Ecker RD, Hanel RA, Levy EI et al (2007) Contralateral vertebral approach for stenting and coil embolization of a large, thrombosed vertebral-posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm. Case report. J Neurosurg 107:1214–1216
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A111101). We thank Ms. Yoon-Kyung Choi for preparation of the illustrations.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, Y.D., Kang, HS., Lee, W.J. et al. Stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Neuroradiology 55, 877–882 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1178-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1178-1