Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this paper is to assess the value of 7 Tesla (7 T) MRI for the depiction of brain stem and cranial nerve (CN) anatomy.
Methods
Six volunteers were examined at 7 T using high-resolution SWI, MPRAGE, MP2RAGE, 3D SPACE T2, T2, and PD images to establish scanning parameters targeted at optimizing spatial resolution. Direct comparisons between 3 and 7 T were performed in two additional subjects using the finalized sequences (3 T: T2, PD, MPRAGE, SWAN; 7 T: 3D T2, MPRAGE, SWI, MP2RAGE). Artifacts and the depiction of structures were evaluated by two neuroradiologists using a standardized score sheet.
Results
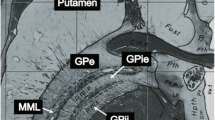
Sequences could be established for high-resolution 7 T imaging even in caudal cranial areas. High in-plane resolution T2, PD, and SWI images provided depiction of inner brain stem structures such as pons fibers, raphe, reticular formation, nerve roots, and periaqueductal gray. MPRAGE and MP2RAGE provided clear depiction of the CNs. 3D T2 images improved depiction of inner brain structure in comparison to T2 images at 3 T. Although the 7-T SWI sequence provided improved contrast to some inner structures, extended areas were influenced by artifacts due to image disturbances from susceptibility differences.
Conclusions
Seven-tesla imaging of basal brain areas is feasible and might have significant impact on detection and diagnosis in patients with specific diseases, e.g., trigeminal pain related to affection of the nerve root. Some inner brain stem structures can be depicted at 3 T, but certain sequences at 7 T, in particular 3D SPACE T2, are superior in producing anatomical in vivo images of deep brain stem structures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Back SA, Kroenke CD, Sherman LS et al (2011) White matter lesions defined by diffusion tensor imaging in older adults. Ann Neurol 70:465–476
Janzen J, van 't Ent D, Lemstra AW (2012) The pedunculopontine nucleus is related to visual hallucinations in Parkinson's disease: preliminary results of a voxel-based morphometry study. J Neurol 259:147–154
Rolland Y, Verin M, Payan CA et al (2011) A new MRI rating scale for progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy: validity and reliability. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:1025–1032
Makino T, Ito S, Kuwabara S (2011) Involvement of pontine transverse and longitudinal fibers in multiple system atrophy: a tractography-based study. J Neurol Sci 303:61–66
Naganawa S, Yamazaki M, Kawai H et al (2011) Anatomical details of the brainstem and cranial nerves visualized by high resolution readout-segmented multi-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted images using unidirectional MPG at 3 T. Magn Reson Med Sci 10:269–275
Ishikura R, Ando K, Wakata Y et al (2010) High Resolution Three-dimensional T(2)*-weighted Imaging at 3 T: Findings of Cerebellopontine Angle Schwannomas and Meningiomas. Magn Reson Med Sci 9:177–178
Nagae-Poetscher LM, Jiang H, Wakana S et al (2004) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging of the brain stem at 3 T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1325–1330
Duong TQ, Yacoub E, Adriany G et al (2003) Microvascular BOLD contribution at 4 and 7 T in the human brain: Gradient-echo and spin-echo fMRI with suppression of blood effects. Magn Reson Med 49:1019–1027
Pfeuffer J, Adriany G, Shmuel A et al (2002) Perfusion-based high-resolution functional imaging in the human brain at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 47:903–911
Pfeuffer J, van de Moortele PF, Yacoub E et al (2002) Zoomed functional imaging in the human brain at 7 Tesla with simultaneous high spatial and high temporal resolution. Neuroimaging 17:272–286
Maderwald S, Thurling M, Kuper M et al (2012) Direct visualization of cerebellar nuclei in patients with focal cerebellar lesions and its application for lesion-symptom mapping. Neuroimaging 63:1421–1431
Rooney WD, Johnson G, Li X et al (2007) Magnetic field and tissue dependencies of human brain longitudinal 1H2O relaxation in vivo. Magn Reson Med 57:308–318
Wrede KH, Johst S, Dammann P et al (2012) Caudal image contrast inversion in MPRAGE at 7 Tesla: problem and solution. Acad Radiol 19:172–178
Schar M, Kozerke S, Fischer SE et al (2004) Cardiac SSFP imaging at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 51:799–806
Sengupta S, Welch EB, Zhao Y et al (2011) Dynamic B0 shimming at 7 T. Magn Reson Imaging 29:483–496
Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB et al (2008) Influence of multichannel combination, parallel imaging and other reconstruction techniques on MRI noise characteristics. Magn Reson Imaging 26:754–762
Diedrichsen J, Maderwald S, Kuper M et al (2011) Imaging the deep cerebellar nuclei: a probabilistic atlas and normalization procedure. Neuroimaging 54:1786–1794
Moenninghoff C, Kraff O, Schlamann M et al (2010) Assessing a dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma (Lhermitte-Duclos disease) with 7 T MR imaging. Korean J Radiol 11:244–248
Nolte IS, Gerigk L, Al-Zghloul M et al (2012) Visualization of the internal globus pallidus: sequence and orientation for deep brain stimulation using a standard installation protocol at 3.0 Tesla. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154:481–494
Habib CA, Liu M, Bawany N et al (2012) Assessing abnormal iron content in the deep gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis versus healthy controls. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:252–258
Wang Y, Butros SR, Shuai X et al (2012) Different iron-deposition patterns of multiple system atrophy with predominant parkinsonism and idiopathetic Parkinson diseases demonstrated by phase-corrected susceptibility-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:266–273
Nowinski WL, Chua BC, Qian GY et al (2012) The human brain in 1700 pieces: Design and development of a three-dimensional, interactive and reference atlas. J Neurosci Methods 204:44–60
Heidemann RM, Ivanov D, Trampel R et al (2012) Isotropic submillimeter fMRI in the human brain at 7 T: Combining reduced field-of-view imaging and partially parallel acquisitions. Magn Reson Med 68(5):1506–1516
Ladd ME (2007) High-field-strength magnetic resonance: potential and limits. Top Magn Reson Imaging 18:139–152
Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z et al (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:19–30
Emir UE, Auerbach EJ, Van De Moortele PF et al (2012) Regional neurochemical profiles in the human brain measured by (1)H MRS at 7 T using local B(1) shimming. NMR Biomed 25:152–160
Kwon DH, Kim JM, Oh SH et al (2012) Seven-Tesla magnetic resonance images of the substantia nigra in Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 71:267–277
Lotfipour AK, Wharton S, Schwarz ST et al (2012) High resolution magnetic susceptibility mapping of the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:48–55
Koopmans PJ, Manniesing R, Niessen WJ et al (2008) MR venography of the human brain using susceptibility weighted imaging at very high field strength. MAGMA 21:149–158
Dietrich O, Raya JG, Reeder SB et al (2007) Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(2):375–385
Aja-Fernandez S, Tristan-Vega A, Hoge WS (2011) Statistical noise analysis in GRAPPA using a parametrized noncentral Chi approximation model. Magn Reson Med 65(4):1195–1206
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Lena Schäfer for assistance in scanning. We also thank the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Wellcome Trust and Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) for study funding.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gizewski, E.R., Maderwald, S., Linn, J. et al. High-resolution anatomy of the human brain stem using 7-T MRI: improved detection of inner structures and nerves?. Neuroradiology 56, 177–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1312-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1312-0