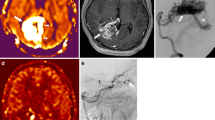
Abstract
Introduction
The objectives of the study are to investigate the application of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) and arterial spin labeling (ASL) imaging in the assessment of shunting and the draining veins in pediatric patients with arteriovenous shunting and compare the utility of SWI and ASL with conventional MR and digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Methods
This study is a retrospective study of 19 pediatric patients with arteriovenous shunting on brain MRI who were also evaluated with DSA. We assessed the ability of conventional MRI sequences, susceptibility magnitude images, phase-filtered SWI images, and pulsed ASL images in the detection of arteriovenous (AV) shunting, number of draining veins and drainage pathways in comparison to DSA.
Results
The mean number of detected draining veins on DSA (3.63) was significantly higher compared to SWI phase-filtered image (mean = 2.72), susceptibility magnitude image (mean = 2.92), ASL (mean = 1.76) and conventional MRI (2.47) (p < 0.05). Pairwise comparison of DSA difference scores (i.e., difference between MR modalities in the number of missed draining veins) revealed no difference between the MR modalities (p > 0.05). ASL was the only method that correctly identified superficial and deep venous drainage in all patients. Regarding detection of shunting, ASL, SWI phase-filtered, and magnitude images demonstrated shunting in 100, 83, and 84 % of patients, respectively.
Conclusion
SWI depicts a higher number of draining vein compared to conventional MR pulse sequences. ASL is a sensitive approach in showing 100 % sensitivity in the detection of AV shunting and in the diagnosis of the pattern of venous drainage. The present findings suggest the added utility of both SWI and ASL in the assessment of AV shunting.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Starke RM, Komotar RJ, Hwang BY, Fischer LE, Garrett MC, Otten ML, Connolly ES (2009) Treatment guidelines for cerebral arteriovenous malformation microsurgery. Br J Neurosurg 23(4):376–386
Soderman M, Andersson T, Karlsson B, Wallace MC, Edner G (2003) Management of patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Eur J Radiol 46(3):195–205
Starke RM, Komotar RJ, Hwang BY, Fischer LE, Otten ML, Merkow MB, Garrett MC, Isaacson SR, Connolly ES Jr (2008) A comprehensive review of radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: outcomes, predictive factors, and grading scales. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86(3):191–199
Geibprasert S, Pongpech S, Jiarakongmun P, Shroff MM, Armstrong DC, Krings T (2010) Radiologic assessment of brain arteriovenous malformations: what clinicians need to know? Radiographics 30(2):483–501
Gupta V, Chugh M, Walia BS, Vaishya S, Jha AN (2008) Use of CT angiography for anatomic localization of arteriovenous malformation Nidal components. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(10):1837–1840
Tanaka H, Numaguchi Y, Konno S, Shrier DA, Shibata DK, Patel U (1997) Initial experience with helical CT and 3D reconstruction in therapeutic planning of cerebral AVMs: comparison with 3D time-of-flight MRA and digital subtraction angiography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21(5):811–817
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiya J (2000) MR digital subtraction angiography of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21(4):707–711
Jagadeesan BD, Delgado Almandoz JE, Moran CJ, Benzinger TL (2011) Accuracy of susceptibility-weighted imaging for the detection of arteriovenous shunting in vascular malformations of the brain. Stroke 42(1):87–92
Jagadeesan BD, Cross DT 3rd, Delgado Almandoz JE, Derdeyn CP, Loy DN, McKinstry RC, Benzinger TL, Moran CJ (2012) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: a new tool in the diagnosis and evaluation of abnormalities of the vein of Galen in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(9):1747–1751
Miyasaka T, Taoka T, Nakagawa H, Wada T, Takayama K, Myochin K, Sakamoto M, Ochi T, Akashi T, Kichikawa K (2012) Application of susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) for evaluation of draining veins of arteriovenous malformation: utility of magnitude images. Neuroradiology 54(11):1221–1227
Jagadeesan BD, Delgado Almandoz JE, Benzinger TL, Moran CJ (2011) Postcontrast susceptibility-weighted imaging: a novel technique for the detection of arteriovenous shunting in vascular malformations of the brain. Stroke 42(11):3127–3131
George U, Jolappara M, Kesavadas C, Gupta AK (2010) Susceptibility-weighted imaging in the evaluation of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurol India 58(4):608–614
Nakagawa I, Taoka T, Wada T, Nakagawa H, Sakamoto M, Kichikawa K, Hironaka Y, Motoyama Y, Park YS, Nakase H (2013) The use of susceptibility-weighted imaging as an indicator of retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage and venous congestion with dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis and follow-up after treatment. Neurosurgery 72(1):47–55
Suazo L, Foerster B, Fermin R, Speckter H, Vilchez C, Oviedo J, Stoeter P (2012) Measurement of blood flow in arteriovenous malformations before and after embolization using arterial spin labeling. Interv Neuroradiol 18(1):42–48
Lüdemann L, Jedrzejewski G, Heidenreich J, Han ET, Bruhn H (2011) Perfusion imaging of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a study comparing quantitative continuous arterial spin labeling and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging at 3 T. Magn Reson Imaging 29(9):1157–1164
Wolf RL, Wang J, Detre JA, Zager EL, Hurst RW (2008) Arteriovenous shunt visualization in arteriovenous malformations with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(4):681–687
Le TT, Fischbein NJ, André JB, Wijman C, Rosenberg J, Zaharchuk G (2012) Identification of venous signal on arterial spin labeling improves diagnosis of dural arteriovenous fistulas and small arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(1):61–68
Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR (2004) Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med 52(3):612–618
Sehgal V, Delproposto Z, Haacke EM, Tong KA, Wycliffe N, Kido DK, Xu Y, Neelavalli J, Haddar D, Reichenbach JR (2005) Clinical applications of neuroimaging with susceptibility-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 22(4):439–450
Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Cheng YC (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(1):19–30
Barnett GH, Little JR, Ebrahim ZY, Jones SC, Friel HT (1987) Cerebral circulation during arteriovenous malformation operation. Neurosurgery 20(6):836–842
Alsop DC, Detre JA (1998) Multisection cerebral blood flow MR imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling. Radiology 208:410–416
Detre JA, Alsop DC, Vives LR et al (1998) Noninvasive MRI evaluation of cerebral blood flow in cerebrovascular disease. Neurology 50:633–641
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the IRB committee of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Due to the retrospective nature of study, the IRB waived informed consent.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabavizadeh, S.A., Edgar, J.C. & Vossough, A. Utility of susceptibility-weighted imaging and arterial spin perfusion imaging in pediatric brain arteriovenous shunting. Neuroradiology 56, 877–884 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1408-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1408-1