Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this investigation is to determine if CT perfusion (CTP) measurements at low doses (LD = 20 or 50 mAs) are similar to those obtained at regular doses (RD = 100 mAs), with and without the addition of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR).
Methods
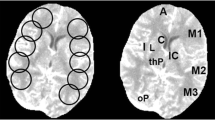
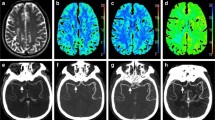
A single-center, prospective study was performed in patients with acute ischemic stroke (n = 37; 54 % male; age = 74 ± 15 years). Two CTP scans were performed on each subject: one at 100 mAs (RD) and one at either 50 or 20 mAs (LD). CTP parameters were compared between the RD and LD scans in regions of ischemia, infarction, and normal tissue. Differences were determined using a within-subjects ANOVA (p < 0.05) followed by a paired t test post hoc analysis (p < 0.01).
Results
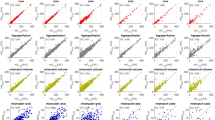
At 50 mAs, there was no significant difference between cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral blood volume (CBV), or time to maximum enhancement (Tmax) values for the RD and LD scans in the ischemic, infarcted, or normal contralateral regions (p < 0.05). At 20 mAs, there were significant differences between the RD and LD scans for all parameters in the ischemic and normal tissue regions (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
CTP-derived CBF and CBV are not different at 50 mAs compared to 100 mAs, even without the addition of ASIR. Current CTP protocols can be modified to reduce the effective dose by 50 % without altering CTP measurements.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall EJ, Brenner DJ (2008) Cancer risks from diagnostic radiology. Br J Radiol 81:362–378
Brenner DJ, Doll R, Goodhead DT, Hall EJ, Land CE, Little JB, Lubin JH, Preston DL, Preston RJ, Puskin JS, Ron E, Sachs RK, Samet JM, Setlow RB, Zaider M (2003) Cancer risks attributable to low doses of ionizing radiation: assessing what we really know. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13761–13766
Mettler FA Jr, Bhargavan M, Faulkner K, Gilley DB, Gray JE, Ibbott GS, Lipoti JA, Mahesh M, McCrohan JL, Stabin MG, Thomadsen BR, Yoshizumi TT (2009) Radiologic and nuclear medicine studies in the United States and worldwide: frequency, radiation dose, and comparison with other radiation sources—1950–2007. Radiology 253:520–531
Mnyusiwalla A, Aviv RI, Symons SP (2009) Radiation dose from multidetector row CT imaging for acute stroke. Neuroradiology 51:635–640
Zhu G, Michel P, Aghaebrahim A, Patrie JT, Xin W, Eskandari A, Zhang W, Wintermark M (2013) Computed tomography workup of patients suspected of acute ischemic stroke: perfusion computed tomography adds value compared with clinical evaluation, noncontrast computed tomography, and computed tomography angiogram in terms of predicting outcome. Stroke 44:1049–1055
Wintermark M, Albers GW, Alexandrov AV, Alger JR, Bammer R, Baron JC, Davis S, Demaerschalk BM, Derdeyn CP, Donnan GA, Eastwood JD, Fiebach JB, Fisher M, Furie KL, Goldmakher GV, Hacke W, Kidwell CS, Kloska SP, Kohrmann M, Koroshetz W, Lee TY, Lees KR, Lev MH, Liebeskind DS, Ostergaard L, Powers WJ, Provenzale J, Schellinger P, Silbergleit R, Sorensen AG, Wardlaw J, Wu O, Warach S (2008) Acute stroke imaging research roadmap. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:e23–e30
Yamauchi-Kawara C, Fujii K, Aoyama T, Yamauchi M, Koyama S (2010) Radiation dose evaluation in multidetector-row CT imaging for acute stroke with an anthropomorphic phantom. Br J Radiol 83:1029–1041
Wintermark M, Maeder P, Verdun FR, Thiran JP, Valley JF, Schnyder P, Meuli R (2000) Using 80 kVp versus 120 kVp in perfusion CT measurement of regional cerebral blood flow. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Digumarthy SR, Hsieh J, Pien H, Singh S, Gilman MD, Shepard JA (2010) Radiation dose reduction with chest computed tomography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique: initial experience. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34:40–45
Sagara Y, Hara AK, Pavlicek W, Silva AC, Paden RG, Wu Q (2010) Abdominal CT: comparison of low-dose CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction and routine-dose CT with filtered back projection in 53 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:713–719
Rapalino O, Kamalian S, Kamalian S, Payabvash S, Souza LC, Zhang D, Mukta J, Sahani DV, Lev MH, Pomerantz SR (2012) Cranial CT with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: improved image quality with concomitant radiation dose reduction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:609–615
Kilic K, Erbas G, Guryildirim M, Arac M, Ilgit E, Coskun B (2011) Lowering the dose in head CT using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1578–1582
Lin CJ, Wu TH, Lin CH, Hung SC, Chiu CF, Liu MJ, Teng MM, Chang FC, Guo WY, Chang CY (2013) Can iterative reconstruction improve imaging quality for lower radiation CT perfusion? Initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol
Huda W, Magill D, He W (2011) CT effective dose per dose length product using ICRP 103 weighting factors. Med Phys 38:1261–1265
Wintermark M, Lev MH (2010) FDA investigates the safety of brain perfusion CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:2–3
Gasparotti R, Grassi M, Mardighian D, Frigerio M, Pavia M, Liserre R, Magoni M, Mascaro L, Padovani A, Pezzini A (2009) Perfusion CT in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intra-arterial thrombolysis: predictive value of infarct core size on clinical outcome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:722–727
Diekmann S, Siebert E, Juran R, Roll M, Deeg W, Bauknecht HC, Diekmann F, Klingebiel R, Bohner G (2010) Dose exposure of patients undergoing comprehensive stroke imaging by multidetector-row CT: comparison of 320-detector row and 64-detector row CT scanners. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1003–1009
Cohnen M, Wittsack HJ, Assadi S, Muskalla K, Ringelstein A, Poll LW, Saleh A, Modder U (2006) Radiation exposure of patients in comprehensive computed tomography of the head in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1741–1745
Wintermark M, Smith WS, Ko NU, Quist M, Schnyder P, Dillon WP (2004) Dynamic perfusion CT: optimizing the temporal resolution and contrast volume for calculation of perfusion CT parameters in stroke patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:720–729
Kamena A, Streitparth F, Grieser C, Lehmkuhl L, Jamil B, Wojtal K, Ricke J, Pech M (2007) Dynamic perfusion CT: optimizing the temporal resolution for the calculation of perfusion CT parameters in stroke patients. Eur J Radiol 64:111–118
Wiesmann M, Berg S, Bohner G, Klingebiel R, Schopf V, Stoeckelhuber BM, Yousry I, Linn J, Missler U (2008) Dose reduction in dynamic perfusion CT of the brain: effects of the scan frequency on measurements of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time. Eur Radiol 18:2967–2974
Abels B, Klotz E, Tomandl BF, Villablanca JP, Kloska SP, Lell MM (2011) CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke: a comparison of 2-second and 1-second temporal resolution. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1632–1639
Ma J, Zhang H, Gao Y, Huang J, Liang Z, Feng Q, Chen W (2012) Iterative image reconstruction for cerebral perfusion CT using a pre-contrast scan induced edge-preserving prior. Phys Med Biol 57:7519–7542
Krissak R, Mistretta CA, Henzler T, Chatzikonstantinou A, Scharf J, Schoenberg SO, Fink C (2011) Noise reduction and image quality improvement of low dose and ultra low dose brain perfusion CT by HYPR-LR processing. PLoS ONE 6:e17098
Konstas AA, Goldmakher GV, Lee TY, Lev MH (2009) Theoretic basis and technical implementations of CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke, part 1: theoretic basis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:662–668
Campbell BC, Christensen S, Levi CR, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM, Parsons MW (2011) Cerebral blood flow is the optimal CT perfusion parameter for assessing infarct core. Stroke 42:3435–3440
Lin K, Do KG, Ong P, Shapiro M, Babb JS, Siller KA, Pramanik BK (2009) Perfusion CT improves diagnostic accuracy for hyperacute ischemic stroke in the 3-hour window: study of 100 patients with diffusion MRI confirmation. Cerebrovasc Dis 28:72–79
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the St. Michael’s Hospital Research Ethics Board and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
T-YL licenses CT Perfusion software to, and receives research funding from, GE Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, A., So, A., Lee, TY. et al. Low dose CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 56, 1055–1062 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1434-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1434-z