Abstract
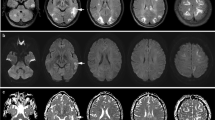
We qualitatively assessed the regional distribution of vasogenic edema in a case of postpartum eclampsia. Although diffusion-weighted imaging showed no abnormalities, bilateral high signal was seen on T2-weighted images and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps. ADC of 1.45 ± 0.10 mm2/s × 10–3 for the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) territory and 1.22 ± 0.12 mm2/s × 10–3 for the watershed areas were significantly higher than those in the territories of the anterior (0.85 ± 0.07 mm2/s × 10–3) and middle cerebral (0.79 ± 0.06 mm2/s × 10–3)arteries (P < 0.05). The predilection of ADC changes within the PCA territory and in a previously undescribed watershed distribution supports the hypothesis that vasogenic edema in eclampsia is due to hypertension-induced failure of vascular autoregulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 July 1999 Accepted: 25 April 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelter, S., Provenzale, J. & Petrella, J. Assessment of vasogenic edema in eclampsia using diffusion imaging. Neuroradiology 42, 818–820 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000439
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000439