Abstract
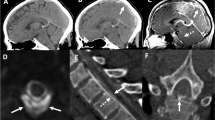
We reviewed the cranial MRI and radionuclide cisternograms of four adults with postural headache indicating spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH). All four underwent clinical and radiological follow-up. MRI showed diffuse, thin meningeal enhancement; bilateral subdural fluid collections; and morphological abnormalities secondary to “sagging” of the brain. Radionuclide cisternography revealed direct or indirect signs of leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) along the spinal axis, and the symptoms resolved after the leak treated by epidural injection of blood at a level indicated by the cisternogram. The diffuse meningeal enhancement decreased but persisted on follow-up MRI, although the patients were asymptomatic. All morphologic abnormalities resolved during 3–5 months follow-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 August 1998 Accepted: 27 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spelle, L., Boulin, A., Tainturier, C. et al. Neuroimaging features of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neuroradiology 43, 622–627 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000529
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000529