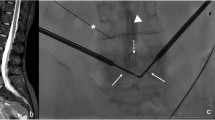
Abstract
Purpose
To determine the safety and effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) to treat sacral metastases for pain palliation and local tumor control (LTC).
Materials and Methods
An institutional tumor ablation registry was retrospectively reviewed for sacral RFA procedures performed between January 2012 and December 2015. Clinical history, pre-procedural imaging, and procedural details were reviewed to document indication for treatment, primary tumor histology, tumor volumes, presence of concurrent cementoplasty after RFA, and the occurrence of peri-procedural complications. Pain scores before and 4 weeks after the procedure were recorded. Post-procedure imaging was reviewed for imaging evidence of tumor progression. Long-term complications and duration of clinical follow-up were recorded.
Results
During the study period, 11 RFA procedures were performed to treat 16 sacral metastases. All procedures were for pain palliation. Four procedures (36 %; 4 out of 11) were also performed with the intention of achieving LTC in patients with oligometastatic disease. Concurrent cementoplasty was performed in 63 % of cases (7 out of 11). The median pain score decreased from 8 (interquartile range, 6–9.25) at baseline to 3 (interquartile range, 1.75–6.3) 1 month following RFA (P = 0.004). In the 4 patients with oligometastatic disease, LTC was achieved in 3 patients (75 %; 3 out of 4) after a median follow-up of 7.6 months (range, 3.6–11.9 months). No acute or long-term complications were documented during the overall median clinical follow-up of 4.7 months (range, 0.9–28.7 months).
Conclusions
Radiofrequency ablation maybe a safe and potentially effective treatment for patients with painful sacral metastases and can achieve LTC in selected patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nader R, Rhines LD, Mendel E. Metastatic sacral tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2004;15(4):453–7.
Finiels H, Finiels P, Jacquot J, Strubel D. Fractures of the sacrum caused by bone insufficiency. Meta-analysis of 508 cases. Presse Med (Paris, France: 1983). 1997;26(33):1568–73.
Kortman K, Ortiz O, Miller T, Brook A, Tutton S, Mathis J, et al. Multicenter study to assess the efficacy and safety of sacroplasty in patients with osteoporotic sacral insufficiency fractures or pathologic sacral lesions. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;5(5):461–6.
Ollila DW, Gleisner AL, Hsueh EC. Rationale for complete metastasectomy in patients with stage IV metastatic melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2011;104(4):420–4.
Singh D, Yi WS, Brasacchio RA, Muhs AG, Smudzin T, Williams JP, et al. Is there a favorable subset of patients with prostate cancer who develop oligometastases? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;58(1):3–10.
Goetz MP, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, Farrell MA, Maus TP, Welch TJ, et al. Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of painful metastases involving bone: a multicenter study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2004;22(2):300–6.
Dupuy DE, Liu D, Hartfeil D, Hanna L, Blume JD, Ahrar K, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of painful osseous metastases. Cancer. 2010;116(4):989–97.
Munk PL, Rashid F, Heran MK, Papirny M, Liu DM, Malfair D, et al. Combined cementoplasty and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of painful neoplastic lesions of bone. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(7):903–11.
Lane MD, Le HB, Lee S, Young C, Heran MK, Badii M, et al. Combination radiofrequency ablation and cementoplasty for palliative treatment of painful neoplastic bone metastasis: experience with 53 treated lesions in 36 patients. Skelet Radiol. 2011;40(1):25–32.
Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Trumm C, Weber C, Helmberger TK, Reiser MF. Radiofrequency ablation in combination with osteoplasty in the treatment of painful metastatic bone disease. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008;19(3):419–25.
Toyota N, Naito A, Kakizawa H, Hieda M, Hirai N, Tachikake T, et al. Radiofrequency ablation therapy combined with cementoplasty for painful bone metastases: initial experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2005;28(5):578–83.
Monga SP, Wadleigh R, Sharma A, Adib H, Strader D, Singh G, et al. Intratumoral therapy of cisplatin/epinephrine injectable gel for palliation in patients with obstructive esophageal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2000;23(4):386–92.
Wallace AN, Greenwood TJ, Jennings JW. Use of imaging in the management of metastatic spine disease with percutaneous ablation and vertebral augmentation. Am J Roentgenol. 2015;205(2):434–41.
Wu JS-Y, Wong R, Johnston M, Bezjak A, Whelan T, Group CCOPGISC. Meta-analysis of dose-fractionation radiotherapy trials for the palliation of painful bone metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;55(3):594–605.
Agarawal J, Swangsilpa T, Van der Linden Y, Rades D, Jeremic B, Hoskin P. The role of external beam radiotherapy in the management of bone metastases. Clin Oncol. 2006;18(10):747–60.
Blomlie V, Rofstad E, Talle K, Sundfør K, Winderen M, Lien H. Incidence of radiation-induced insufficiency fractures of the female pelvis: evaluation with MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(5):1205–10.
Stinauer MA, Kavanagh BD, Schefter TE, Gonzalez R, Flaig T, Lewis K, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: impact of single fraction equivalent dose on local control. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:34.
Khan AJ, Mehta S, Zusag TW, Bonomi PD, Faber LP, Shott S, et al. Long term disease-free survival resulting from combined modality management of patients presenting with oligometastatic, non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Radiother Oncol. 2006;81(2):163–7.
Miles WK, Chang DW, Kroll SS, Miller MJ, Langstein HN, Reece GP, et al. Reconstruction of large sacral defects following total sacrectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105(7):2387–94.
Thanos L, Mylona S, Galani P, Tzavoulis D, Kalioras V, Tanteles S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of osseous metastases for the palliation of pain. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(3):189–94.
Wallace AN, Greenwood TJ, Jennings JW. Radiofrequency ablation and vertebral augmentation for palliation of painful spinal metastases. J Neuro-Oncol. 2015;124(1):111–8.
Yano T, Okamoto T, Haro A, Fukuyama S, Yoshida T, Kohno M, et al. Local treatment of oligometastatic recurrence in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2013;82(3):431–5.
MacDermed DM, Weichselbaum RR, Salama JK. A rationale for the targeted treatment of oligometastases with radiotherapy. J Surg Oncol. 2008;98(3):202–6.
McMenomy BP, Kurup AN, Johnson GB, Carter RE, McWilliams RR, Markovic SN, et al. Percutaneous cryoablation of musculoskeletal oligometastatic disease for complete remission. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(2):207–13.
Wallace A, Tomasian A, Vaswani D, Vyhmeister R, Chang R, Jennings J. Radiographic local control of spinal metastases with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and vertebral augmentation. Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;37(4):759–65.
Anchala PR, Irving WD, Hillen TJ, Friedman MV, Georgy BA, Coldwell DM, et al. Treatment of metastatic spinal lesions with a navigational bipolar radiofrequency ablation device: a multicenter retrospective study. Pain Physician. 2014;17(4):317.
Hillen TJ, Anchala P, Friedman MV, Jennings JW. Treatment of metastatic posterior vertebral body osseous tumors by using a targeted bipolar radiofrequency ablation device: technical note. Radiology. 2014;273(1):261–7.
Moussazadeh N, Laufer I, Werner T, Krol G, Boland P, Bilsky MH, et al. Sacroplasty for cancer-associated insufficiency fractures. Neurosurgery. 2015;76(4):446–50. discussion 450.
Pereira LP, Clarencon F, Cormier E, Rose M, Jean B, Le Jean L, et al. Safety and effectiveness of percutaneous sacroplasty: a single-centre experience in 58 consecutive patients with tumours or osteoporotic insufficient fractures treated under fluoroscopic guidance. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(10):2764–72.
Halpin RJ, Bendok BR, Sato KT, Liu JC, Patel JD, Rosen ST. Combination treatment of vertebral metastases using image-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and vertebroplasty: a case report. Surg Neurol. 2005;63(5):469–74.
Schaefer O, Lohrmann C, Herling M, Uhrmeister P, Langer M. Combined radiofrequency thermal ablation and percutaneous cementoplasty treatment of a pathologic fracture. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(10):1047–50.
Georgy B, Wong W. Plasma-mediated radiofrequency ablation assisted percutaneous cement injection for treating advanced malignant vertebral compression fractures. Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(4):700–5.
Baque P, Karimdjee B, Iannelli A, Benizri E, Rahili A, Benchimol D, et al. Anatomy of the presacral venous plexus: implications for rectal surgery. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004;26(5):355–8.
Wallace AN, Vyhmeister R, Hsi AC, Robinson CG, Chang RO, Jennings JW. Delayed vertebral body collapse after stereotactic radiosurgery and radiofrequency ablation: case report with histopathologic–MRI correlation. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015;1(6):742–9.
Hage WD, Aboulafia AJ, Aboulafia DM. Incidence, location, and diagnostic evaluation of metastatic bone disease. Orthop Clin N Am. 2000;31(4):515–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
The treating physician obtained informed consent before each procedure. The local institutional review board provided an exemption for collecting additional informed consent after the initial procedure, given the retrospective nature of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madaelil, T.P., Wallace, A.N. & Jennings, J.W. Radiofrequency ablation alone or in combination with cementoplasty for local control and pain palliation of sacral metastases: preliminary results in 11 patients. Skeletal Radiol 45, 1213–1219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-016-2404-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-016-2404-9