Abstract.
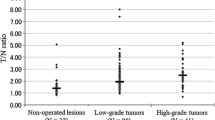
3-[123I]Iodo-α-methyl-L-tyrosine (IMT) is employed clinically as a tracer of amino acid transport in brain tumours using single-photon emission tomography (SPET). This study investigates the role of IMT SPET in the non-invasive histological grading and prognostic evaluation of cerebral gliomas. The files of patients investigated by IMT SPET in our clinic between 1988 and 1996 were evaluated retrospectively. Complete follow-up was available for 58 patients with cerebral gliomas investigated by IMT SPET shortly after tumour diagnosis. Seventeen patients had low-grade gliomas (WHO grade II), 14 had anaplastic gliomas (WHO grade III) and 27 had glioblastomas (WHO grade IV). Thirty-six cases were primary tumours and 22 cases, recurrences. Maximal and mean tumour-to-brain (T/B) ratios of IMT uptake at the first IMT SPET investigation were related to histological grading and survival time. Patients with low-grade gliomas showed significantly longer survival than patients with high-grade (grade III or IV) tumours. Gliomas without contrast enhancement on computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scans were associated with longer patient survival than tumours with contrast enhancement. The T/B ratios of IMT SPET showed no differences in relation to histological grading [WHO grade II: 1.73±0.59; WHO grade III: 1.74±0.38; WHO grade IV: 1.59±0.35, (mean±SD, T/B ratios of mean tumour uptake)]. The median survival time of patients with a high T/B ratio on IMT SPET was not significantly different from that of patients with a low T/B ratio (T/B ratio <1.6, 14.8 months; T/B ratio ≥1.6, 13.0 months). Thus, no evidence could be found for a relationship between IMT uptake in cerebral gliomas and either histological grading or survival time. Nevertheless, IMT SPET constitutes a useful method for the detection of primary and recurrent gliomas, determination of tumour extent and individual follow-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 28 January and in revised form 15 April 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, D., Gottwald, U., Langen, KJ. et al. 3-[123I]Iodo-α-methyl-L-tyrosine uptake in cerebral gliomas: relationship to histological grading and prognosis. Eur J Nucl Med 28, 855–861 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590100553
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002590100553