Abstract
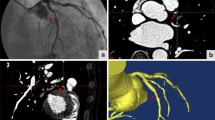
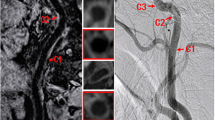
The aim of this study was to assess the reproducibility and anatomical accuracy of automated 3D CT angiography analysis software in the evaluation of carotid artery stenosis with reference to rotational DSA (rDSA). Seventy-two vessels in 36 patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis were evaluated by 3D CT angiography and conventional DSA (cDSA). Thirty-one patients also underwent rotational 3D DSA (rDSA). Multislice CT was performed with bolus tracking and slice thickness of 1.5 mm (1-mm collimation, table feed 5 mm/s) and reconstruction interval of 1.0 mm. Two observers independently performed the stenosis measurements on 3D CTA and on MPR rDSA according to the NASCET criteria. The first measurements on CTA utilized an analysis program with automatic stenosis recognition and quantitation. In the subsequent measurements, manual corrections were applied when necessary. Interfering factors for stenosis quantitation, such as calcifications, ulcerations, and adjacent vessels, were registered. Intraobserver and interobserver correlation for CTA were 0.89 and 0.90, respectively. (p<0.001). The interobserver correlation between two observers for MPR rDSA was 0.90 (p<0.001). The intertechnique correlation between CTA and rDSA was 0.69 (p<0.001) using automated measurements but increased to 0.81 (p<0.001) with the manually corrected measurements. Automated stenosis recognition achieved a markedly poorer correlation with MPR rDSA in carotids with interfering factors than those in cases where there were no such factors. Automated 3D CT angiography analysis methods are highly reproducible. Manually corrected measurements facilitated avoidance of the interfering factors, such as ulcerations, calcifications, and adjacent vessels, and thus increased anatomical accuracy of arterial delineation by automated CT angiography with reference to MPR rDSA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peiper C, Nowack J, Ktenidis K, Hopstein S, Keresztury G, Horsch S (2001) Prophylactic urgent revascularization of the internal carotid artery in the symptomatic patient. Vasa 30:247–251
Levinson MM, Rodriguez DI (1999) Endarterectomy for preventing stroke in symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid stenosis: review of clinical trials and recommendations for surgical therapy. Heart Surg Forum 2:147–168
(1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. North american symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial collaborators. N Engl J Med 325:445–453
Barnett HJ, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Ferguson GG, Haynes RB, Rankin RN, Clagett GP, Hachinski VC, Sackett DL, Thorpe KE, Meldrum HE (1998) Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. North American symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial collaborators. N Engl J Med 339:1415–1425
Inzitari D, Eliasziw M, Gates P, Sharpe BL, Chan RK, Meldrum HE, Barnett HJ (2000) The causes and risk of stroke in patients with asymptomatic internal-carotid-artery stenosis. North American symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial collaborators. N Engl J Med 342:1693–1700
Alvarez-Linera J, Benito-Leon J, Escribano J, Campollo J, Gesto R (2003) Prospective evaluation of carotid artery stenosis: elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR angiography and spiral CT angiography compared with digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1012–1019
Elgersma OE, Buijs PC, Wust AF, van der Graaf Y, Eikelboom BC, Mali WP (1999) Maximum internal carotid arterial stenosis: assessment with rotational angiography vs conventional intraarterial digital subtraction angiography. Radiology 213:777–783
Mattos MA, Sumner DS, Bohannon WT, Parra J, McLafferty RB, Karch LA, Ramsey DE, Hodgson KJ (2001) Carotid endarterectomy in women: challenging the results from ACAS and NASCET. Ann Surg 234:438–446
Gray WA, White HJ Jr, Barrett DM, Chandran G, Turner R, Reisman M (2002) Carotid stenting and endarterectomy: a clinical and cost comparison of revascularization strategies. Stroke 33:1063–1070
Rotstein AH, Gibson RN, King PM (2002) Direct b-mode NASCET-style stenosis measurement and Doppler ultrasound as parameters for assessment of internal carotid artery stenosis. Australas Radiol 46:52–56
Staikov IN, Nedeltchev K, Arnold M, Remonda L, Schroth G, Sturzenegger M, Herrmann C, Rivoir A, Mattle HP (2002) Duplex sonographic criteria for measuring carotid stenoses. J Clin Ultrasound 30:275–281
Sundgren PC, Sunden P, Lindgren A, Lanke J, Holtas S, Larsson EM (2002) Carotid artery stenosis: contrast-enhanced MR angiography with two different scan times compared with digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 44:592–599
Link J, Brossmann J, Penselin V, Gluer CC, Heller M (1997) Common carotid artery bifurcation: preliminary results of CT angiography and color-coded duplex sonography compared with digital subtraction angiography. Am J Roentgenol 168:361–365
Anderson GB, Ashforth R, Steinke DE, Ferdinandy R, Findlay JM (2000) CT angiography for the detection and characterization of carotid artery bifurcation disease. Stroke 31:2168–2174
Nederkoorn PJ, Mali WP, Eikelboom BC, Elgersma OE, Buskens E, Hunink MG, Kappelle LJ, Buijs PC, Wust AF, van der Lugt A, van der Graaf Y (2002) Preoperative diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis: accuracy of noninvasive testing. Stroke 33:2003–2008
Berg MH, Manninen HI, Rasanen HT, Vanninen RL, Jaakkola PA (2002) CT angiography in the assessment of carotid artery atherosclerosis. Acta Radiol 43:116–124
Phillips CD, Bubash LA (2002) CT angiography and MR angiography in the evaluation of extracranial carotid vascular disease. Radiol Clin North Am 40:783–798
Carvi Y, Nievas MN, Haas E, Hollerhage HG, Drathen C (2002) Complementary use of computed tomographic angiography in treatment planning for posterior fossa subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 50:1283–1289
Villablanca JP, Jahan R, Hooshi P, Lim S, Duckwiler G, Patel A, Sayre J, Martin N, Frazee J, Bentson J, Vinuela F (2002) Detection and characterization of very small cerebral aneurysms by using 2D and 3D helical CT angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 23:1187–1198
Cinat M, Lane CT, Pham H, Lee A, Wilson SE, Gordon I (1998) Helical CT angiography in the preoperative evaluation of carotid artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg 28:290–300
Vanninen R, Manninen H, Koivisto K, Tulla H, Partanen K, Puranen M (1994) Carotid stenosis by digital subtraction angiography: reproducibility of the European carotid surgery trial and the North American symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial measurement methods and visual interpretation. Am J Neuroradiol 15:1635–1641
Hirai T, Korogi Y, Ono K, Murata Y, Takahashi M, Suginohara K, Uemura S (2001) Maximum stenosis of extracranial internal carotid artery: effect of luminal morphology on stenosis measurement by using CT angiography and conventional DSA. Radiology 221:802–809
Leclerc X, Godefroy O, Pruvo JP, Leys D (1995) Computed tomographic angiography for the evaluation of carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 26:1577–1581
Marcus CD, Ladam-Marcus VJ, Bigot JL, Clement C, Baehrel B, Menanteau BP (1999) Carotid arterial stenosis: evaluation at CT angiography with the volume-rendering technique. Radiology 211:775–780
Randoux B, Marro B, Koskas F, Duyme M, Sahel M, Zouaoui A, Marsault C (2001) Carotid artery stenosis: prospective comparison of CT, three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR, and conventional angiography. Radiology 220:179–185
Marks MP, Napel S, Jordan JE, Enzmann DR (1993) Diagnosis of carotid artery disease: preliminary experience with maximum-intensity-projection spiral CT angiography. Am J Roentgenol 160:1267–1271
Cumming MJ, Morrow IM (1994) Carotid artery stenosis: a prospective comparison of CT angiography and conventional angiography. Am J Roentgenol 163:517–523
Moll R, Dinkel HP (2001) Value of the CT angiography in the diagnosis of common carotid artery bifurcation disease: CT angiography vs digital subtraction angiography and color-flow Doppler. Eur J Radiol 39:155–162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Berg, M.H., Ikonen, A.E.J. et al. Carotid artery stenosis: reproducibility of automated 3D CT angiography analysis method. Eur Radiol 14, 665–672 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2130-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2130-2