Abstract
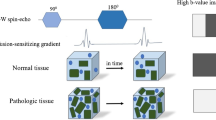
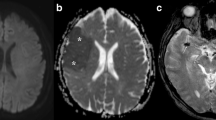
Diffusion-weighted MRI has become more and more popular in the last couple of years. It is already an accepted diagnostic tool for patients with acute stroke, but is more difficult to use for extracranial applications due to technical challenges mostly related to motion sensitivity and susceptibility variations (e.g., respiration and air-tissue boundaries). However, thanks to the newer technical developments, applications of body DW-MRI are starting to emerge. In this review, we aim to provide an overview of the current status of the published data on DW-MRI in extracranial applications. A short introduction to the physical background of this promising technique is provided, followed by the current status, subdivided into three main topics, the functional evaluation, tissue characterization and therapy monitoring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carr HY, Purcell EM (1954) Effects of diffusion on free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Phys Rev 94:630–638
Hahn EL (1950) Spin echoes. Phys Rev 80:580–594
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:288–292
Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Mintorovitch J, Chileuitt L, Shimizu H, Kucharczyk J, Wendland MF, Weinstein PR (1990) Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 14:330–346
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Neil JJ, Ackerman JH (1992) Detection of pseudodiffusion in rat brain following blood substitution wth perfluorocarbon. J Magn Reson 97:194–201
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345
Murtz P, Flacke S, Traber F, van den Brink JS, Gieseke J, Schild HH (2002) Abdomen: diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pulse-triggered single-shot sequences. Radiology 224:258–264
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Boesch C, Hermans R (2004) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the parotid gland: influence of the choice of b-values on the apparent diffusion coefficient value. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:786–790
Mardor Y, Pfeffer R, Spiegelmann R, Roth Y, Maier SE, Nissim O, Berger R, Glicksman A, Baram J, Orenstein A, Cohen JS, Tichler T (2003) Early detection of response to radiation therapy in patients with brain malignancies using conventional and high b-value diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Clin Oncol 21:1094–1100
Lyng H, Haraldseth O, Rofstad EK (2000) Measurement of cell density and necrotic fraction in human melanoma xenografts by diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 43:828–836
Bammer R (2003) Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol 45:169–184
Ries M, Jones RA, Basseau F, Moonen CT, Grenier N (2001) Diffusion tensor MRI of the human kidney. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:42–49
Muller MF, Prasad P, Siewert B, Nissenbaum MA, Raptopoulos V, Edelman RR (1994) Abdominal diffusion mapping with use of a whole-body echo-planar system. Radiology 190:475–478
Siegel CL, Aisen AM, Ellis JH, Londy F, Chenevert TL (1995) Feasibility of MR diffusion studies in the kidney. J Magn Reson Imaging 5:617–620
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H (1999) Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 210:617–623
Jones RA, Grattan-Smith JD (2003) Age dependence of the renal apparent diffusion coefficient in children. Pediatr Radiol 33:850–854
Prasad PV, Priatna A (1999) Functional imaging of the kidneys with fast MRI techniques. Eur J Radiol 29:133–148
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Mitsuzaki K, Nakayama Y, Tang Y, Takashani M (1999) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in diffuse renal disease by diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:832–837
Chow LC, Bammer R, Moseley ME, Sommer FG (2003) Single breath-hold diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:377–382
Yang D, Ye Q, Williams DS, Hitchens TK, Ho C (2004) Normal and transplanted rat kidneys: diffusion MR imaging at 7T. Radiology 231:702–709
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Oyen RH, Peeters RR (2005) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in healthy volunteers and patients with parenchymal diseases: initial experience. Radiology 235:911–917
Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with single-shot echo-planar imaging in the upper abdomen: preliminary clinical experience in 61 patients. Abdom Imaging 24:456–461
Muller MF, Prasad PV, Bimmler D, Kaiser A, Edelman RR (1994) Functional imaging of the kidney by means of measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 193:711–715
Pedersen M, Wen JG, Shi Y, Beigi N, Christensen TB, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Frokiaer J (2003) The effect of unilateral ureteral obstruction on renal function in pigs measured by diffusion-weighted MRI. APMIS Suppl 109:29–34
Ries M, Basseau F, Tyndal B, Jones R, Deminiere C, Catargi B, Combe C, Moonen CW, Grenier N (2003) Renal diffusion and BOLD MRI in experimental diabetic nephropathy. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:104–113
Liu AS, Xie JX (2003) Functional evaluation of normothermic ischemia and reperfusion injury in dog kidney by combining MR diffusion-weighted imaging and Gd-DTPA enhanced first-pass perfusion. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:683–693
Fukuda Y, Ohashi I, Hanafusa K, Nakagawa T, Ohtani S, An-naka Y, Hayashi T, Shibuya H (2000) Anisotropic diffusion in kidney: apparent diffusion coefficient measurements for clinical use. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:156–160
Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH, Fung SL, Cheung YK, Chan MS, Yuen MK, Mak SF, Wong KP (2001) MR diffusion-weighted imaging of kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis. Clin Imaging 25:110–113
Toyoshima S, Noguchi K, Seto H, Shimizu M, Watanabe N (2000) Functional evaluation of hydronephrosis by diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Relationship between apparent diffusion coefficient and split glomerular filtration rate. Acta Radiol 41:642–646
Squillaci E, Manenti G, Di Stefano F, Miano R, Strigari L, Simonetti G (2004) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the evaluation of renal tumours. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 23:39–45
Sumi M, Takagi Y, Uetani M, Morikawa M, Hayashi K, Kabasawa H, Aikawa K, Nakamura T (2002) Diffusion-weighted echoplanar MR imaging of the salivary glands. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:959–965
Yoshino N, Yamada I, Ohbayashi N, Honda E, Ida M, Kurabayashi T, Maruyama K, Sasaki T (2001) Salivary glands and lesions: evaluation of apparent diffusion coefficients with split-echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging-initial results. Radiology 221:837–842
Zhang L, Murata Y, Ishida R, Ohashi I, Yoshimura R, Shibuya H (2001) Function evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MRI in irradiated salivary glands: a correlative study with salivary gland scintigraphy. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:223–229
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Claus FG, Sunaert S, Hermans R (2005) Gustatorystimulation changes the apparent diffusion coefficient of salivary glands. Radiology 235:629–634
Habermann CR, Cramer MC, Graessner J, Gossrau P, Reitmeier F, Fiehler J, Schoder V, Jaehne M, Adam G (2004) Functional imaging of parotid glands: diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI before and after stimulation. Rofo 176:1385–1389
Habermann CR, Gossrau P, Graessner J, Arndt C, Cramer MC, Reitmeier F, Jaehne M, Adam G (2005) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI: a valuable tool for differentiating primary parotid gland tumors? RoFo 177:940–945
Erturk SM, Ichikawa T, Motosugi U, Sou H, Araki T (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function before and after secretin stimulation. Am J Gastroenterol 101:133–136
Lang P, Wendland MF, Saeed M, Gindele A, Rosenau W, Mathur A, Gooding CA, Genant HK (1998) Osteogenic sarcoma: noninvasive in vivo assessment of tumor necrosis with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 206:227–235
Gupta RK, Cloughesy TF, Sinha U, Garakian J, Lazareff J, Rubino G, Rubino L, Becker DP, Vinters HV, Alger JR (2000) Relationships between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficient and quantitative histopathology in human glioma. J Neurooncol 50:215–226
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, Ikushima I, Shigematu Y, Hirai T, Okuda T, Liang L, Ge Y, Komohara Y, Ushio Y, Takahashi M (1999) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:53–60, 1999
Uhl M, Altehoefer C, Kontny U, Il’yasov K, Büchert M, Langer M (2002) MRI-diffusion imaging of neuroblastomas: first results and correlation with histology. Eur Radiol 12:2335–2338
Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Tsuda K, Nakamura H (1999) Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173:393–398
Issa B (2002) In vivo measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and malignant prostatic tissues using echo-planar imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:196–200
Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Thomas DL, Lythgoe MF, Guilfoyle D, Williams SR, Doran SJ (2000) Burst excitation for quantitative diffusion imaging with multiple b-values. Magn Reson Med 44:737–745
Koinuma M, Ohashi I, Hanafusa K, Shibuya H (2005) Apparent diffusion coefficient measurements with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of hepatic fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:80–85
Taouli B, Vilgrain V, Dumont E, Daire JL, Fan B, Menu Y (2003) Evaluation of liver diffusion isotropy and characterization of focal hepatic lesions with two single-shot echo-planar MR imaging sequences: prospective study in 66 patients. Radiology 226:71–78
Naganawa S, Sato C, Nakamura T, Kumada H, Ishigaki T, Miura S, Maruyama K, Takizawa O (2005) Diffusion-weighted images of the liver: comparison of tumor detection before and after contrast enhancement with superparamagnetic iron oxide. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:836–840
Sinha S, Lucas-Quesada FA, Sinha U, DeBruhl N, Bassett LW (2002) In vivo diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast: potential for lesion characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:693–704
Guo Y, Cai YQ, Cai ZL, Gao YG, An NY, Ma L, Mahankali S, Gao JH (2002) Differentiation of clinically benign and malignant breast lesions using diffusion-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:172–178
Woodhams R, Matsunaga K, Iwabuchi K, Kan S, Hata H, Kuranami M, Watanabe M, Hayakawa K (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of malignant breast tumors: the usefulness of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value and ADC map for the detection of malignant breast tumors and evaluation of cancer extension. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:644–649
Sumi M, Sakihama N, Sumi T, Morikawa M, Uetani M, Kabasawa H, Shigeno K, Hayashi K, Takahashi H, Nakamura T (2003) Discrimination of metastatic cervical lymph nodes with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1627–1634
Dubrulle F, Souillard R, Chechin D, Vaneecloo FM, Desaulty A, Vincent C (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging sequence in the detection of postoperative recurrent cholesteatoma. Radiology 238:604–610
Vercruysse JP, De Foer B, Pouillon M, Somers T, Casselman J, Offeciers E (2006) The value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the diagnosis of primary acquired and residual cholesteatoma: a surgical verified study of 100 patients. Eur Radiol 16(7):1461–1467
Stasolla A, Magliulo G, Parrotto D, Luppi G, Marini M (2004) Detection of postoperative relapsing/residual cholesteatomas with diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging. Otol Neurotol 25:879–884
Stasolla A, Magliulo G, Lo Mele L, Prossomariti G, Luppi G, Marini M (2004) Value of echo-planar diffusion-weighted MRI in the detection of secondary and postoperative relapsing/residual cholesteatoma. Radiol Med (Torino) 107:556–568
Aikele P, Kittner T, Offergeld C, Kaftan H, Huttenbrink KB, Laniado M (2003) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of cholesteatoma in pediatric and adult patients who have undergone middle ear surgery. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:261–265
Herneth AM, Philipp MO, Naude J, Funovics M, Beichel RR, Bammer R, Imhof H (2002) Vertebral metastases: assessment with apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 225:889–894
Park SW, Lee JH, Ehara S, Park YB, Sung SO, Choi JA, Joo YE (2004) Single shot fast spin echo diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the spine; is it useful in differentiating malignant metastatic tumor infiltration from benign fracture edema? Clin Imaging 28:102–108
Baur A, Stabler A, Bruning R, Bartl R, Krodel A, Reiser M, Deimling M (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of bone marrow: differentiation of benign versus pathologic compression fractures. Radiology 207:349–356
Chan JH, Peh WC, Tsui EY, Chau LF, Cheung KK, Chan KB, Yuen MK, Wong ET, Wong KP (2002) Acute vertebral body compression fractures: discrimination between bening and malignant causes using apparent diffusion coefficients. Br J Radiol 75:207–214
Baur A, Huber A, Ertl-Wagner B, Durr R, Zysk S, Arbogast S, Deimling M, Reiser M (2001) Diagnostic value of increased diffusion weighting of a steady-state free precession sequence for differentiating acute bening osteoporotic fractures from pathologic vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:366–372
Byun WM, Shin SO, Chang Y, Lee SJ, Finsterbusch J, Frahm J (2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of metastatic disease of the spine: assessment of response to therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:906–912
van Rijswijk CS, Kunz P, Hogendoorn PC, Taminiau AH, Doornbos J, Bloem JL (2002) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of soft-tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:302–307
Einarsdottir H, Karlsson M, Wejde J, Bauer HC (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI of soft tissue tumours. Eur Radiol 14:959–963
Katayama M, Masui T, Kobayashi S, Ito T, Sakahara H, Nozaki A, Kabasawa H (2002) Diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging of ovarian tumors: is it useful to measure apparent diffusion coefficients? J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:250–256
Nakayama T, Yoshimitsu K, Irie H, Aibe H, Tajima T, Nishie A, Asayama Y, Matake K, Kakihara D, Matsuura S, Nakano H, Honda H (2005) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging and ADC mapping in the differential diagnosis of ovarian cystic masses: usefulness of detecting keratinoid substances in mature cystic teratomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:271–278
Shimofusa R, Fujimoto H, Akamata H, Motoori K, Yamamoto S, Ueda T, Ito H (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of prostate cancer. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29:149–153
Hosseinzadeh K, Schwarz SD (2004) Endorectal diffusion-weighted imaging in prostate cancer to differentiate malignant and benign peripheral zone tissue. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:654–661
Pickles MD, Gibbs P, Sreenivas M, Turnbull LW (2006) Diffusion-weighted imaging of normal and malignant prostate tissue at 3.0T. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:130–134
Dzik-Jurasz A, Domenig C, George M, Wolber J, Padhani A, Brown G, Doran S (2002) Diffusion MRI for prediction of response of rectal cancer to chemoradiation. Lancet 360:307–308
DeVries AF, Kremser C, Hein PA, Griebel J, Krezcy A, Ofner D, Pfeiffer KP, Lukas P, Judmaier W (2003) Tumor microcirculation and diffusion predict therapy outcome for primary rectal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:958–965
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Chen F, Ni Y, Landuyt W, Verbeken EK, Bosmans H, Marchal G, Hermans R (2005) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in monitoring the effect of a vascular targeting agent on rhabdomyosarcoma in rats. Radiology 234:756–764
Chenevert TL, Stegman LD, Taylor JM, Robertson PL, Greenberg HS, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD (2000) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: an early surrogate marker of therapeutic efficacy in brain tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:2029–2035
Galons JP, Altbach MI, Paine-Murrieta GD, Taylor CW, Gillies RJ (1999) Early increases in breast tumor xenograft water mobility in response to paclitaxel therapy detected by non-invasive diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Neoplasia 1:113–117
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Vandecaveye V, Chen F, Sun X, Bosmans H, Hermans R, Verbeken EK, Boesch C, Marchal G, Landuyt W, Ni Y (2005) Effect of vascular targeting agent in rat tumor model: dynamic contrast-enhanced versus diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 237:492–499
Jacobs MA, Herskovits EH, Kim HS (2005) Uterine fibroids: diffusion-weighted MR imaging for monitoring therapy with focused ultrasound surgery-preliminary study. Radiology 236:196–203
Kamel IR, Bluemke DA, Ramsey D, Abusedera M, Torbenson M, Eng J, Szarf G, Geschwind JF (2003) Role of diffusion-weighted imaging in estimating tumor necrosis after chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:708–710
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Dr. Anwar R. Padhani of the Mount Vernon Cancer Centre, London, for his many helpful comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thoeny, H.C., De Keyzer, F. Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 17, 1385–1393 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0547-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0547-0