Abstract
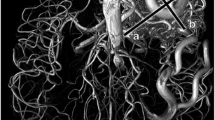
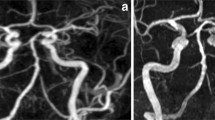
The aim of this study was to assess whether the addition of a black blood (BB) sequence to standard three-dimensional time-of-flight (3D-TOF) imaging yields improved quantitative assessment of intracranial aneurysms. Thirty seven patients with 42 proven intracranial aneurysms underwent intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography, 3D-TOF and BB MRI imaging. This multimodality imaging was used to create a composite reference aneurysm description. The 3D-TOF and BB imaging were graded on a subjective seven-point scale to determine what improvement if any the addition of BB imaging yielded. Comparison of measurements from all imaging modalities demonstrated no significant difference (p < 0.01) in aneurysm length/width or parent vessel width. Aneurysm neck measurements were underestimated on 3D-TOF images although there was still a significant correlation (R 2 = 0.72, p < 0.05). Comparison of TOF and BB examinations to the composite reference using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test showed significant improvement in the demonstration of the aneurysm to parent/branch vessels and the morphology/size of the aneurysm neck, particularly in the setting of local haematoma or slow flow (p < 0.001). We propose the addition of the BB sequence as a useful adjunct to 3D-TOF imaging particularly when detailed aneurysm morphology is required or there is thrombus in subarachnoid space.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colpan ME, Sekerci Z, Hekimoglu B, Mogul DJ (2006) Computer-assisted intraaneurysmal thrombus visualization. J Neuroimaging 16:59–68
van der Schaaf IC, Velthuis BK, Wermer MJ et al (2005) New detected aneurysms on follow-up screening in patients with previously clipped intracranial aneurysms: comparison with DSA or CTA at the time of SAH. Stroke 36:1753–1758
Wermer MJ, Buskens E, van der Schaaf IC, Bossuyt PM, Rinkel GJ (2004) Yield of screening for new aneurysms after treatment for subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 62:369–375
Wermer MJ, van der Schaaf IC, Velthuis BK, Majoie CB, Albrecht KW, Rinkel GJ (2006) Yield of short-term follow-up CT/MR angiography for small aneurysms detected at screening. Stroke 37:414–418
Alexander AL, Buswell HR, Sun Y, Chapman BE, Tsuruda JS, Parker DL (1998) Intracranial black-blood MR angiography with high-resolution 3D fast spin echo. Magn Reson Med 40:298–310
Liu K, Margosian P (2001) Multiple contrast fast spin-echo approach to black-blood intracranial MRA: use of complementary and supplementary information. Magn Reson Imaging 19:1173–1181
Adams WM, Laitt RD, Jackson A (2000) The role of MR angiography in the pretreatment assessment of intracranial aneurysms: a comparative study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1618–1628
Velthuis BK, Rinkel GJ, Ramos LM et al (1998) Subarachnoid hemorrhage: aneurysm detection and preoperative evaluation with CT angiography. Radiology 208:423–430
Costalat V, Lebars E, Sarry L et al (2006) In vitro evaluation of 2D-digital subtraction angiography versus 3D-time-of-flight in assessment of intracranial cerebral aneurysm filling after endovascular therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:177–184
Tipper G, U-King-Im JM, Price SJ et al (2005) Detection and evaluation of intracranial aneurysms with 16-row multislice CT angiography. Clin Radiol 60:565–572
Chen CY, Hsieh SC, Choi WM, Chiang PY, Chien JC, Chan WP (2006) Computed tomography angiography in detection and characterization of ruptured anterior cerebral artery aneurysms at uncommon location for emergent surgical clipping. Clin Imaging 30:87–93
Carstairs SD, Tanen DA, Duncan TD et al (2006) Computed tomographic angiography for the evaluation of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acad Emerg Med 13:486–492
Amir K, Zvi HR, Maimon S (2006) Brain computed tomography angiographic scans as the sole diagnostic examination for excluding aneurysms in patients with perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 59:798–802
Uysal E, Yanbuloglu B, Erturk M, Kilinc BM, Basak M (2005) Spiral CT angiography in diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms of cases with acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Diagn Interv Radiol 11:77–82
Goddard AJ, Tan G, Becker J (2005) Computed tomography angiography for the detection and characterization of intra-cranial aneurysms: current status. Clin Radiol 60:1221–1236
Karamessini MT, Kagadis GC, Petsas T et al (2004) CT angiography with three-dimensional techniques for the early diagnosis of intracranial aneurysms. Comparison with intra-arterial DSA and the surgical findings. Eur J Radiol 49:212–223
Kangasniemi M, Makela T, Koskinen S, Porras M, Poussa K, Hernesniemi J (2004) Detection of intracranial aneurysms with two-dimensional and three-dimensional multislice helical computed tomographic angiography. Neurosurgery 54:336–340; discussion 340–331
Suzuki Y, Nakajima M, Ikeda H, Ikeda Y, Abe T (2004) Preoperative evaluation of the venous system for potential interference in the clipping of cerebral aneurysm. Surg Neurol 61:357–364; discussion 364
Wintermark M, Ko NU, Smith WS, Liu S, Higashida RT, Dillon WP (2006) Vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: utility of perfusion CT and CT angiography on diagnosis and management. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:26–34
Sakuma I, Tomura N, Kinouchi H et al (2006) Postoperative three-dimensional CT angiography after cerebral aneurysm clipping with titanium clips: detection with single detector CT. Comparison with intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography. Clin Radiol 61:505–512
Tomandl BF, Hammen T, Klotz E, Ditt H, Stemper B, Lell M (2006) Bone-subtraction CT angiography for the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:55–59
Sakamoto S, Kiura Y, Shibukawa M, Ohba S, Arita K, Kurisu K (2006) Subtracted 3D CT angiography for evaluation of internal carotid artery aneurysms: comparison with conventional digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1332–1337
Kouskouras C, Charitanti A, Giavroglou C et al (2004) Intracranial aneurysms: evaluation using CTA and MRA. Correlation with DSA and intraoperative findings. Neuroradiology 46:842–850
Vaphiades MS, Horton JA (2005) MRA or CTA, that’s the question. Surv Ophthalmol 50:406–410
Kahara V (2006) Postprocedural monitoring of cerebral aneurysms. Acta Radiol 47:320–327
Okahara M, Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Yamashita M, Nagatomi H, Mori H (2004) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography for evaluation of intracranial aneurysms after endosaccular packing with Guglielmi detachable coils: comparison with 3D digital subtraction angiography. Eur Radiol 14:1162–1168
Anzalone N, Righi C, Simionato F et al (2000) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:746–752
Cottier JP, Bleuzen-Couthon A, Gallas S et al (2003) Intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: is contrast material necessary in the follow-up with 3D time-of-flight MR angiography? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1797–1803
Jager HR, Ellamushi H, Moore EA, Grieve JP, Kitchen ND, Taylor WJ (2000) Contrast-enhanced MR angiography of intracranial giant aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1900–1907
Evans AL, Coley SC, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2005) First-line investigation of acute intracerebral hemorrhage using dynamic magnetic resonance angiography. Acta Radiol 46:625–630
Thomas B, Sunaert S, Thamburaj K, Wilms G (2005) Spurious absence of signal on 3D time-of-flight MR angiograms on 1 and 3 tesla magnets in cerebral arteries associated with a giant ophthalmic segment aneurysm: the need for alternative techniques. JBR-BTR 88:241–244
Moody AR, Pollock JG, O'Connor AR, Bagnall M (1998) Lower-limb deep venous thrombosis: direct MR imaging of the thrombus. Radiology 209:349–355
Derdeyn CP, Graves VB, Turski PA, Masaryk AM, Strother CM (1997) MR angiography of saccular aneurysms after treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils: preliminary experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:279–286
Yamada N, Hayashi K, Murao K, Higashi M, Iihara K (2004) Time-of-flight MR angiography targeted to coiled intracranial aneurysms is more sensitive to residual flow than is digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1154–1157
Naganawa S, Ito T, Shimada H et al (1997) Cerebral black blood MR angiography with the interleaved multi-slab three-dimensional fast spin echo sequence. Radiat Med 15:385–388
Hinton DP, Cury RC, Chan RC et al (2006) Bright and black blood imaging of the carotid bifurcation at 3.0T. Eur J Radiol 57:403–411
Cury RC, Houser SL, Furie KL et al (2006) Vulnerable plaque detection by 3.0 tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 41:112–115
Bernstein MA, Huston J, Lin C, Gibbs GF, Felmlee JP (2001) High-resolution intracranial and cervical MRA at 3.0T: technical considerations and initial experience. Magn Reson Med 46:955–962
Okumura A, Araki Y, Nishimura Y et al (2001) The clinical utility of contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography for cerebrovascular disease. Neurol Res 23:767–771
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stivaros, S.M., Harris, J.N., Adams, W. et al. Does black blood MRA have a role in the assessment of intracerebral aneurysms?. Eur Radiol 19, 184–192 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1127-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1127-2