Abstract
Objective
Careful follow up is necessary after intracranial stenting because in-stent restenosis (ISR) or residual stenosis (RS) is not rare. A minimally invasive follow-up imaging technique is desirable. The objective was to compare the visualisation of stents in Flat Detector-CT Angiography (FD-CTA) after intravenous contrast medium injection (i.v.) with Multi Detector Computed Tomography Angiography (MD-CTA) and Digital Subtracted Angiography (DSA) in an animal model.
Methods
Stents were implanted in the carotid artery of 12 rabbits. In 6 a residual stenosis (RS) was surgically created. Imaging was performed using FD-CTA, MD-CTA and DSA. Measurements of the inner and outer diameter and cross-section area of the stents were performed. Stenosis grade was calculated.
Results
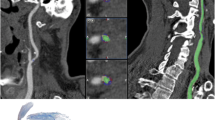
In subjective evaluation FD-CTA was superior to MD-CTA. FD-CTA was more accurate compared with DSA than MD-CTA. Cross-sectional area of the stent lumen was significantly larger (p < 0.05) in FD-CTA in comparison to MD-CTA. Accurate evaluation of stenosis was impossible in MD-CTA. There was no statistically significant difference in the stenosis grade of DSA and FD-CTA.
Conclusion
Our results show that visualisation of stent and stenosis using intravenous FD-CTA compares favourably with DSA and may replace DSA in the follow-up of patients treated with intracranial stents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose A, Hartmann M, Henkes H, Liu HM, Teng MM, Szikora I et al (2007) A novel, self-expanding, nitinol stent in medically refractory intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses: the Wingspan study. Stroke 38:1531–1537
Levy EI, Turk AS, Albuquerque FC, Niemann DB, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Pride L et al (2007) Wingspan in-stent restenosis and thrombosis: incidence, clinical presentation, and management. Neurosurgery 61:644–650
Fiorella DJ, Levy EI, Turk AS, Albuquerque FC, Pride GL Jr, Woo HH et al (2009) Target lesion revascularization after wingspan: assessment of safety and durability. Stroke 40:106–110
Trossbach M, Hartmann M, Braun C, Sartor K, Hähnel S (2004) Small vessel stents for intracranial angioplasty: in vitro evaluation of in-stent stenoses using CT angiography. Neuroradiology 46:459–463
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2, 899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Prabhakaran S, Warrior L, Wells KR, Jhaveri MD, Chen M, Lopes DK (2009) The utility of quantitative magnetic resonance angiography in the assessment of intracranial in-stent stenosis. Stroke 40:991–993
Hähnel S, Trossbach M, Braun C, Heiland S, Knauth M, Sartor K et al (2003) Small-vessel stents for intracranial angioplasty: in vitro comparison of different stent designs and sizes by using CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1512–1516
Turk AS, Rowley HA, Niemann DB, Fiorella D, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Pulfer K et al (2007) CT angiographic appearance of in-stent restenosis of intracranial arteries treated with the Wingspan stent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1752–1754
Maintz D, Seifarth H, Flohr T, Krämer S, Wichter T, Heindel W et al (2003) Improved coronary artery stent visualisation and in-stent stenosis detection using 16-slice computed-tomography and dedicated image reconstruction technique. Invest Radiol 38:790–795
Choo KS, Lee TH, Choi CH, Park KP, Kim CW, Kim S (2009) Assessment of the intracranial stents patency and re-stenosis by 16-slice ct angiography with optimized sharp kernel: preliminary study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 45:284–288
Kalender WA, Kyriakou Y (2007) Flat-detector computed tomography (FD-CT). Eur Radiol 17:2767–2779
Benndorf G, Strother CM, Claus B, Naeini R, Morsi H, Klucznik R, Mawad ME (2005) Angiographic CT in cerebrovascular stenting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1813–1818
Benndorf G, Klucznik RP, Strother CM (2006) Images in cardiovascular medicine: angiographic computed tomography for imaging of underdeployed intracranial stent. Circulation 114:e499–e500
Richter G, Engelhorn T, Struffert T, Doelken M, Ganslandt O, Hornegger J et al (2007) Flat panel detector angiographic CT for stent-assisted coil embolization of broad-based cerebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1902–1908
Cloft HJ, Altes TA, Marx WF, Raible RJ, Hudson SB, Helm GA et al (1999) Endovascular creation of an in vivo bifurcation aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:223–228
Kallmes DF, Helm GA, Hudson SB, Altes TA, Do HM, Mandell JW et al (1999) Histologic evaluation of platinum coil embolization in an aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:217–222
Doerfler A, Becker W, Wanke I, Goericke S, Oezkan N, Forsting M (2004) Multimodal imaging in the elastase-induced aneurysm model in rabbits: a comparative study using serial DSA, MRA and CTA. Röfo 176:590–596
Struffert T, Roth C, Romeike B, Grunwald IQ, Reith W (2008) Onyx in an experimental aneurysm model: histological and angiographic results. J Neurosurg 109:77–82
Struffert T, Doelken M, Adamek E, Schwarz M, Engelhorn T, Kloska S (2010) Flat-detector computed tomography with intravenous contrast material application in experimental aneurysms: comparison with multislice CT and conventional angiography. Acta Radiol 51:431–437
Nguyen-Huynh MN, Wintermark M, English J, Lam J, Vittinghoff E, Smith WS et al (2008) How accurate is CT angiography in evaluating intracranial atherosclerotic disease? Stroke 39:1184–1188
Struffert T, Eyupoglu IY, Huttner HB, Engelhorn T, Doelken M, Saake M et al (2010) Clinical evaluation of flat-panel detector compared with multislice computed tomography in 65 patients with acute intracranial hemorrhage: initial results. J Neurosurg 113:901–907
Struffert T, Richter G, Engelhorn T, Doelken M, Goelitz P, Kalender WA et al (2009) Visualisation of intracerebral haemorrhage with flat-detector CT compared to multislice CT: results in 44 cases. Eur Radiol 19:619–625
Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Strother CM, Kalender WA et al (2010) Flat detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1462–1469
Buhk JH, Lingor P, Knauth M (2008) Angiographic CT with intravenous administration of contrast medium is a noninvasive option for follow-up after intracranial stenting. Neuroradiology 50:349–354
Struffert T, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Ott S, Doelken M et al (2011) Optimized intravenous flat detector CT for non-invasive visualisation of intracranial stents: first results. Eur Radiol 21:411–418
Kühn AL, Roth C, Romeike B, Grunwald IQ (2009) Treatment of elastase-induced intracranial aneurysms in New Zealand white rabbits by use of a novel neurovascular embolization stent device. Neuroradiology. doi:10.1007/s00234-009-0605-9
Ahlhelm F, Roth C, Kaufmann R, Schulte-Altedorneburg G, Romeike BF, Reith W (2007) Treatment of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms with a novel self-expanding two-zonal endovascular stent device. Neuroradiology 49:1023–1028
Ishii A, Viñuela F, Murayama Y, Yuki I, Nien YL, Yeh DT et al (2006) Swine model of carotid artery atherosclerosis: experimental induction by surgical partial ligation and dietary hypercholesterolemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1893–1899
Prell D, Kyriakou Y, Struffert T, Dörfler A, Kalender WA (2010) Metal artifact reduction for clipping and coiling in interventional C-arm CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:634–639
Acknowledgement
The work described in this study was supported by a grant from the ELAN-Fonds, Erlangen, Germany (www.elan.uk-erlangen.de), Project number 07.07.18.1. Boston Scientific/Target supported our work by supporting stents and other angiographic equipment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struffert, T., Ott, S., Adamek, E. et al. Flat-detector computed tomography in the assessment of intracranial stents: comparison with multi detector CT and conventional angiography in a new animal model. Eur Radiol 21, 1779–1787 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2093-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2093-7