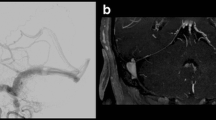
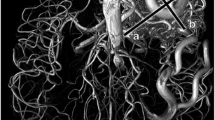
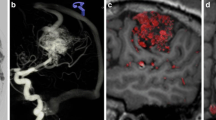
Abstract
Objectives
DSA is currently the criterion standard for the assessment of dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVF). Recently, evolving MRA techniques have emerged as a non-invasive alternative. The aim of this study is to assess the value of 3 T MRI in detecting and describing dAVF and to determine whether MRI can replace DSA as diagnostic procedure.
Methods
A total of 19 patients with dAVF and 19 without dAVF underwent the same MRI protocol, including 3D time-of-flight MRA and time-resolved contrast-enhanced MRA. The images were evaluated retrospectively by three independent readers with different levels of experience blinded to clinical information. The readers assessed the presence, the site, the venous drainage and the feeders of dAVF. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, intertechnique and interobserver agreements were calculated.
Results
DAVF can be detected with high sensitivity, specificity and accuracy by experienced and also by less experienced readers. However, MRI has limitations when used for grading and evaluation of the angioarchitecture of the dAVF. Different experience, the limited resolution of MRI and its inability to selectively display arteries were the reasons for these limitations.
Conclusions
With MRI dAVF can be detected reliably. Nevertheless, at present MRI can not fully replace DSA, especially for treatment planning.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, ter Brugge K, Tolia A, Hurth M, Bernstein M (1986) Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64:724–730
Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, Chiras J, Merland JJ (1995) Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 194:671–680
De Marco JK, Dillon WP, Halbach VV, Tsuruda JS (1990) Dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 175:193–199
Chen JC, Tsuruda JS, Halbach VV (1992) Suspected dural arteriovenous fistula: results with screening MR angiography in seven patients. Radiology 183:265–271
Cellerini M, Mascalchi M, Mangiafico S, Ferrito GP, Scardigli V, Pellicanò G, Quilici N (1999) Phase-contrast MR angiography of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae. Neuroradiology 41:487–492
Kwon BJ, Han MH, Kang HS, Chang KH (2005) MR imaging findings of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: relations with venous drainage patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2500–2507
Coley SC, Romanowski CA, Hodgson TJ, Griffiths PD (2002) Dural arteriovenous fistulae: noninvasive diagnosis with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:404–407
Ziyeh S, Strecker R, Berlis A, Weber J, Klisch J, Mader I (2005) Dynamic 3D MR angiography of intra- and extracranial vascular malformations at 3T: a technical note. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630–634
Meckel S, Maier M, Ruiz DS, Yilmaz H, Scheffler K, Radue EW, Wetzel SG (2007) MR angiography of dural arteriovenous fistulas: diagnosis and follow-up after treatment using a time-resolved 3D contrast-enhanced technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:877–884
Noguchi K, Kuwayama N, Kubo M, Kamisaki Y, Tomizawa G, Kameda K, Kawabe H, Ogawa S, Kato H, Shimizu M, Watanabe N, Seto H (2007) Dural arteriovenous fistula involving the transverse sigmoid sinus after treatment: assessment with magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 49:639–643
Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Johnstone DM, Terbrugge KG (2009) Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis and classification with time-resolved MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1546–1551
Nishimura S, Hirai T, Sasao A, Kitajima M, Morioka M, Kai Y, Omori Y, Okuda T, Murakami R, Fukuoka H, Awai K, Kuratsu JI, Yamashita Y (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas with 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:80–85
Sakamoto S, Shibukawa M, Kiura Y, Matsushige T, Abe N, Kurisu K (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas of cavernous sinus before and after endovascular treatment using time-resolved MR angiography. Neurosurg Rev 33:217–222, discussion 222–223
Noguchi K, Melhem ER, Kanazawa T, Kubo M, Kuwayama N, Seto H (2004) Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with combined 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and MR digital subtraction angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:183–190
Akiba H, Tamakawa M, Hyodoh H, Hyodoh K, Yama N, Nonaka T, Minamida Y, Hashimoto M, Hareyama M (2008) Assessment of dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinuses on 3D dynamic MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1652–1657
Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA (1995) A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 82:166–179
Wu Y, Kim N, Korosec FR, Turk A, Rowley HA, Wieben O, Mistretta CA, Turski PA (2007) 3D time-resolved contrast-enhanced cerebrovascular MR angiography with subsecond frame update times using radial k-space trajectories and highly constrained projection reconstruction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:2001–2004
van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Beute GN (2007) Intracranial dural fistulas with exclusive perimedullary drainage: the need for complete cerebral angiography for diagnosis and treatment planning. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:348–351
Brouwer PA, Bosman T, van Walderveen MA, Krings T, Leroux AA, Willems PW (2010) Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:767–770
Willems PW, Brouwer PA, Barfett JJ, terBrugge KG, Krings T (2011) Detection and classification of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using 4D-CT angiography: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:49–53
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Marina Heibel, Stefanie Pellikan and Lars Göttig for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bink, A., Berkefeld, J., Wagner, M. et al. Detection and grading of dAVF: prospects and limitations of 3T MRI. Eur Radiol 22, 429–438 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2268-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2268-2