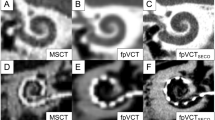
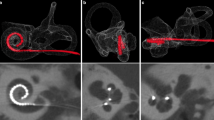
Abstract
Objectives
Anatomical information of the middle and inner ear is becoming increasingly important in post-operative evaluation especially after stapesplasty with unsuccessful improvement of the air-bone gap (ABG). So far computed tomography (CT) has been the first choice for detection of reasons for recurrent hearing loss. CT has the disadvantage of metal-induced artefacts after insertion of middle ear implants and of a relatively high irradiation dose.
Methods
Flat panel CT (fpCT) was performed in three temporal bone specimen after experimental insertion of different stapes prostheses, aiming to validate the accuracy of fpCT of the middle and inner ear. Additionally, 28 consecutive patients, supplied with different stapes prostheses underwent post-operative fpCT to compare the pre- and post-operative hearing results with the determined prosthesis position in the middle and inner ear.
Results
In all cases, fpCT showed a statistically significant correlation between hearing improvement and prosthesis position. This technique provided detailed post-operative information of the implant position in patients and temporal bone specimen.
Conclusions
The new imaging technique of fpCT allows the immediate and almost artefact-free evaluation of surgical results following stapesplasty. Further benefits are a lower irradiation dose and higher isovolumetric resolution compared with standard CT.
Key Points
• Flat panel computed tomography (fpCT) helps otosurgeons design precise stapes protheses
• fpCT allows a prediction of the postoperative hearing outcome in patients
• fpCT is an adequate imaging technique for immediate postoperative quality control. Postoperative management of patients with prosthesis-related complications is more appropriate





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huttenbrink KB (2003) Biomechanics of stapesplasty: a review. Otol Neurotol 24:548–557, discussion 557–549
Golabek W, Szymanski M, Siwiec H, Morshed K (2003) Incus subluxation and luxation during stapedectomy. Ann Univ Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med 58:302–305
Meyer SE (1999) The effect of stapes surgery on high frequency hearing in patients with otosclerosis. Am J Otol 20:36–40
Oberascher G, Grobovschek M (1988) Identification of middle ear implants in high-resolution computerized tomography. Laryngol Rhinol Otol (Stuttg) 67:17–22
Kosling S, Bootz F (2001) CT and MR imaging after middle ear surgery. Eur J Radiol 40:113–118
Bozzato A, Struffert T, Hertel V, Iro H, Hornung J (2009) Analysis of the accuracy of high-resolution computed tomography techniques for the measurement of stapes prostheses. Eur Radiol 20:566–571
Naumann IC, Porcellini B, Fisch U (2005) Otosclerosis: incidence of positive findings on high-resolution computed tomography and their correlation to audiological test data. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 114:709–716
Offergeld C, Pilling E, Lazurashvili N et al (2007) Conventional tomographic investigations of the reconstructed middle ear in temporal bone specimen. Laryngorhinootologie 86:501–506
Offergeld C, Kromeier J, Aschendorff A et al (2007) Rotational tomography of the normal and reconstructed middle ear in temporal bones: an experimental study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264:345–351
Aschendorff A, Kubalek R, Turowski B et al (2005) Quality control after cochlear implant surgery by means of rotational tomography. Otol Neurotol 26:34–37
Offergeld C, Kromeier J, Merchant SN et al (2010) Experimental investigation of rotational tomography in reconstructed middle ears with clinical implications. Hear Res 263(1–2):191–197
Hausler R (2007) General history of stapedectomy. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 65:1–5
Cremers CW, Beusen JM, Huygen PL (1991) Hearing gain after stapedotomy, partial platinectomy, or total stapedectomy for otosclerosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 100:959–961
Plath P, Lenart R, Matschke RG, Kruppa E (1992) Long-term results of stapedectomy and stapedotomy. HNO 40:52–55
Fritsch MH (2007) MRI scanners and the stapes prosthesis. Otol Neurotol 28:733–738
Chuang MT, Chiang IC, Liu GC et al (2006) Multidetector row CT demonstration of inner and middle ear structures. Clin Anat 19:337–344
Rodt T, Ratiu P, Becker H et al (2002) 3D visualisation of the middle ear and adjacent structures using reconstructed multi-slice CT datasets, correlating 3D images and virtual endoscopy to the 2D cross-sectional images. Neuroradiology 44:783–790
Pickuth D, Brandt S, Berghaus A, Spielmann RP, Heywang-Kobrunner SH (2000) Vertigo after stapes surgery: the role of high resolution CT. Br J Radiol 73:1021–1023
Roosli C, Hoffmann A, Treumann T, Linder TE (2008) Significance of computed tomography evaluation before revision stapes surgery. HNO 56:895–900
Hahn Y, Diaz R, Hartman J, Bobinski M, Brodie H (2009) Assessing stapes piston position using computed tomography: a cadaveric study. Otol Neurotol 30:223–230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaoui, K., Kromeier, J., Neudert, M. et al. Flat panel CT following stapes prosthesis insertion: an experimental and clinical study. Eur Radiol 22, 837–844 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2317-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2317-x