Abstract
Objectives
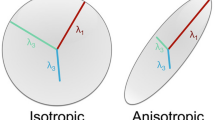
The degree and status of white matter myelination can be sensitively monitored using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). This study looks at the measurement of fractional anistropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) using an automated ROI with an existing DTI atlas.
Methods
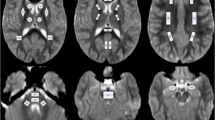
Anatomical MRI and structural DTI were performed cross-sectionally on 26 normal children (newborn to 48 months old), using 1.5-T MRI. The automated processing pipeline was implemented to convert diffusion-weighted images into the NIfTI format. DTI-TK software was used to register the processed images to the ICBM DTI-81 atlas, while AFNI software was used for automated atlas-based volumes of interest (VOIs) and statistical value extraction.
Results
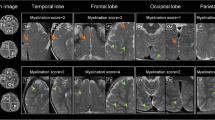
DTI exhibited consistent grey–white matter contrast. Triphasic temporal variation of the FA and MD values was noted, with FA increasing and MD decreasing rapidly early in the first 12 months. The second phase lasted 12–24 months during which the rate of FA and MD changes was reduced. After 24 months, the FA and MD values plateaued.
Conclusion
DTI is a superior technique to conventional MR imaging in depicting WM maturation. The use of the automated processing pipeline provides a reliable environment for quantitative analysis of high-throughput DTI data.
Key Points
• Diffusion tensor imaging outperforms conventional MRI in depicting white matter maturation.
• DTI will become an important clinical tool for diagnosing paediatric neurological diseases.
• DTI appears especially helpful for developmental abnormalities, tumours and white matter disease.
• An automated processing pipeline assists quantitative analysis of high throughput DTI data.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilman S (1998) Imaging the brain. N Engl J Med 338:812–820
Barkovich A, Kjos B, Jackson D Jr, Norman D (1988) Normal maturation of the neonatal and infant brain: MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology 166:173
Knaap M, Valk J (1990) MR imaging of the various stages of normal myelination during the first year of life. Neuroradiology 31:459–470
Mukherjee P, Miller J, Shimony J et al (2001) Normal brain maturation during childhood: developmental trends characterized with diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 221:349
Hermoye L, Saint-Martin C, Cosnard G et al (2006) Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. Neuroimage 29:493–504
Ozturk A, Sasson AD, Farrell JAD et al (2008) Regional differences in diffusion tensor imaging measurements: assessment of intrarater and interrater variability. Am J Neuroradiol 29:1124–1127
Mori S, Oishi K, Jiang H et al (2008) Stereotaxic white matter atlas based on diffusion tensor imaging in an ICBM template. Neuroimage 40:570–582
Schneider JFL, Il’yasov KA, Hennig J, Martin E (2004) Fast quantitative diffusion-tensor imaging of cerebral white matter from the neonatal period to adolescence. Neuroradiology 46:258–266
Lee SK, Kim DI, Kim J et al (2005) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: a new method of describing aberrant fiber connections in developmental CNS anomalies. Radiographics 25:53
Brody B, Kinney H, Kloman A, Gilles F (1987) Sequence of central nervous system myelination in human infancy. I. An autopsy study of myelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:283
Kinney H (1988) Sequence of central nervous system myelination in human infancy. II. Patterns of myelination in autopsied infants. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:217
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system – a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loh, K.B., Ramli, N., Tan, L.K. et al. Quantification of diffusion tensor imaging in normal white matter maturation of early childhood using an automated processing pipeline. Eur Radiol 22, 1413–1426 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2396-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2396-3