Abstract
Objectives
Susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences may demonstrate various signal intensities of draining veins in cases of high-flow vascular malformation (HFVM), including arteriovenous malformation (AVM) and dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF). Our objective was to evaluate susceptibility-weighted angiography (SWAN) for the detection of HFVM.
Methods
Fifty-eight consecutive patients with a suspected intracranial vascular malformation were explored with SWAN and post-contrast MRI sequences at 3 T. The diagnosis of slow-flow vascular malformation (SFVM), including developmental venous anomaly (DVA) or brain capillary telangiectasia (BCT), was based on MRI. Patients with suspected HFVM underwent digital subtraction angiography (DSA). SWAN images were analysed by three blinded readers according to a three-point scale of the venous signal.
Results
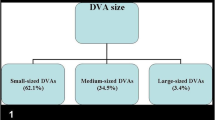
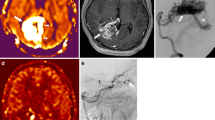
Thirty-one patients presented 35 SFVM (26 DVA and 9 BCT) that systematically appeared hypointense on SWAN images. In patients with atypical MRI findings, DSA revealed one patient with an atypical DVA and 26 patients with HFVM (22 AVM and 4 dAVF). SWAN revealed at least one venous hyperintensity in all patients with HFVM. Agreement between readers was excellent.
Conclusions
SWAN appears reliable for characterising blood flow dynamics in brain veins. In clinical practice, SWAN can routinely rule out HFVM in patients with atypical brain veins.
Key Points
• Susceptibility-weighted angiography (SWAN) offers new perspectives for detecting intracranial vascular malformations.
• SWAN sequence provides non-invasive characterisation of blood flow dynamics.
• SWAN can differentiate between high and slow flowing venous blood.
• SWAN can routinely rule out high-flow vascular malformations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SFVM:
-
Slow-flow vascular malformation
- HFVM:
-
High-flow vascular malformation
- AVM:
-
Arteriovenous malformation
- dAVF:
-
Dural arteriovenous fistula
- DVA:
-
Developmental venous anomaly
- BCT:
-
Brain capillary telangiectasia
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- SWI:
-
Susceptibility-weighted imaging
- SWAN:
-
Susceptibility-weighted angiography
References
Chaloupka JC, Huddle DC (1998) Classification of vascular malformations of the central nervous system. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 8:295–321
Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z et al (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:19–30
Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC et al (2004) Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med 52:612–618
Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ et al (1997) Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology 204:272–277
El-Koussy M, Schroth G, Gralla J et al (2011) Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging for diagnosis of capillary telangiectasia of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:715–720
Gasparetto EL, Pires CE, Domingues RC (2011) Susceptibility-weighted MR phase imaging can demonstrate retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage in patients with dural arteriovenous fistula. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:E54
Noguchi K, Kuwayama N, Kubo M et al (2010) Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde cortical venous drainage: Use of susceptibility-weighted imaging in combination with dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1903–1910
Saini J, Thomas B, Bodhey NK et al (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging in cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:E6
Jagadeesan BD, Delgado Almandoz JE, Moran CJ et al (2011) Accuracy of susceptibility-weighted imaging for the detection of arteriovenous shunting in vascular malformations of the brain. Stroke 42:87–92
Letourneau-Guillon L, Krings T (2012) Simultaneous arteriovenous shunting and venous congestion identification in dural arteriovenous fistulas using susceptibility-weighted imaging: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:301–307
Annamraju R, Venkatesan R, Vu A (2008) T2* weighted angiography (SWAN): T2* weighted non-contrast imaging with multi-echo acquisition and reconstruction. Proceedings of the ESMRMB, Valencia, October 2–4, 2008:abstract 482
Boeckh-Behrens T, Lutz J, Lummel N et al (2011) Susceptibility-weighted angiography (SWAN) of cerebral veins and arteries compared to TOF-MRA. Eur J Radiol 81:1238–1245
Lummel N, Boeckh-Behrens T, Schoepf V et al (2011) Presence of a central vein within white matter lesions on susceptibility weighted imaging: A specific finding for multiple sclerosis? Neuroradiology 53:311–317
Hodel J, Gerber S, Zins M et al (2011) MR imaging findings in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula shunt with retrograde cortical venous drainage using susceptibility-weighted angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:196–197
Ruiz DS, Yilmaz H, Gailloud P (2009) Cerebral developmental venous anomalies: Current concepts. Ann Neurol 66:271–283
Barr RM, Dillon WP, Wilson CB (1996) Slow-flow vascular malformations of the pons: Capillary telangiectasias? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:71–78
Castillo M, Morrison T, Shaw JA et al (2001) MR imaging and histologic features of capillary telangiectasia of the basal ganglia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1553–1555
Kuker W, Nacimiento W, Block F et al (2000) Presumed capillary telangiectasia of the pons: MRI and follow-up. Eur Radiol 10:945–950
Hadizadeh DR, von Falkenhausen M, Gieseke J et al (2008) Cerebral arteriovenous malformation: Spetzler-Martin classification at subsecond-temporal-resolution four-dimensional MR angiography compared with that at DSA. Radiology 246:205–213
Lee RR, Becher MW, Benson ML et al (1997) Brain capillary telangiectasia: MR imaging appearance and clinicohistopathologic findings. Radiology 205:797–805
Schmitz BL, Aschoff AJ, Hoffmann MH et al (2005) Advantages and pitfalls in 3 T MR brain imaging: a pictorial review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2229–2237
Du YP, Jin Z, Hu Y et al (2009) Multi-echo acquisition of MR angiography and venography of the brain at 3 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:449–454
Jagadeesan BD, Delgado Almandoz JE, Benzinger TL et al (2011) Postcontrast susceptibility-weighted imaging: a novel technique for the detection of arteriovenous shunting in vascular malformations of the brain. Stroke 42:3127–3131
Leach JL, Strub WM, Gaskill-Shipley MF (2007) Cerebral venous thrombus signal intensity and susceptibility effects on gradient recalled-echo MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:940–945
Acknowledgements
Cécile Rabrait is an employee of General Electric.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodel, J., Blanc, R., Rodallec, M. et al. Susceptibility-weighted angiography for the detection of high-flow intracranial vascular lesions: preliminary study. Eur Radiol 23, 1122–1130 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2690-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2690-0