Abstract
Objectives
To compare spatial patterns of cortical thickness alterations in neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and multiple sclerosis (MS); and to investigate the correlations between cortical thinning and clinical variables in NMO and MS.
Methods
We studied 23 patients with NMO, 27 patients with MS and 26 healthy controls (HCs). The global, brain region and vertex-based cortical thickness (CTh) were analysed and compared among the three groups. A general linear model was used to investigate the correlations between cortical thinning and clinical measures.
Results
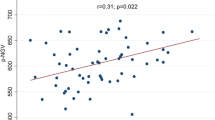
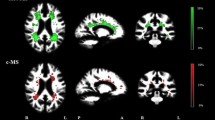
A limited number of cortical regions in visual cortex were found to be significantly thinner in NMO patients than in HCs. The MS patients exhibited more widespread cortical thinning compared with HCs, and significantly greater cortical thinning in the insula and the parahippocampus compared with NMO. The extent of cortical thinning in several brain regions correlated with cognitive measures in MS, but not in NMO.
Conclusions
Neocortical thinning in NMO mainly affects visual cortex, while MS patients show much more extensive cortical thinning. Cognitive changes are correlated with cortical atrophy in MS not in NMO. The substrates of cognitive changes in MS and NMO could therefore be different.
Key Points
• MS patients show much more extensive cortical thinning than NMO.
• Cortical thinning of insula and parahippocampus particularly distinguishes MS from NMO.
• Cognitive changes are correlated with cortical atrophy in MS but not in NMO.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTh:
-
Cortical thickness
- HC:
-
Healthy control
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- NMO:
-
Neuromyelitis optica
- WM:
-
White matter
References
Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Lucchinetti CF, Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG (2007) The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol 6:805–815
Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG (2006) Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 66:1485–1489
Pittock SJ, Lennon VA, Krecke K, Wingerchuk DM, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG (2006) Brain abnormalities in neuromyelitis optica. Arch Neurol 63:390–396
Rocca MA, Agosta F, Mezzapesa DM et al (2004) A functional MRI study of movement-associated cortical changes in patients with Devic's neuromyelitis optica. Neuroimage 21:1061–1068
Rocca MA, Agosta F, Mezzapesa DM et al (2004) Magnetization transfer and diffusion tensor MRI show gray matter damage in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 62:476–478
Liu Y, Duan Y, He Y et al (2012) A tract-based diffusion study of cerebral white matter in neuromyelitis optica reveals widespread pathological alterations. Mult Scler 18:1013–1021
Blanc F, Zephir H, Lebrun C et al (2008) Cognitive functions in neuromyelitis optica. Arch Neurol 65:84–88
Popescu BF, Parisi JE, Cabrera-Gomez JA et al (2010) Absence of cortical demyelination in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 75:2103–2109
Yu C, Lin F, Li K et al (2008) Pathogenesis of normal-appearing white matter damage in neuromyelitis optica: diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 246:222–228
Liu Y, Duan Y, He Y et al (2012) Altered topological organization of white matter structural networks in patients with neuromyelitis optica. PLoS One 7:e48846
Duan Y, Liu Y, Liang P et al (2012) Comparison of grey matter atrophy between patients with neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis: a voxel-based morphometry study. Eur J Radiol 81:e110–e114
Blanc F, Noblet V, Jung B et al (2012) White matter atrophy and cognitive dysfunctions in neuromyelitis optica. PLoS One 7:e33878
Chanson JB, Lamy J, Rousseau F et al (2013) White matter volume is decreased in the brain of patients with neuromyelitis optica. Eur J Neurol 20:361–367
Lerch JP, Pruessner JC, Zijdenbos A, Hampel H, Teipel SJ, Evans AC (2005) Focal decline of cortical thickness in Alzheimer's disease identified by computational neuroanatomy. Cereb Cortex 15:995–1001
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11050–11055
Calabrese M, Agosta F, Rinaldi F et al (2009) Cortical lesions and atrophy associated with cognitive impairment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 66:1144–1150
Calabrese M, Rinaldi F, Mattisi I et al (2010) Widespread cortical thinning characterizes patients with MS with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 74:321–328
Sailer M, Fischl B, Salat D et al (2003) Focal thinning of the cerebral cortex in multiple sclerosis. Brain 126:1734–1744
Singh V, Chertkow H, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Dorr AE, Kabani NJ (2006) Spatial patterns of cortical thinning in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Brain 129:2885–2893
Calabrese M, Oh MS, Favaretto A et al (2012) No MRI evidence of cortical lesions in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 79:1671–1676
Chiaravalloti ND, DeLuca J (2008) Cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 7:1139–1151
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G et al (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann Neurol 58:840–846
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1998) A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17:87–97
Zijdenbos AP, Forghani R, Evans AC (2002) Automatic “pipeline” analysis of 3-D MRI data for clinical trials: application to multiple sclerosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21:1280–1291
MacDonald D, Kabani N, Avis D, Evans AC (2000) Automated 3-D extraction of inner and outer surfaces of cerebral cortex from MRI. Neuroimage 12:340–356
Lerch JP, Evans AC (2005) Cortical thickness analysis examined through power analysis and a population simulation. Neuroimage 24:163–173
Chung MK, Worsley KJ, Robbins S et al (2003) Deformation-based surface morphometry applied to gray matter deformation. Neuroimage 18:198–213
Kabani N, Le Goualher G, MacDonald D, Evans AC (2001) Measurement of cortical thickness using an automated 3-D algorithm: a validation study. Neuroimage 13:375–380
Charil A, Dagher A, Lerch JP, Zijdenbos AP, Worsley KJ, Evans AC (2007) Focal cortical atrophy in multiple sclerosis: relation to lesion load and disability. Neuroimage 34:509–517
Querbes O, Aubry F, Pariente J et al (2009) Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease using cortical thickness: impact of cognitive reserve. Brain 132:2036–2047
Voineskos AN, Foussias G, Lerch J et al (2013) Neuroimaging evidence for the deficit subtype of schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry 70:472–480
von Glehn F, Jarius S, Cavalcanti Lira RP et al (2014) Structural brain abnormalities are related to retinal nerve fiber layer thinning and disease duration in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mult Scler
Ceccarelli A, Rocca MA, Pagani E et al (2008) A voxel-based morphometry study of grey matter loss in MS patients with different clinical phenotypes. Neuroimage 42:315–322
Saji E, Arakawa M, Yanagawa K et al (2013) Cognitive impairment and cortical degeneration in neuromyelitis optica. Ann Neurol 73:65–76
Rueda Lopes FC, Doring T, Martins C et al (2012) The role of demyelination in neuromyelitis optica damage: diffusion-tensor MR imaging study. Radiology 263:235–242
Suzuki M, Obara K, Sasaki Y et al (2003) Comparison of perivascular astrocytic structure between white matter and gray matter of rats. Brain Res 992:294–297
Rossi A, Crane JM, Verkman AS (2011) Aquaporin-4 Mz isoform: brain expression, supramolecular assembly and neuromyelitis optica antibody binding. Glia 59:1056–1063
Lucchinetti CF, Popescu BF, Bunyan RF et al (2011) Inflammatory cortical demyelination in early multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 365:2188–2197
Filippi M, Rocca MA, Benedict RH et al (2010) The contribution of MRI in assessing cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 75:2121–2128
Hulst HE, Steenwijk MD, Versteeg A et al (2013) Cognitive impairment in MS: impact of white matter integrity, gray matter volume, and lesions. Neurology 80:1025–1032
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Alan Evans for kindly providing the MNI CIVET software.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Kuncheng Li. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. This study has received funding by the McDonald Fellowship from Multiple Sclerosis International Federation (Y.L.), 973 Program (2013CB837300), the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81101038,30930029, 30800267, 81000633 and 81030028), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 81225012), the Beijing Natural Science fund (No.7133244), the Beijing Funding for Training Talents (Y.H.), Major Project of National Social Science Foundation (No. 11&ZD186) and Beijing Nova Program (No. xx2013045). Dr Ni Shu and Dr. Teng Xie have significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective, cross sectional study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yaou Liu and Teng Xie contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Xie, T., He, Y. et al. Cortical Thinning Correlates with Cognitive Change in Multiple Sclerosis but not in Neuromyelitis Optica. Eur Radiol 24, 2334–2343 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3239-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3239-1