Abstract
Objective
To evaluate prospectively 7 Tesla time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and 7 Tesla non-contrast-enhanced magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient-echo (MPRAGE) for delineation of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in comparison to 1.5 Tesla TOF MRA and digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Methods
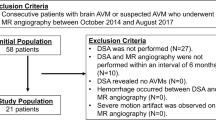
Twenty patients with single or multifocal AVMs were enrolled in this trial. The study protocol comprised 1.5 and 7 Tesla TOF MRA and 7 Tesla non-contrast-enhanced MPRAGE sequences. All patients underwent an additional four-vessel 3D DSA. Image analysis of the following five AVM features was performed individually by two radiologists on a five-point scale: nidus, feeder(s), draining vein(s), relationship to adjacent vessels, and overall image quality and presence of artefacts.
Results
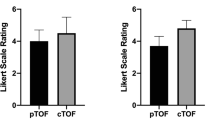
A total of 21 intracerebral AVMs were detected. Both sequences at 7 Tesla were rated superior over 1.5 Tesla TOF MRA in the assessment of all considered AVM features. Image quality at 7 Tesla was comparable with DSA considering both sequences. Inter-observer accordance was good to excellent for the majority of ratings.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates excellent image quality for depiction of intracerebral AVMs using non-contrast-enhanced 7 Tesla MRA, comparable with DSA. Assessment of untreated AVMs is a promising clinical application of ultra-high-field MRA.
Key Points
• Non-contrast-enhanced 7 Tesla MRA demonstrates excellent image quality for intracerebral AVM depiction.
• Image quality at 7 Tesla was comparable with DSA considering both sequences.
• Assessment of intracerebral AVMs is a promising clinical application of ultra-high-field MRA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman MF, Sciacca RR, Pile-Spellman J et al (2000) The epidemiology of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 47:389–397
Hartmann A, Mast H, Mohr JP et al (1998) Morbidity of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Stroke 29:931–934
Soderman M, Andersson T, Karlsson B, Wallace MC, Edner G (2003) Management of patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Eur J Radiol 46:195–205
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483
Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C et al (2014) Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 383:614–621
Hernesniemi JA, Dashti R, Juvela S, Vaart K, Niemela M, Laakso A (2008) Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: a long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery 63:823–829, discussion 829–831
Yu S, Yan L, Yao Y et al (2012) Noncontrast dynamic MRA in intracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM), comparison with time of flight (TOF) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Magn Reson Imaging 30:869–877
Umutlu L, Theysohn N, Maderwald S et al (2013) 7 Tesla MPRAGE imaging of the intracranial arterial vasculature: nonenhanced versus contrast-enhanced. Acad Radiol 20:628–634
Wrede KH, Dammann P, Mönninghoff C et al (2014) Non-enhanced MR imaging of cerebral aneurysms: 7 tesla versus 1.5 tesla. PLoS ONE 9, e84562
Nowinski WL, Puspitasaari F, Volkau I, Marchenko Y, Knopp MV (2013) Comparison of magnetic resonance angiography scans on 1.5, 3, and 7 tesla units: a quantitative study of 3-dimensional cerebrovasculature. J Neuroimaging. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2011.00597.x:86–95
Wrede KH, Johst S, Dammann P et al (2012) Caudal image contrast inversion in MPRAGE at 7 tesla problem and solution. Acad Radiol 19:172–178
Johst S, Wrede KH, Ladd ME, Maderwald S (2012) Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography at 7 T using venous saturation pulses with reduced flip angles. Investig Radiol 47:445–450
Wrede KH, Johst S, Dammann P et al (2014) Improved cerebral time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography at 7 tesla – feasibility study and preliminary results using optimized venous saturation pulses. PLoS ONE 9, e106697
Cohen J (1960) A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas 20:37–46
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Burger R, Warmuth-Metz M, Hofmann E, Solymosi L (1999) Silent embolism in diagnostic cerebral angiography and neurointerventional procedures: a prospective study. Lancet 354:1594–1597
Buis DR, Bot JC, Barkhof F et al (2012) The predictive value of 3D time-of-flight MR angiography in assessment of brain arteriovenous malformation obliteration after radiosurgery. Am J Neuroradiol 33:232–238
Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Patel AK, Bissonette DJ, Lunsford LD (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging: an accurate method to evaluate arteriovenous malformations after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 85:1044–1049
Reinacher PC, Stracke P, Reinges MHT, Hans FJ, Krings T (2007) Contrast-enhanced time-resolved 3-D MRA: applications in neurosurgery and interventional neuroradiology. Neuroradiology 49:S3–S13
Hadizadeh DR, Von Falkenhausen M, Gieseke J et al (2008) Cerebral arteriovenous malformation: spetzler-Martin classification at subsecond-temporal-resolution four-dimensional MR angiography compared with that at DSA. Radiology 246:205–213
Eddleman CS, Jeong HJ, Hurley MC et al (2009) 4D radial acquisition contrast-enhanced MR angiography and intracranial arteriovenous malformations: quickly approaching digital subtraction angiography. Stroke 40:2749–2753
Monninghoff C, Maderwald S, Theysohn JM et al (2009) Evaluation of intracranial aneurysms with 7 T versus 1.5 T time-of-flight MR angiography - initial experience. RöFo 181:16–23
Gibbs GF, Huston J 3rd, Bernstein MA, Riederer SJ, Brown RD Jr (2004) Improved image quality of intracranial aneurysms: 3.0-T versus 1.5-T time-of-flight MR angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 25:84–87
Edelstein WA, Glover GH, Hardy CJ, Redington RW (1986) The intrinsic signal-to-noise ratio in NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med 3:604–618
Majoie CBLM, Sprengers ME, Van Rooij WJJ et al (2005) MR angiography at 3T versus digital subtraction angiography in the follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1349–1356
Grinstead JW, Rooney W, Laub G (2010) The origins of bright blood MPRAGE at 7 tesla and a simultaneous method for T1 imaging and non-contrast MRA. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 18:1429
Fischer A, Maderwald S, Johst S et al (2014) Initial evaluation of non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease at 7 T. Investig Radiol 49:331–338
Johst S, Orzada S, Fischer A et al (2014) Sequence comparison for non-enhanced MRA of the lower extremity arteries at 7 tesla. PLoS ONE 9, e86274
Umutlu L, Maderwald S, Kinner S et al (2013) First-pass contrast-enhanced renal MRA at 7 tesla: initial results. Eur Radiol 23:1059–1066
Zwanenburg JJ, Hendrikse J, Takahara T, Visser F, Luijten PR (2008) MR angiography of the cerebral perforating arteries with magnetization prepared anatomical reference at 7 T: comparison with time-of-flight. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:1519–1526
Heverhagen JT, Bourekas E, Sammet S, Knopp MV, Schmalbrock P (2008) Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography at 7 tesla. Investig Radiol 43:568–573
Kraff O, Wrede KH, Schoemberg T et al (2013) MR safety assessment of potential RF heating from cranial fixation plates at 7 T. Med Phys 40:042302
Blauwblomme T, Naggara O, Brunelle F et al (2015) Arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging: toward noninvasive diagnosis and follow-up of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15:451–458
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Lena C. Schäfer (RT) for performing all the 7 Tesla examinations.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Karsten H. Wrede. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. This study has received funding by University Duisburg Essen (IFORES grant). Dr. Ulrike Krahn kindly provided statistical advice for this manuscript. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: prospective, observational, multicenter study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wrede, K.H., Dammann, P., Johst, S. et al. Non-Enhanced MR Imaging of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations at 7 Tesla. Eur Radiol 26, 829–839 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3875-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3875-0