Abstract
Background
Multiple studies have shown a clinical benefit of thrombectomy in acute ischaemic stroke, but most of them excluded octogenarians. The purpose of this study was to compare the outcomes between octogenarians and younger patients after thrombectomy.
Materials and methods
One hundred and sixty-six patients with large cerebral artery occlusion and consecutive thrombectomy were evaluated and divided into two patient age groups: younger than 80 years and older than 80 years. We compared recanalization rates, complications experienced, disability, death after discharge and at a 90-day follow-up between these age groups.
Results
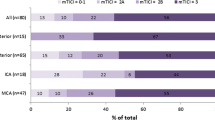
Sixty-eight percent of octogenarians and 72 % of younger patients were registered with successful recanalization (p = 1.0). There was no significant difference in symptomatic intracerebral haemorrhage between the groups (p = 0.32). However, octogenarians had a significantly lower rate of good clinical outcome (24 % vs. 48 %; p = 0.008) and a higher mortality rate (36 % vs. 12 %; p = 0.0013).
Conclusion
Octogenarians have a lower chance of good clinical outcome and a higher mortality rate despite successful recanalization. Nevertheless, 24 % of octogenarians were documented with mRS ≤2. As this age group of octogenarians will grow prospectively, careful patient selection should be mandatory when considering octogenarians for thrombectomy.
Key Points
• Careful patient selection for thrombectomy should be mandatory in octogenarians.
• Octogenarians have a higher mortality rate despite successful recanalization.
• Nearly one-third of octogenarians were documented with a good clinical outcome.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
Basilar artery
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiogram
- DWI:
-
Diffusion weighted sequences
- ECASS III:
-
European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III
- EMA:
-
European Medicines Agency
- IAT:
-
Intra-arterial thrombolysis
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- ICH:
-
Intracerebral haemorrhage
- IVT:
-
Intravenous thrombolysis
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- mRS:
-
Modified Rankin Scale
- NIHSS:
-
National Institutes of Health Scale
- rtPA:
-
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator
- SITS-MOST:
-
Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study
- TICI:
-
Thrombolysis in cerebral infarction
References
(2004) WHO publishes definitive atlas on global heart disease and stroke epidemic. Indian J Med Sci 58:405–406.
Foerch C, Sitzer M, Steinmetz H, Neumann-Haefelin T, Arbeitsgruppe Schlaganfall H (2009) Future demographic trends decrease the proportion of ischemic stroke patients receiving thrombolytic therapy: a call to set-up therapeutic studies in the very old. Stroke 40:1900–1902
Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K et al (2008) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 117:e25–e146
Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Anderson CS (2003) Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol 2:43–53
Kaste M, Thomassen L, Grond M et al (2001) Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke: a consensus statement of the 3rd Karolinska Stroke Update, October 30–31, 2000. Stroke 32:2717–2718
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E et al (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359:1317–1329
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 352:1245–1251
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274:1017–1025
Nogueira RG, Schwamm LH, Hirsch JA (2009) Endovascular approaches to acute stroke, part 1: drugs, devices, and data. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:649–661
(1995) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 333:1581–1587
Smith WS, Sung G, Saver J et al (2008) Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: final results of the Multi MERCI trial. Stroke 39:1205–1212
Saver JL, Jahan R, Levy EI et al (2012) Solitaire flow restoration device versus the Merci Retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT): a randomised, parallel-group, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 380:1241–1249
Nogueira RG, Lutsep HL, Gupta R et al (2012) Trevo versus Merci retrievers for thrombectomy revascularisation of large vessel occlusions in acute ischaemic stroke (TREVO 2): a randomised trial. Lancet 380:1231–1240
Broussalis E, Trinka E, Hitzl W, Wallner A, Chroust V, Killer-Oberpfalzer M (2013) Comparison of stent-retriever devices versus the Merci retriever for endovascular treatment of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:366–372
Investigators IMSS (2004) Combined intravenous and intra-arterial recanalization for acute ischemic stroke: the Interventional Management of Stroke Study. Stroke 35:904–911
Ciccone A, Valvassori L, Nichelatti M et al (2013) Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 368:904–913
Investigators IIT (2007) The Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS) II Study. Stroke 38:2127–2135
Kelly-Hayes M, Beiser A, Kase CS, Scaramucci A, D’Agostino RB, Wolf PA (2003) The influence of gender and age on disability following ischemic stroke: the Framingham study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 12:119–126
Dennis MS, Burn JP, Sandercock PA, Bamford JM, Wade DT, Warlow CP (1993) Long-term survival after first-ever stroke: the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. Stroke 24:796–800
Heuschmann PU, Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Misselwitz B et al (2004) Predictors of in-hospital mortality and attributable risks of death after ischemic stroke: the German Stroke Registers Study Group. Arch Intern Med 164:1761–1768
Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM et al (2013) Endovascular therapy after intravenous t-PA versus t-PA alone for stroke. N Engl J Med 368:893–903
Saver JL, Jahan R, Levy EI et al (2012) SOLITAIRE with the intention for thrombectomy (SWIFT) trial: design of a randomized, controlled, multicenter study comparing the SOLITAIRE Flow Restoration device and the MERCI Retriever in acute ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 9:658–668
Ghobrial GM, Chalouhi N, Rivers L et al (2013) Multimodal endovascular management of acute ischemic stroke in patients over 75 years old is safe and effective. J Neurointerv Surg 5(Suppl 1):i33–i37
Chandra RV, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Oh DC et al (2012) Elderly patients are at higher risk for poor outcomes after intra-arterial therapy. Stroke 43:2356–2361
Loh Y, Kim D, Shi ZS et al (2010) Higher rates of mortality but not morbidity follow intracranial mechanical thrombectomy in the elderly. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1181–1185
Fields JD, Lutsep HL, Smith WS, Investigators MMM (2011) Higher degrees of recanalization after mechanical thrombectomy for acute stroke are associated with improved outcome and decreased mortality: pooled analysis of the MERCI and Multi MERCI trials. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:2170–2174
Bloch RF (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19:1448
Stemer A, Lyden P (2010) Evolution of the thrombolytic treatment window for acute ischemic stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 10:29–33
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A et al (2007) Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study (SITS-MOST): an observational study. Lancet 369:275–282
Sylaja PN, Cote R, Buchan AM, Hill MD, Canadian Alteplase for Stroke Effectiveness Study I (2006) Thrombolysis in patients older than 80 years with acute ischaemic stroke: Canadian Alteplase for Stroke Effectiveness Study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:826–829
Mishra NK, Ahmed N, Andersen G et al (2010) Thrombolysis in very elderly people: controlled comparison of SITS International Stroke Thrombolysis Registry and Virtual International Stroke Trials Archive. BMJ 341:c6046
Luedi R, Hsieh K, Slezak A et al (2014) Age dependency of safety and outcome of endovascular therapy for acute stroke. J Neurol 261:1622–1627
Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C et al (2004) Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet 363:768–774
Wardlaw JM, Sandercock PA, Berge E (2003) Thrombolytic therapy with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: where do we go from here? A cumulative meta-analysis. Stroke 34:1437–1442
Micieli G, Marcheselli S, Tosi PA (2009) Safety and efficacy of alteplase in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:397–409
Weisstanner C, Gratz PP, Schroth G et al (2014) Thrombus imaging in acute stroke: correlation of thrombus length on susceptibility-weighted imaging with endovascular reperfusion success. Eur Radiol 24:1735–1741
Kurre W, Aguilar-Perez M, Niehaus L et al (2013) Predictors of outcome after mechanical thrombectomy for anterior circulation large vessel occlusion in patients aged >/=80 years. Cerebrovasc Dis 36:430–436
Nakayama H, Jorgensen HS, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS (1994) The influence of age on stroke outcome. The Copenhagen Stroke Study. Stroke 25:808–813
Singer OC, Haring HP, Trenkler J et al (2013) Age dependency of successful recanalization in anterior circulation stroke: the ENDOSTROKE study. Cerebrovasc Dis 36:437–445
Duffis EJ, He W, Prestigiacomo CJ, Gandhi CD (2013) Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke in octogenarians compared with younger patients: a meta-analysis. Int J Stroke 9:308–312
Kim D, Ford GA, Kidwell CS et al (2007) Intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute stroke in patients 80 and older: a comparison of results in patients younger than 80 years. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:159–163
Struffert T, Kohrmann M, Engelhorn T et al (2009) Penumbra Stroke System as an “add-on” for the treatment of large vessel occlusive disease following thrombolysis: first results. Eur Radiol 19:2286–2293
Meyers PM, Schumacher HC, Alexander MJ et al (2012) Performance and training standards for endovascular acute ischemic stroke treatment. Neurology 79:S234–S238
Rai AT, Jhadhav Y, Domico J, Hobbs GR (2012) Procedural predictors of outcome in patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:1332–1339
Mono ML, Romagna L, Jung S et al (2012) Intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in octogenarians. Cerebrovasc Dis 33:116–122
Broussalis E, Trinka E, Wallner A, Hitzl W, Killer M (2014) Thrombectomy in patients with large cerebral artery occlusion: a single-center experience with a new stent retriever. Vasc Endovasc Surg 48:144–152
Bauer KA, Weiss LM, Sparrow D, Vokonas PS, Rosenberg RD (1987) Aging-associated changes in indices of thrombin generation and protein C activation in humans. Normative Aging Study. J Clin Invest 80:1527–1534
Castano C, Dorado L, Guerrero C et al (2010) Mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire AB device in large artery occlusions of the anterior circulation: a pilot study. Stroke 41:1836–1840
Machi P, Costalat V, Lobotesis K et al (2012) Solitaire FR thrombectomy system: immediate results in 56 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurointerv Surg 4:62–66
Shi ZS, Loh Y, Walker G, Duckwiler GR, Merci MMI (2010) Clinical outcomes in middle cerebral artery trunk occlusions versus secondary division occlusions after mechanical thrombectomy: pooled analysis of the Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia (MERCI) and Multi MERCI trials. Stroke 41:953–960
Bozzato A, Struffert T, Hertel V, Iro H, Hornung J (2010) Analysis of the accuracy of high-resolution computed tomography techniques for the measurement of stapes prostheses. Eur Radiol 20:566–571
Broussalis E, Hitzl W, McCoy M, Trinka E, Killer M (2013) Comparison of endovascular treatment versus conservative medical treatment in patients with acute basilar artery occlusion. Vasc Endovasc Surg 47:429–437
Sanak D, Herzig R, Kral M et al (2010) Is atrial fibrillation associated with poor outcome after thrombolysis? J Neurol 257:999–1003
Lisabeth LD, Brown DL, Hughes R, Majersik JJ, Morgenstern LB (2009) Acute stroke symptoms: comparing women and men. Stroke 40:2031–2036
Ford GA, Ahmed N, Azevedo E et al (2010) Intravenous alteplase for stroke in those older than 80 years old. Stroke 41:2568–2574
Engelter ST, Bonati LH, Lyrer PA (2006) Intravenous thrombolysis in stroke patients of > or = 80 versus <80 years of age—a systematic review across cohort studies. Age Ageing 35:572–580
Qureshi AI, Suri MF, Georgiadis AL, Vazquez G, Janjua NA (2009) Intra-arterial recanalization techniques for patients 80 years or older with acute ischemic stroke: pooled analysis from 4 prospective studies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1184–1189
Samsa GP, Matchar DB, Goldstein L et al (1998) Utilities for major stroke: results from a survey of preferences among persons at increased risk for stroke. Am Heart J 136:703–713
Broussalis E, Trinka E, Wallner A, Hitzl W, Killer M (2013) Thrombectomy in patients with large cerebral artery occlusion: a single-center experience with a new stent retriever. Vasc Endovasc Surg 48:144–152
Abou-Chebl A, Lin R, Hussain MS et al (2010) Conscious sedation versus general anesthesia during endovascular therapy for acute anterior circulation stroke: preliminary results from a retrospective, multicenter study. Stroke 41:1175–1179
Davis MJ, Menon BK, Baghirzada LB et al (2012) Anesthetic management and outcome in patients during endovascular therapy for acute stroke. Anesthesiology 116:396–405
Jansen O, von Kummer R, Forsting M, Hacke W, Sartor K (1995) Thrombolytic therapy in acute occlusion of the intracranial internal carotid artery bifurcation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:1977–1986
Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L et al (1999) Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in Acute Cerebral Thromboembolism. JAMA 282:2003–2011
Brandt T, von Kummer R, Muller-Kuppers M, Hacke W (1996) Thrombolytic therapy of acute basilar artery occlusion. Variables affecting recanalization and outcome. Stroke 27:875–881
Ding D (2015) Endovascular mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: a new standard of care. J Stroke 17:123–126
Acknowledgments
Monika Killer is the scientific guarantor of our publication. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was not required because of the retrospective nature of the analysis. Written informed consent was not required for this study because it was a retrospective analysis. No study subjects or cohorts have been previously reported. Methodology: retrospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broussalis, E., Weymayr, F., Hitzl, W. et al. Endovascular mechanical recanalization of acute ischaemic stroke in octogenarians. Eur Radiol 26, 1742–1750 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3969-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3969-8