Abstract
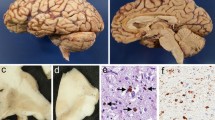
This report concerns a clinicopathological study of three additional patients with corticobasal degeneration (CBD), described here for the first time, and a clinicopathological correlation between pyramidal signs and upper motor neuron involvement, in ten autopsy cases of CBD, including seven cases reported by us previously. We investigated pyramidal signs, including hyperreflexia, Babinski sign, and spasticity, and involvement of the primary motor cortex and pyramidal tract, focusing on the astrocytosis of the fifth layer of the primary motor cortex. Pyramidal signs were observed in six (60%) of the ten cases. Hyperreflexia was evident in six patients (60%), with spasticity being observed in three patients (30%). Loss of Betz cells associated with prominent astrocytosis and presence of ballooned neurons in the fifth layer of the primary motor cortex was observed in all ten cases. In all cases, involvement of the pyramidal tract was obvious in the medulla oblongata, without involvement of the pyramidal tract in the midbrain. Constant and severe involvement of the fifth layer of the primary motor cortex, including the Betz cells, has not previously been reported in CBD. We suggest that the pyramidal signs in CBD have been disregarded.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agid Y (2000) Conclusions. Adv Neurol 82:241–244
Arima K, Uesugi H, Fujita I, Sakurai Y, Oyanagi S, Andoh S, Izumiyama Y, Inose T (1994) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia presenting with primary progressive aphasia: ultrastructural and immunocytochemical studies. J Neurol Sci 127:186–197
Armstrong RA, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL (2000) A quantitative study of the pathological lesions in the neocortex and hippocampus of twelve patients with corticobasal degeneration. Exp Neurol 163:348–356
Bergeron C, Pollanen MS, Weyer L, Black SE, Lang AE (1996) Unusual clinical presentations of cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Ann Neurol 40:893–900
Bergeron C, Davis A, Lang AE (1998) Corticobasal ganglionic degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy presenting with cognitive decline. Brain Pathol 8: 355-365
Boeve BF, Maraganore DM, Parisi JE, Ahlskog JE, Graff-Radford N, Caselli RJ, Dickson DW, Kokmen E, Petersen RC (1999) Pathologic heterogeneity in clinically diagnosed corticobasal degeneration. Neurology 53:795–800
Constantinidis J (1985) Pick dementia: anatomoclinical correlations and pathophysiological considerations. In: Rose FC (ed) Interdisciplinary topics in gerontology, vol 19. Karger, Basel, pp 72–97
Constantinidis J, Richard J, Tissot R (1974) Pick’s disease. Histological and clinical correlations. Eur Neurol 11:208–217
Dickson DW (1999) Neuropathologic differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. J Neurol 246 [Suppl 2]:II/6–II/15
Dickson DW, Litvan I (2003) Corticobasal degeneration. In: Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorder. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 115–123
Dickson DW, Liu W-K, Ksiezak-Reding H, Yen S-H (2000) Neuropathologic and molecular considerations. Adv Neurol 82:9–27
Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Duyckaerts C, Horoupian D, Ikeda K, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, Lippa CF, Mirra SS, Tabaton M, Vonsattel JP, Wakabayashi K, Litvan I (2002) Office of rare diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:935–946
Duyckaerts C, Hauw J-J (2000) Diagnostic controversies: another view. Adv Neurology 82:233–240
Feany MB, Dickson DW (1995) Widespread cytoskeletal pathology characterizes corticobasal degeneration. Am J Pathol 146:1388–1396
Feany MB, Mattiace LA, Dickson DW (1996) Neuropathologic overlap of progressive supranuclear palsy, Pick’s disease and corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:53–67
Ferrer I, Hernández I, Boada M, Llorente A, Rey MJ, Cardozo A, Ezquerra M, Puig B (2003) Primary progressive aphasia as the initial manifestation of corticobasal degeneration and unusual tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol 106:419–435
Forman MS, Zhukareva V, Bergeron C, Chin S S-M, Grossman M, Clark C, Lee V M-Y, Trojanowski JQ (2002) Signature tau neuropathology in gray and white matter of corticobasal degeneration. Am J Pathol 160:2045–2053
Gibb WRG, Luthert PJ, Marsden CD (1989) Corticobasal degeneration. Brain 112:1171–1192
Goetz CG (2000) Nineteenth century studies of atypical parkinsonism: Charcot and his Salpêtrière school. Adv Neurology 82:1–8
Grimes DA, Lang AE, Bergeron CB (1999) Dementia as the most common presentation of cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology 53:1969–1974
Hattori M, Hashizume Y, Yoshida M, Iwasaki I, Hishikawa N, Ueda R, Ojika K (2003) Distribution of astrocytic plaques in the corticobasal degeneration brain and comparison with tuft-shaped astrocytes in the progressive supranuclear palsy brain. Acta Neuropathol 106:143–149
Hauw J-J, Agid Y (2003) Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) or Steele-Richardson-Olszewski disease. In: Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: The molecular pathology of dementia and movements disorder. ISN Neuropath Press, Basel, pp 103–114
Hauw J-J, Verny M, Delaère P, Cervera P, He Y, Duyckaerts C (1990) Constant neurofibrillary changes in progressive supranuclear palsy. Basic differences with Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Neurosci Lett 119:182–186
Hauw J-J, Daniel SE, Dickson D, Horoupian DS, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, McKee A, Tabaton M, Litvan I (1994) Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology 44:2015–2019
Hauw J-J, Verny M, Ruberg M, Duyckaerts C (1998) The neuropathology of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) or Steele-Richardson-Olszewski disease. In: Markesbery WR (ed) Neuropathology of dementing disorders. Arnold, London, pp 193–218
Holmes G (1909) The pathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Rev Neurol Psychiatry 8:693–725
Horoupian DS, Chu PL (1994) Unusual case of corticobasal degeneration with tau/Gallyas-positive neuronal and glial tangles. Acta Neuropathol 88:592–598
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Iritani S, Kase K, Arai T, Niizato K, Kuroki N, Kosaka K (1996) Corticobasal degeneration with primary progressive aphasia and accentuated cortical lesion in superior temporal gyrus: case report and review. Acta Neuropathol 92:534–539
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Arai T, Tsuchiya K (2002) Pick-body-like inclusions in corticobasal degeneration differ from Pick bodies in Pick’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 103:115–118
Jellinger KA, Bancher C (1992) Neuropathology. In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Clinical and research approaches. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 44–88
Katsuse O, Iseki E, Arai T, Akiyama H, Togo T, Uchikado H, Kato M, Silva R de, Lees A, Kosaka K (2003) 4-report tauopathy sharing pathological and biochemical features of corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 106:251–260
Kertesz A (1998) Pick’s disease and Pick complex: introductory nosology. In: Kertesz A, Munoz DG (eds), Pick’s disease and Pick complex, Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 1–11
Kertesz A, Munoz DG (1998) Clinical and pathological overlap in Pick complex. In: Kertesz A, Munoz DG (eds) Pick’s disease and Pick complex. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 281–286
Komori T (1999) Tau-positive glial inclusions in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration and Pick’s disease. Brain Pathol 9:663–679
Komori T, Arai N, Oda M, Nakayama H, Mori H, Yagishita S, Takahashi T, Amano N, Murayama S, Murakami S, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, Sasaki S, Iwata M (1998) Astrocytic plaques and tufts of abnormal fibers do not coexist in corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 96:401–408
Kompoliti K, Goetz CG, Boeve BF, Maraganore DM, Ahlskog JE, Marsden CD, Bhatia KP, Greene PE, Przedborski S, Seal EC, Burns RS, Hauser RA, Gauger LL, Factor SA, Molho ES, Riley DE (1998) Clinical presentation and pharmacological therapy in corticobasal degeneration. Arch Neurol 55:957–961
Lang AE, Riley DE, Bergeron C (1994) Cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. In: Calne DB (ed) Neurodegenerative diseases, Saunders, Philadelpia, pp 877–894
Mathuranath PS, Xuereb JH, Bak T, Hodge JR (2000) Corticobasal ganglionic degeneration and/or frontotemporal dementia? A report of two overlap cases and review of literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 68:304–312
Mimura M, Oda T, Tsuchiya K, Kato M, Ikeda K, Hori K, Kashima H (2001) Corticobasal degeneration presenting with nonfluent primary progressive aphasia: a clinicopathological study. J Neurol Sci 183:19–26
Mitani K, Uchihara T, Tamaru F, Endo K, Tsukagoshi H (1993) Corticobasal degeneration: clinicopathological studies on two cases (in Japanese with English abstract). Clin Neurol (Tokyo) 33:155–161
Miyazaki H, Saito Y, Kijima Y, Akabane H, Tsuchiya K (1997) An autopsy case of corticobasal degeneration mimicking frontal Pick’s disease (in Japanese with English abstract). No To Shinkei 49:277–282
Mizuno Y, Ozeki M, Iwata H, Takeuchi T, Ishihara R, Hashimoto N, Kobayashi H, Iwai K, Ogasawara S, Ukai K, Shibayama H (2002) A case of clinically and neuropathologically atypical corticobasal degeneration with widespread iron deposition. Acta Neuropathol 103:288–294
Mori H, Nishimura M, Namba Y, Oda M (1994) Coritcobasal degeneration: a disease with widespread appearance of abnormal tau and neurofibrillary tangles, and its relation to progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 88:113–121
Munoz DG (1998) The pathology of Pick complex. In: Kertesz A, Munoz DG (eds), Pick’s disease and Pick complex. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 211–241
Murayama S, Inoue K, Kawakami H, Bouldin TW, Suzuki K (1991) A unique pattern of astrocytosis in the primary motor area in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 82:456–461
Murayama S, Bouldin TW, Suzuki K (1992) Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural studies of upper motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 83:518–524
Nakano I, Donnenfeld H, Hirano A (1983) A neuropathological study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. With special reference to central chromatolysis and spheroid in the spinal anterior horn and some pathological changes of the motor cortex (in Japanese with English abstract). Neurol Med (Tokyo) 18:136–144
Nathan PW, Smith MC, Deacon P (1990) The corticospinal tract in man. Course and location of fibers at different segmental leves. Brain 113:303–324
Oda T, Kogure T, Tominaga I, Onaya M, Mimura M, Kato Y, Iwabuchi K, Haga C (1994) An autopsy case of progressive supranuclear palsy with echolalia showing psychiatric symptoms at the beginning (in Japanese). Seishinigaku 36:1159–1166
Oda T, Ikeda K, Akamatsu W, Iwabuchi K, Akiyama H, Kondo H, Seta K, Kato Y, Kogure T, Hori K, Tominaga I, Onaya M (1995) An autopsy case of corticobasal degeneration clinically misdiagnosed as Pick’s disease (in Japanese with English abstract). Psychiatr Neurol Jpn 97:757–769
Oyanagi K, Tsuchiya K, Yamazaki M, Ikeda K (2001) Substantia nigra in progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, and parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: specific pathological features. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:393–402
Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny EH, Richardson EP Jr (1967) Corticodentatonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia: a progressive disorder of late adult life. Trans Am Neurol Assoc 92:23–26
Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny EH, Richardson EP Jr (1968) Corticodentatonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. Arch Neurol 18: 20-33
Riley DE, Lang AE, Lewis A, Resch L, Ashby P, Hornykiewicz O, Black S (1990) Cortico-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology 40:1203-1212
Rinne JO, Lee MS, Thompson PD, Marsden CD (1994) Corticobasal degeneration. A clinical study of 36 cases. Brain 117:1183–1196
Rossor MN, Tyrrell PJ, Warrington EK, Thompson PD, Marsden CD, Lantos P (1999) Progressive frontal gait disturbance with atypical Alzheimer’s disease and corticobasal degeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:345–352
Schneider JA, Watts RL, Gearing M, Brewer RP, Mirra SS (1997) Corticobasal degeneration: Neuropathologic and clinical heterogeneity. Neurology 48:959–969
Su M, Yoshida Y, Hirata Y, Satoh Y, Nagata K (2000) Degeneration of the cerebellar dentate nucleus in corticobasal degeneration: neuropathological and morphometric investigations. Acta Neuropathol 99:365–370
Tolnay M, Probst A (2002) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration—tau as a pied piper? Neurogenetics 4:63–75
Tsuchiya K, Ikeda K (2002) Basal ganglia lesions in ‘ Pick complex’: A topographic neuropathological study of 19 autopsy cases. Neuropathology 22:323–336
Tsuchiya K, Ikeda K, Watabiki S, Shiotsu H, Hashimoto K, Mitani K, Okiyama R, Sano M, Kondo H, Shimada H (1996) An unusual autopsy case of corticobasal degeneration—with special reference to clinicopathological differentiation from progressive supranuclear palsy and slowly progressive aphasia (in Japanese with English abstract). No To Shinkei 48:559–565
Tsuchiya K, Ikeda K, Uchihara T, Oda T, Shimada H (1997) Distribution of cerebral cortical lesions in corticobasal degeneration: a clinicopathological study of five autopsy cases in Japan. Acta Neuropathol 94:416–424
Tsuchiya K, Uchihara T, Oda T, Arima K, Ikeda K, Shimada H (1997) Basal ganglia lesions in corticobasal degeneration differ from those in Pick’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: a topographic neuropathology of six autopsy cases. Neuropathology 17:208–216
Tsuchiya K, Miyazaki H, Ikeda K, Watabiki S, Kijima Y, Sano M, Shimada H (1997) Serial brain CT in corticobasal degeneration: radiological and pathological correlation of two autopsy cases. J Neurol Sci 152:23–29
Tsuchiya K, Arima K, Fukui T, Kuroiwa T, Haga C, Iritani S, Hirai S, Nakano I, Takemura T, Matsushita M, Ikeda K (1999) Distribution of basal ganglia lesions in Pick’s disease with Pick bodies: a topographic neuropathological study of eight autopsy cases. Neuropathology 19:370–379
Tsuchiya K, Osawa E, Haga C, Watabiki S, Ikeda M, Sano M, Ooe K, Taki K, Ikeda K (2000) Constant involvement of the Betz cells and pyramidal tract in multiple system atrophy: a clinicopathological study of seven autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 99:628–636
Tsuchiya K, Ishizu H, Nakano I, Kita Y, Sawabe M, Haga C, Kuyama K, Nishinaka T, Oyanagi K, Ikeda K, Kuroda S (2001) Distribution of basal ganglia lesions in generalized variant of Pick’s disease: a clinicopathological study of four autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 102:441–448
Tsuchiya K, Ikeda M, Hasegawa K, Fukui T, Kuroiwa T, Haga C, Oyanagi S, Nakano I, Matsushita M, Yagishita S, Ikeda K (2001) Distribution of cerebral cortical lesions in Pick’s disease with Pick bodies: a clinicopathological study of six autopsy cases showing unusual clinical presentations. Acta Neuropathol 102:553–571
Tsuchiya K, Nakayama H, Iritani S, Arai T, Niizato K, Haga C, Matsushita M, Ikeda K (2002) Distribution of basal ganglia lesions in diffuse neurofibrillary tangles with calcification: a clinicopathological study of five autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 103:555–564
Tsuchiya K, Ikeda K, Mimura M, Takahashi M, Miyazaki H, Anno M, Shiotsu H, Akabane H, Niizato K, Uchihara T, Tominaga I, Nakano I (2002) Constant involvement of the Betz cells and pyramidal tract in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with dementia: a clinicopathological study of eight autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 104:249–259
Uchihara T, Mitani K, Mori H, Kondo H, Yamada M, Ikeda K (1994) Abnormal cytoskeletal pathology peculiar to corticobasal degeneration is different from that of Alzheimer’s disease or progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 88:379–383
Uchihara T, Mizusawa H, Tsuchiya K, Kondo H, Oda T, Ikeda K (1998) Discrepancy between tau immunoreactivity and argyrophilia by the Bodian method in neocortical neurons of corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 96:553–557
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2004) Pathological heterogeneity in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Neuropathology 24:79–86
Wakabayashi K, Oyanagi K, Makifuchi T, Ikuta F, Homma A, Homma Y, Horikawa Y, Tokiguchi S (1994) Corticobasal degeneration: etiopathological significance of the cytoskeletal alterations. Acta Neuropathol 87:545–553
Wakabayashi K, Mori F, Oyama Y, Kurihara A, Kamada M, Yoshimoto M, Takahashi H (2003) Lewy bodies in Betz cells of the motor cortex in a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 105:189–192
Wenning GK, Litvan I, Jankovic J, Granata R, Mangone CA, McKee A, Poewe W, Jellinger K, Ray Chaudhuri K, D’Olhaberriague L, Pearce RKB (1998) Natural history and survival of 14 patients with corticobasal degeneration confirmed at postmortem examination. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64:184–189
Acknowledgements
We wish to express our gratitude to former Prof. H. Tsukagoshi (Department of Neurology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University) for his valuable advice. We also wish to thank to Mr. Y. Shoda and Ms E. Matsui for their photographic assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuchiya, K., Murayama, S., Mitani, K. et al. Constant and severe involvement of Betz cells in corticobasal degeneration is not consistent with pyramidal signs: a clinicopathological study of ten autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 109, 353–366 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0966-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0966-4