Abstract
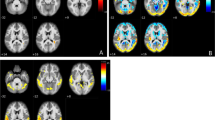
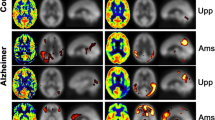
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI), the transitional clinical stage between cognition in normal aging and dementia, have been linked to abnormalities in brain perfusion. Pulsed arterial spin labeling (PASL) is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for evaluating brain perfusion. The present study aimed to determine regional perfusion abnormalities in 19 patients with mild dementia in AD and 24 patients with MCI as compared to 24 cognitively healthy elderly controls using PASL. In line with nuclear imaging methods, lower perfusion in patients with MCI and AD was found mainly in the parietal lobe, but also in angular and middle temporal areas as well as in the left middle occipital lobe and precuneus. Our data imply that PASL may be a valuable instrument for investigating perfusion changes in the transition from normal aging to dementia and indicate that it might become an alternative to nuclear imaging techniques in AD diagnostics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexopoulos P, Greim B, Nadler K, Martens U, Krecklow B, Domes G, Herpertz S, Kurz A (2006) Validation of the Addenbrooke’s cognitive examination for detecting early Alzheimer’s disease and mild vascular dementia in a German population. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22:385–391
Alexopoulos P, Grimmer T, Perneczky R, Domes G, Kurz A (2006) Progression to dementia in clinical subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22:27–34
Alsop DC, Casement M, de Bazelaire C, Fong T, Press DZ (2008) Hippocampal hyperperfusion in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 42:1267–1274
Alsop DC, Dai W, Grossman M, Detre JA (2010) Arterial spin labeling blood flow MRI: its role in the early characterization of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 20:871–880
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (1999) Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Hum Brain Mapp 7:254–266
Bradley KM, O’Sullivan VT, Soper ND, Nagy Z, King EM, Smith AD, Shepstone BJ (2002) Cerebral perfusion SPET correlated with Braak pathological stage in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 125:1772–1781
Buxton RB, Frank LR, Wong EC, Siewert B, Warach S, Edelman RR (1998) A general kinetic model for quantitative perfusion imaging with arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 40:383–396
Buxton RB, Uludag K, Dubowitz DJ, Liu TT (2004) Modeling the hemodynamic response to brain activation. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S220–S233
Celone KA, Calhoun VD, Dickerson BC, Atri A, Chua EF, Miller SL, DePeau K, Rentz DM, Selkoe DJ, Blacker D, Albert MS, Sperling RA (2006) Alterations in memory networks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: an independent component analysis. J Neurosci 26:10222–10231
Chen W, Song X, Beyea S, D’Arcy R, Zhang Y, Rockwood K (2010) Advances in perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7(2):185–196
D’Esposito M, Deouell LY, Gazzaley A (2003) Alterations in the BOLD fMRI signal with ageing and disease: a challenge for neuroimaging. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:863–872
Dai W, Lopez OL, Carmichael OT, Becker JT, Kuller LH, Gach HM (2009) Mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer disease: patterns of altered cerebral blood flow at MR imaging. Radiology 250:856–866
de Leon MJ, Convit A, Wolf OT, Tarshish CY, DeSanti S, Rusinek H, Tsui W, Kandil E, Scherer AJ, Roche A, Imossi A, Thorn E, Bobinski M, Caraos C, Lesbre P, Schlyer D, Poirier J, Reisberg B, Fowler J (2001) Prediction of cognitive decline in normal elderly subjects with 2-[(18)F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose/poitron-emission tomography (FDG/PET). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10966–10971
Dickerson BC, Sperling RA (2008) Functional abnormalities of the medial temporal lobe memory system in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: insights from functional MRI studies. Neuropsychologia 46:1624–1635
Dougall NJ, Bruggink S, Ebmeier KP (2004) Systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-HMPAO-SPECT in dementia. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 12:554–570
Drzezga A, Lautenschlager N, Siebner H, Riemenschneider M, Willoch F, Minoshima S, Schwaiger M, Kurz A (2003) Cerebral metabolic changes accompanying conversion of mild cognitive impairment into Alzheimer’s disease: a PET follow-up study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:1104–1113
Falkai P, Moller HJ (2010) Understanding mental disorders from neuronal networks to glial cells and proteomics. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260:441–442
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Fukumoto H, Cheung BS, Hyman BT, Irizarry MC (2002) Beta-secretase protein and activity are increased in the neocortex in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 59:1381–1389
Golay X, Petersen ET, Hui F (2005) Pulsed star labeling of arterial regions (PULSAR): a robust regional perfusion technique for high field imaging. Magn Reson Med 53:15–21
Grimmer T, Drzezga A, Kurz A (2010) Visualization of amyloid with positron emission tomography. Useful improvement in the diagnosis of dementia? Nervenarzt 81:602–606
Hanyu H, Shimizu S, Tanaka Y, Takasaki M, Koizumi K, Abe K (2004) Differences in regional cerebral blood flow patterns in male versus female patients with Alzheimer disease. Ajnr 25:1199–1204
Heo S, Prakash RS, Voss MW, Erickson KI, Ouyang C, Sutton BP, Kramer AF (2010) Resting hippocampal blood flow, spatial memory and aging. Brain Res 1315:119–127
Herholz K, Carter SF, Jones M (2007) Positron emission tomography imaging in dementia. Br J Radiol 80(Spec No 2):S160–S167
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL (1984) Alzheimer’s disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225:1168–1170
Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, Xu YC, O’Brien PC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Boeve BF, Waring SC, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E (1999) Prediction of AD with MRI-based hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 52:1397–1403
Jarstfer BS, Rich NM, Hobson RW 2nd, Geer TM (1980) Smoking, lipids, and atherosclerosis. Mil Med 145:521–524
Johnson KA (2006) Amyloid imaging of Alzheimer’s disease using Pittsburgh Compound B. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 6:496–503
Johnson KA, Moran EK, Becker JA, Blacker D, Fischman AJ, Albert MS (2007) Single photon emission computed tomography perfusion differences in mild cognitive impairment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:240–247
Johnson NA, Jahng GH, Weiner MW, Miller BL, Chui HC, Jagust WJ, Gorno-Tempini ML, Schuff N (2005) Pattern of cerebral hypoperfusion in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment measured with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging: initial experience. Radiology 234:851–859
Luh WM, Wong EC, Bandettini PA, Hyde JS (1999) QUIPSS II with thin-slice TI1 periodic saturation: a method for improving accuracy of quantitative perfusion imaging using pulsed arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 41:1246–1254
Mansfield P (1984) Real-time echo-planar imaging by NMR. Br Med Bull 40:187–190
Martins-de-Souza D (2010) Is the word ‘biomarker’ being properly used by proteomics research in neuroscience? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260:561–562
McKhann G, Drachmann D, Folstein M, Katzmann R, Price D, Stadlan E (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Minati L, Edginton T, Bruzzone MG, Giaccone G (2009) Current concepts in Alzheimer’s disease: a multidisciplinary review. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 24:95–121
Mosconi L, Tsui WH, De Santi S, Li J, Rusinek H, Convit A, Li Y, Boppana M, de Leon MJ (2005) Reduced hippocampal metabolism in MCI and AD: automated FDG-PET image analysis. Neurology 64:1860–1867
Nichols T, Hayasaka S (2003) Controlling the familywise error rate in functional neuroimaging: a comparative review. Stat Methods Med Res 12:419–446
Nöth U, Meadows GE, Kotajima F, Deichmann R, Corfield DR, Turner R (2006) Cerebral vascular response to hypercapnia: determination with perfusion MRI at 1.5 and 3.0 Tesla using a pulsed arterial spin labeling technique. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1229–1235
Pertoldi C, Hansen MM, Loeschcke V, Madsen AB, Jacobsen L, Baagoe H (2001) Genetic consequences of population decline in the European otter (Lutra lutra): an assessment of microsatellite DNA variation in Danish otters from 1883 to 1993. Proc Biol Sci 268:1775–1781
Placanica L, Zhu L, Li YM (2009) Gender- and age-dependent gamma-secretase activity in mouse brain and its implication in sporadic Alzheimer disease. PLoS One 4:e5088
Price JL, Davis PB, Morris JC, White DL (1991) The distribution of tangles, plaques and related immunohistochemical markers in healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 12:295–312
Raji CA, Becker JT, Tsopelas ND, Price JC, Mathis CA, Saxton JA, Lopresti BJ, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, DeKosky ST, Klunk WE (2008) Characterizing regional correlation, laterality and symmetry of amyloid deposition in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound B. J Neurosci Methods 172:277–282
Reddy PH, Beal MF (2008) Amyloid beta, mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage: implications for cognitive decline in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 14:45–53
Roberts DA, Detre JA, Bolinger L, Insko EK, Leigh JS Jr (1994) Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of human brain perfusion at 1.5 T using steady-state inversion of arterial water. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:33–37
Rodriguez G, Warkentin S, Risberg J, Rosadini G (1988) Sex differences in regional cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:783–789
Rosazza C, Minati L, Ghielmetti F, Maccagnano E, Erbetta A, Villani F, Epifani F, Spreafico R, Bruzzone MG (2009) Engagement of the medial temporal lobe in verbal and nonverbal memory: assessment with functional MR imaging in healthy subjects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1134–1141
Thalmann B, Monsch A (1997) The consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologische Testbatterie. Memory Clinic Basel, Basel
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15:273–289
Warkentin S, Ohlsson M, Wollmer P, Edenbrandt L, Minthon L (2004) Regional cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease: classification and analysis of heterogeneity. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:207–214
WHO (1994) Internationale Klassifikation psychischer Störungen, ICD-10 Kapitel V(F) Forschungskriterien. Hans Huber, Bern
Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, Nordberg A, Backman L, Albert M, Almkvist O, Arai H, Basun H, Blennow K, de Leon M, DeCarli C, Erkinjuntti T, Giacobini E, Graff C, Hardy J, Jack C, Jorm A, Ritchie K, van Duijn C, Visser P, Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment–beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med 256:240–246
Wong EC, Buxton RB, Frank LR (1998) Quantitative imaging of perfusion using a single subtraction (QUIPSS and QUIPSS II). Magn Reson Med 39:702–708
Worsley KJ (2003) Detecting activation in fMRI data. Stat Methods Med Res 12:401–418
Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Hanse E (2010) Amyloid beta and APP as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol 45:23–29
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the healthy and diseased volunteers who participated in this study. AMW is supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, BMBF grant 01EV0710.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexopoulos, P., Sorg, C., Förschler, A. et al. Perfusion abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia in Alzheimer’s disease measured by pulsed arterial spin labeling MRI. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262, 69–77 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0226-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0226-2