Abstract
Whereas it is important to gain prognostic information in patients with clinically isolated syndromes (CIS) suggestive of multiple sclerosis (MS), there is still a lack of definitive data about the significance of normal-appearing white (NAWM) and gray (NAGM) matter damage in these patients. The aim of this study was to clarify the role of magnetization transfer magnetic resonance imaging (MT MRI) in assessing “occult” damage at the earliest clinical stage of MS.
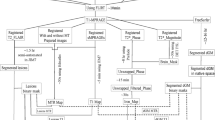
Dual echo, post-contrast T1-weighted, and MT MRI were obtained from 43 CIS patients with paraclinical evidence of spatial disease dissemination within 3 months from disease onset and from 22 controls. In patients, conventional MRI was obtained after 3 and 12 months from the baseline assessment, to detect disease dissemination in time (DIT). A neurological examination was also conducted to ascertain the occurrence of relapses for an average follow up period of 1389 (range = 420–1847) days. MTR maps were derived and NAWM and NAGM MT ratio (MTR) histograms were analyzed.
During the follow up, 30 patients showed MRI evidence of DIT, and 21 experienced a relapse. T2 lesion volume (LV) was significantly higher in patients with DIT than in those without (p = 0.005). MTR histogram variables did not significantly differ between patients with MRI or clinical DIT. T2 LV was the only significant predictor of clinical DIT at follow-up (p = 0.001).
This study shows that MT MRI-detectable damage to NAWM and NAGM may not be an important feature of all patients at presentation with a CIS highly suggestive of MS and that such a damage may develop with subsequent disease evolution.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audoin B, Fernando KT, Swanton JK, Thompson AJ, Plant GT, Miller DH (2006) Selective magnetization transfer ratio decrease in the visual cortex following optic neuritis. Brain 129:1031–1039
Bozzali M, Cercignani M, Sormani MP, Comi G, Filippi M (2002) Quantification of brain grey matter damage in different MS phenotypes by use of diffusion tensor MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:985–988
Brex PA, Gomez-Anson B, Parker GJM, Molyneux PD, Miszkiel KA, Barker GJ, MacManus DG, Davie CA, Plant GT, Miller DH (1999) Proton MR spectroscopy in clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 166:16–22
Brex PA, Leary SM, Plant GT, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2001) Magnetization transfer imaging in patients with clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:947–951
Dalton CM, Chard DT, Davies GR, Miszkiel KA, Altmann DR, Fernando K, Plant GT, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2004) Early development of multiple sclerosis is associated with progressive grey matter atrophy in patients presenting with clinically isolated syndromes. Brain 127:1101–1107
Dehmeshki J, Barker GJ, Tofts PS (2002) Classification of disease subgroup and correlation with disease severity using magnetic resonance imaging whole-brain histograms: application to magnetization transfer ratios and multiple sclerosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21:320–331
Evangelou N, Konz D, Esiri MM, Smith S, Palace J, Matthews PM (2000) Regional axonal loss in the corpus callosum correlates with cerebral white matter lesion volume and distribution in multiple sclerosis. Brain 123:1845–1849
Fernando KTM, McLean MA, Chard DT, MacManus DG, Dalton CM, Miszkiel KA, Gordon RM, Plant GT, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2004) Elevated white matter myo-inositol in clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Brain 127:1361–1369
Fernando KTM, Tozer DJ, Miszkiel KA, Gordon RM, Swanton JK, Dalton CM, Barker GJ, Plant GT, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2005) Magnetization transfer histograms in clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Brain 128:2911–2925
Filippi M, Iannucci G, Tortorella C, Minicucci L, Horsfield MA, Colombo B, Sormani MP, Comi G (1999) Comparison of MS clinical phenotypes using conventional and magnetization transfer MRI. Neurology 52:588–594
Filippi M, Inglese M, Rovaris M, Sormani MP, Horsfield MA, Iannucci G, Colombo B, Comi G (2000) Magnetization transfer imaging to monitor the evolution of MS: a one-year follow up study. Neurology 55:940–946
Filippi M, Bozzali M, Rovaris M, Gonen O, Kesavadas C, Ghezzi A, Martinelli V, Grossman RI, Scotti G, Comi G, Falini A (2003) Evidence for widespread axonal damage at the earliest clinical stage of multiple sclerosis. Brain 126:433–437
Gallo A, Rovaris M, Riva R, Ghezzi A, Benedetti B, Martinelli V, Falini A, Comi G, Filippi M (2005) Diffusion tensor MRI detects normal-appearing white matter damage unrelated to short-term disease activity in patients at the earliest clinical stage of multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62:803–808
Ge Y, Grossman RI, Udupa JK, Babb JS, Kolson DL, McGowan JC (2001) Magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis of gray matter in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:470–475
Iannucci G, Tortorella C, Rovaris M, Sormani MP, Comi G, Filippi M (2000) Prognostic value of MR and magnetization transfer imaging findings in patients with clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis at presentation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1034–1038
Kaiser JS, Grossman RI, Polansky M, Udupa JK, Miki Y, Galetta SL (2000) Magnetization transfer histogram analysis of monosymptomatic episodes of neurologic dysfunction: preliminary findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1043–1047
Kidd D, Barkhof F, McConnel R, Algra PR, Allen IV, Revesz T (1999) Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Brain 122:17–26
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, van den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127
Miller DH, Thompson AJ, Filippi M (2003) Magnetic resonance studies of abnormalities in the normal appearing white matter and grey matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 250:1407–1419
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Montalban X, Thompson AJ, Filippi M (2005) Clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis, part I: natural history, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis. Lancet Neurol 4:281–288
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Montalban X, Thompson AJ, Filippi M (2005) Clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of MS, part II: non-conventional MRI, recovery processes, and management. Lancet Neurol 4:341–348
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Ebers GC, Johnson KP, Sibley WA, Silberberg DH, Tourtellotte WW (1983) New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol 13:227–231
Ranjeva JP, Pelletier J, Confort-Gouny S, Ibarrola D, Audoin B, Le Fur Y, Viout P, Cherif AA, Cozzone PJ (2003) MRI/MRS of corpus callosum in patients with clinically isolated syndrome suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 9:554–565
Rocca MA, Mezzapesa DM, Ghezzi A, Falini A, Agosta F, Martinelli V, Scotti G, Comi G, Filippi M (2003) Cord damage elicits brain functional reorganization after a single episode of myelitis. Neurology 61:1078–1085
Rovaris M, Agosta F, Sormani MP, Inglese M, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M (2003) Conventional and magnetization transfer MRI predictors of clinical multiple sclerosis evolution: a medium-term follow-up study. Brain 126:2323–2332
Rovaris M, Bozzali M, Iannucci G, Ghezzi A, Caputo D, Montanari E, Bertolotto A, Bergamaschi R, Capra R, Mancardi GL, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M (2002) Assessment of normal-appearing white and gray matter in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 59:1406–1412
Rovaris M, Bozzali M, Rodegher M, Tortorella C, Comi G, Filippi M (1999) Brain MRI correlates of magnetization transfer imaging metrics in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 166:58–63
Rovaris M, Filippi M, Calori G, Colombo B, Campi A, Rodegher M, Comi G (1997) Intra-observer reproducibility in measuring new putative MR markers of demyelination and axonal loss in multiple sclerosis: a comparison with conventional T2-weighted images. J Neurol 244:266–270
Santos CA, Narayanan S, De Stefano N, Tartaglia MC, Francis SJ, Arnaoutelis R, Caramanos Z, Antel JP, Pike GB, Arnold DL (2002) Magnetization transfer can predict clinical evolution in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 249:662–668
Schmierer K, Scaravilli F, Altmann DR, Barker GJ, Miller DH (2004) Magnetization transfer ratio and myelin in post mortem multiple sclerosis brain. Ann Neurol 56:407–415
Smith SM, Zhang Y, Jenkinson M, Chen J, Matthews PM, Federico A, De Stefano N (2002) Accurate, robust, and automated longitudinal and cross-sectional brain change analysis. NeuroImage 17:479–489
Sormani MP, Iannucci G, Rocca MA, Mastronardo G, Cercignani M, Minicucci L, Filippi M (2000) Reproducibility of magnetization transfer ratio histogram-derived measures of the brain in healthy volunteers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:133–136
Traboulsee A, Dehmeshki J, Brex PA, Dalton CM, Chard D, Barker GJ, Plant GT, Miller DH (2002) Normal-appearing brain tissue MTR histograms in clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of MS. Neurology 59:126–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received in revised form: 14 April 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallo, A., Rovaris, M., Benedetti, B. et al. A brain magnetization transfer MRI study with a clinical follow up of about four years in patients with clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 254, 78–83 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0283-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0283-z