Abstract
Background
Postoperative cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks and headaches remain potential complications after retrosigmoid approaches for lesions in the posterior fossa and cerebellopontine angle. The authors describe a simple repair technique with an autologous fat graft-assisted Medpor Titan cranioplasty and investigate the incidence of postoperative CSF leaks and headaches using this technique.
Methods
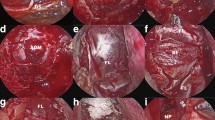
A retrospective chart review was conducted on all cases (n = 60) of retrosigmoid craniectomy from September 2009 to May 2014 in patients who underwent fat graft-assisted cranioplasty. After obtaining a watertight dural closure and sealing off any visible mastoid air cells with bone wax, an autologous fat graft was placed over the dural suture line and up against the waxed-off air cells. The fat graft filled the retrosigmoid cranial defect and was then bolstered with a Medpor Titan (titanium mesh embedded in porous polyethylene) cranioplasty. A postoperative mastoid pressure dressing was applied for 48 h, and prophylactic lumbar drainage was not used. Factors examined in this study included postoperative CSF leak (incisional, rhinorrhea, otorrhea), pseudomeningocele formation, incidence and severity of postoperative headache, length of hospital stay, and length of follow-up.
Results
No patients developed postoperative CSF leaks (0 %), pseudomeningoceles (0 %), or new-onset postoperative headaches (0 %) with the described repair technique. There were no cases of graft site morbidity such as hematoma or wound infection. Mean duration of postoperative hospital stay was 3.8 days (range 2–10 days). Mean postoperative follow-up was 12.4 months (range 2.0–41.1 months).
Conclusions
Our multilayer repair technique with a fat graft-assisted Medpor Titan cranioplasty appears effective in preventing postoperative CSF leaks and new-onset postoperative headaches after retrosigmoid approaches. Postoperative lumbar drainage may not be necessary.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuzayed B, Tuzgen S, Canbaz B, Yuksel O, Tutunculer B, Sanus GZ (2009) Reconstruction of growing skull fracture with in situ galeal graft duraplasty and porous polyethylene sheet. J Craniofac Surg 20:1245–1249
Ansari SF, Terry C, Cohen-Gadol AA (2012) Surgery for vestibular schwannomas: a systematic review of complications by approach. Neurosurg Focus 33:E14
Arlt F, Trantakis C, Krupp W, Renner C, Winkler D, Strauss G, Meixensberger J (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid leak after microsurgical surgery in vestibular schwannomas via retrosigmoidal craniotomy. Neurol Res 33:947–952
Aydin S, Kucukyuruk B, Abuzayed B, Aydin S, Sanus GZ (2011) Cranioplasty: Review of materials and techniques. J Neurosci Rural Pract 2:162–167
Baird CJ, Hdeib A, Suk I, Francis HW, Holliday MJ, Tamargo RJ, Brem H, Long DM (2007) Reduction of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea after vestibular schwannoma surgery by reconstruction of the drilled porus acusticus with hydroxyapatite bone cement. J Neurosurg 107:347–351
Bani A, Gilsbach JM (2002) Incidence of cerebrospinal fluid leak after microsurgical removal of vestibular schwannomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:979–982, discussion 982
Becker SS, Jackler RK, Pitts LH (2003) Cerebrospinal fluid leak after acoustic neuroma surgery: a comparison of the translabyrinthine, middle fossa, and retrosigmoid approaches. Otol Neurotol 24:107–112
Black P (2000) Cerebrospinal fluid leaks following spinal or posterior fossa surgery: use of fat grafts for prevention and repair. Neurosurg Focus 9:e4
Boghani Z, Choudhry OJ, Schmidt RF, Jyung RW, Liu JK (2013) Reconstruction of cranial base defects using the medpor titan implant: Cranioplasty applications in acoustic neuroma surgery. Laryngoscope 123:1361–1368
Brennan JW, Rowed DW, Nedzelski JM, Chen JM (2001) Cerebrospinal fluid leak after acoustic neuroma surgery: influence of tumor size and surgical approach on incidence and response to treatment. J Neurosurg 94:217–223
Catalano PJ, Jacobowitz O, Post KD (1996) Prevention of headache after retrosigmoid removal of acoustic tumors. Am J Otol 17:904–908
Charalampakis S, Koutsimpelas D, Gouveris H, Mann W (2011) Post-operative complications after removal of sporadic vestibular schwannoma via retrosigmoid-suboccipital approach: current diagnosis and management. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-L 268:653–660
Choudhry OJ, Christiano LD, Arnaout O, Adel JG, Liu JK (2013) Reconstruction of pterional defects after frontotemporal and orbitozygomatic craniotomy using Medpor Titan implant: Cosmetic results in 98 patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:1716–1720
Ciric I, Zhao JC, Rosenblatt S, Wiet R, O’Shaughnessy B (2005) Suboccipital retrosigmoid approach for removal of vestibular schwannomas: facial nerve function and hearing preservation. Neurosurgery 56:560–570, discussion 560-570
Couldwell WT, Chen TC, Weiss MH, Fukushima T, Dougherty W (1994) Cranioplasty with the Medpor porous polyethylene flexblock implant. Technical Notes J Neurosurg 81:483–486
Cueva RA, Mastrodimos B (2005) Approach design and closure techniques to minimize cerebrospinal fluid leak after cerebellopontine angle tumor surgery. Otol Neurotol 26:1176–1181
Elhammady MS, Telischi FF, Morcos JJ (2012) Retrosigmoid approach: indications, techniques, and results. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 45:375–397, ix
Feghali JG, Elowitz EH (1998) Split calvarial graft cranioplasty for the prevention of headache after retrosigmoid resection of acoustic neuromas. Laryngoscope 108:1450–1452
Fishman AJ, Hoffman RA, Roland JT Jr, Lebowitz RA, Cohen NL (1996) Cerebrospinal fluid drainage in the management of CSF leak following acoustic neuroma surgery. Laryngoscope 106:1002–1004
Fishman AJ, Marrinan MS, Golfinos JG, Cohen NL, Roland JT Jr (2004) Prevention and management of cerebrospinal fluid leak following vestibular schwannoma surgery. Laryngoscope 114:501–505
Gal TJ, Bartels LJ (1999) Use of bone wax in the prevention of cerebrospinal fluid fistula in acoustic neuroma surgery. Laryngoscope 109:167–169
Galer C, Bowdino B, Leibrock L, Moore GF (2006) Complication Rate of Retrosigmoid Craniotomy with and without Closed-Suction Wound Drainage. Skull Base 16:A090
Gerganov V, Bussarsky V, Romansky K, Popov R, Djendov S, Dimitrov I (2003) Cerebellopontine angle meningiomas. Clin Features Surg Treat J Neurosurg Sci 47:129–135, discussion 135
Gormley WB, Sekhar LN, Wright DC, Kamerer D, Schessel D (1997) Acoustic neuromas: results of current surgical management. Neurosurgery 41:50–58, discussion 58-60
Harner SG, Beatty CW, Ebersold MJ (1993) Headache after acoustic neuroma excision. Am J Otol 14:552–555
Harner SG, Beatty CW, Ebersold MJ (1995) Impact of cranioplasty on headache after acoustic neuroma removal. Neurosurgery 36:1097–1099, discussion 1099-1100
Heman-Ackah SE, Cosetti MK, Gupta S, Golfinos JG, Roland JT Jr (2012) Retrosigmoid approach to cerebellopontine angle tumor resection: surgical modifications. Laryngoscope 122:2519–2523
Hoffman RA (1994) Cerebrospinal fluid leak following acoustic neuroma removal. Laryngoscope 104:40–58
Kucukyuruk B, Biceroglu H, Abuzayed B, Ulu MO, Sanus GZ (2010) Intraosseous meningioma: a rare tumor reconstructed with porous polyethylene. J Craniofac Surg 21:936–939
Leonetti J, Anderson D, Marzo S, Moynihan G (2001) Cerebrospinal fluid fistula after transtemporal skull base surgery. Otolaryng Head Neck Surg 124:511–514
Levo H, Pyykko I, Blomstedt G (2000) Postoperative headache after surgery for vestibular schwannoma. Ann Oto Rhinol Laryn 109:853–858
Liu JK, Gottfried ON, Cole CD, Dougherty WR, Couldwell WT (2004) Porous polyethylene implant for cranioplasty and skull base reconstruction. Neurosurg Focus 16:ECP1
Lüdemann WO, Stieglitz LH, Gerganov V, Samii A, Samii M (2008) Fat implant is superior to muscle implant in vestibular schwannoma surgery for the prevention of cerebrospinal fluid fistulae. Neurosurgery 63:ONS38–42, discussion 42-33
Mangham CA Jr (2004) Retrosigmoid versus middle fossa surgery for small vestibular schwannomas. Laryngoscope 114:1455–1461
Millen SJ, Meyer G (1993) Surgical management of CSF otorhinorrhea following retrosigmoid removal of cerebellopontine angle tumors. Am J Otol 14:585–589
Moreira-Gonzalez A, Jackson IT, Miyawaki T, Barakat K, DiNick V (2003) Clinical outcome in cranioplasty: critical review in long-term follow-up. J Craniofac Surg 14:144–153
Nutik SL, Korol HW (1995) Cerebrospinal fluid leak after acoustic neuroma surgery. Surg Neurol 43:553–556, discussion 556-557
Ojemann RG (2001) Retrosigmoid approach to acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma). Neurosurgery 48:553–558
Oliveira RV, de Souza Nunes LS, Filho HN, de Andrade HL, Ribeiro DA, Matsumoto MA (2009) Fibrovascularization and osteogenesis in high-density porous polyethylene implants. J Craniofac Surg 20:1120–1124
Park CE, Park BJ, Lim YJ, Yeo SG (2011) Functional outcomes in retrosigmoid approach microsurgery and gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery in vestibular schwannoma. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-L 268:955–959
Pedrosa CA, Ahern DK, McKenna MJ, Ojemann RG, Acquadro MA (1994) Determinants and impact of headache after acoustic neuroma surgery. Am J Otol 15:793–797
Porter RG Sr, Leonetti JP, Ksiazek J, Anderson D (2009) Association between adipose graft usage and postoperative headache after retrosigmoid craniotomy. Otol Neurotol 30:635–639
Revuelta-Gutiérrez R, Díaz-Romero Paz RF, Vales-Hidalgo LO, Hinojosa-González R, Barges-Coll J (2009) Cerebellopontine angle epidermoid cysts. Experience of 43 cases with long-term follow-up. Cir 77(257–265):241–258
Roberti F, Sekhar LN, Kalavakonda C, Wright DC (2001) Posterior fossa meningiomas: surgical experience in 161 cases. Surg Neurol 56:8–20, discussion 20-21
Samii M, Gerganov VM, Samii A (2010) Functional outcome after complete surgical removal of giant vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg 112:860–867
Samii M, Matthies C (1997) Management of 1000 vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): surgical management and results with an emphasis on complications and how to avoid them. Neurosurgery 40:11–21, discussion 21-13
Schaller B, Baumann A (2003) Headache after removal of vestibular schwannoma via the retrosigmoid approach: a long-term follow-up-study. Otolaryng Head Neck Surg 128:387–395
Schessel DA, Rowed DW, Nedzelski JM, Feghali JG (1993) Postoperative pain following excision of acoustic neuroma by the suboccipital approach: observations on possible cause and potential amelioration. Am J Otol 14:491–494
Selesnick SH, Liu JC, Jen A, Newman J (2004) The incidence of cerebrospinal fluid leak after vestibular schwannoma surgery. Otol Neurotol 25:387–393
Soumekh B, Levine SC, Haines SJ, Wulf JA (1996) Retrospective study of postcraniotomy headaches in suboccipital approach: diagnosis and management. Am J Otol 17:617–619
Staecker H, Nadol JB Jr, Ojeman R, Ronner S, McKenna MJ (2000) Hearing preservation in acoustic neuroma surgery: middle fossa versus retrosigmoid approach. Am J Otol 21:399–404
Stieglitz LH, Giordano M, Gerganov V, Raabe A, Samii A, Samii M, Lüdemann WO (2010) Petrous bone pneumatization is a risk factor for cerebrospinal fluid fistula following vestibular schwannoma surgery. Neurosurgery 67:509–515
Strieth S, Weger T, Bartesch C, Bittmann P, Stelter K, Berghaus A (2010) Biocompatibility of porous polyethylene implants tissue-engineered by extracellular matrix and VEGF. J Biomed Mater Res A 93:1566–1573
Tonn JC, Schlake HP, Goldbrunner R, Milewski C, Helms J, Roosen K (2000) Acoustic neuroma surgery as an interdisciplinary approach: a neurosurgical series of 508 patients. J Neurol Neurosur Ps 69:161–166
Valtonen HJ, Poe DS, Heilman CB, Tarlov EC (1997) Endoscopically assisted prevention of cerebrospinal fluid leak in suboccipital acoustic neuroma surgery. Am J Otol 18:381–385
Wazen JJ, Sisti M, Lam SM (2000) Cranioplasty in acoustic neuroma surgery. Laryngoscope 110:1294–1297
Wellisz T, Dougherty W, Gross J (1992) Craniofacial applications for the Medpor porous polyethylene flexblock implant. J Craniofac Surg 3:101–107
Yamakami I, Uchino Y, Kobayashi E, Yamaura A, Oka N (2004) Removal of large acoustic neurinomas (vestibular schwannomas) by the retrosigmoid approach with no mortality and minimal morbidity. J Neurol Neurosur Ps 75:453–458
Financial disclosures
None.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, P.Y., Mendelson, Z.S., Reddy, R.K. et al. Reconstruction after retrosigmoid approaches using autologous fat graft-assisted Medpor Titan cranioplasty: assessment of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks and headaches in 60 cases. Acta Neurochir 156, 1879–1888 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2190-x