Abstract
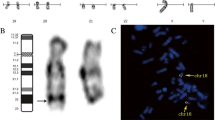
Patients with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) frequently harbour chromosome rearrangements and segmental aneuploidies, which allow us to identify candidate genes. In a boy with mild facial dysmorphisms, speech delay and ASD, we reconstructed by karyotyping, FISH and SNP array-based segmental aneuploidy profiling a highly complex chromosomal rearrangement involving at least three breaks in chromosome 1 and seven breaks in chromosome 7. Chromosome banding revealed an inversion of region 7q32.1–7q35 on the derivative chromosome 7. FISH with region-specific BACs mapped both inversion breakpoints and revealed additional breaks and structural changes in the CNTNAP2 gene. Two gene segments were transposed and inserted into the 1q31.2 region, while the CNTNAP2 segment between the two transposed parts as well as intron 13 to the 5-UTR were retained on the der(7). SNP array analysis revealed an additional de novo deletion encompassing the distal part of intron1 and exon 2 of CNTNAP2, which contains FOXP2 binding sites. Second, we found another de novo deletion on chromosome 1q41, containing 15 annotated genes, including KCTD3 and USH2A. Disruptions of the CNTNAP2 gene have been associated with ASD and with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome (GTS). Comparison of disruptions of CNTNAP2 in patients with GTS and ASD suggests that large proximal disruptions result in either GTS or ASD, while relatively small distal disruptions may be phenotypically neutral. For full-blown ASD to develop, a proximal disruption of CNTNAP2 may have to occur concomitantly with additional genome mutations such as hemizygous deletions of the KCTD3 and USH2A genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harel S, Greenstein Y, Kramer U, Yifat R, Samuel E, Nevo Y, Leitner Y, Kutai M, Fattal A, Shinnar S (1996) Clinical characteristics of children referred to a child development center for evaluation of speech, language, and communication disorders. Pediatr Neurol 15:305–311
Lai CS, Fisher SE, Hurst JA, Vargha-Khadem F, Monaco AP (2001) A forkhead-domain gene is mutated in a severe speech and language disorder. Nature 413:519–523
Lichtenbelt KD, Hochstenbach R, van Dam WM, Eleveld MJ, Poot M, Beemer FA (2005) Supernumerary ring chromosome 7 mosaicism: case report, investigation of the gene content, and delineation of the phenotype. Am J Med Genet A 132A:93–100
Ropers HH, Hamel BC (2005) X-linked mental retardation. Nat Rev Genet 6:46–57
Verkerk AJ, Mathews CA, Joosse M, Eussen BH, Heutink P, Oostra BA, Tourette Syndrome Association International Consortium for Genetics (2003) CNTNAP2 is disrupted in a family with Gilles de la Tourette syndrome and obsessive compulsive disorder. Genomics 82:1–9
Belloso JM, Bache I, Guitart M, Caballin MR, Halgren C, Kirchhoff M, Ropers HH, Tommerup N, Tümer Z (2007) Disruption of the CNTNAP2 gene in a t(7;15) translocation family without symptoms of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 15:711–713
Poot M, v. ‘t Slot R, Leupert R, Beyer V, Passarge E, Haaf T (2009) Three de novo losses and one insertion within a pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 in a patient with complete absence of expressive speech and reduced pain perception. Eur J Med Genet 52:27–30
Wirth J, Nothwang HG, van der Maarel S, Menzel C, Borck G, Lopez-Pajares I, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Tommerup N, Bugge M, Ropers HH, Haaf T (1999) Systematic characterization of disease associated balanced chromosome rearrangements by FISH: cytogenetically and genetically anchored YACs identify microdeletions and candidate regions for mental retardation genes. J Med Genet 36:271–278
Yue Y, Grossmann B, Holder SE, Haaf T (2005) De novo t(7;10)(q33;q23) translocation and closely juxtaposed microdeletion in a patient with macrocephaly and developmental delay. Hum Genet 117:1–8
Vernes SC, Newbury DF, Abrahams BS, Winchester L, Nicod J, Groszer M, Alarcón M, Oliver PL, Davies KE, Geschwind DH, Monaco AP, Fisher SE (2008) A functional genetic link between distinct developmental language disorders. N Engl J Med 359:2337–2345
Alarcon M, Abrahams BS, Stone JL, Duvall JA, Perederiy JV, Bomar JM, Sebat J, Wigler M, Martin CL, Ledbetter DH, Nelson SF, Cantor RM, Geschwind DH (2008) Linkage, association, and gene-expression analyses identify CNTNAP2 as an autism-susceptibility gene. Am J Hum Genet 82:150–159
Marshall CR, Noor A, Vincent JB, Lionel AC, Feuk L, Skaug J, Shago M, Moessner R, Pinto D, Ren Y, Thiruvahindrapduram B, Fiebig A, Schreiber S, Friedman J, Ketelaars CE, Vos YJ, Ficicioglu C, Kirkpatrick S, Nicolson R, Sloman L, Summers A, Gibbons CA, Teebi A, Chitayat D, Weksberg R, Thompson A, Vardy C, Crosbie V, Luscombe S, Baatjes R, Zwaigenbaum L, Roberts W, Fernandez B, Szatmari P, Scherer SW (2008) Structural variation of chromosomes in autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet 82:477–488
Luciani P, Deledda C, Rosati F, Benvenuti S, Cellai I, Dichiara F, Morello M, Vannelli GB, Danza G, Serio M, Peri A (2008) Seladin-1 is a fundamental mediator of the neuroprotective effects of estrogen in human neuroblast long-term cell cultures. Endocrinology 149:4256–4266
Pedretti A, Bocci E, Maggi R, Vistoli G (2008) Homology modelling of human DHCR24 (seladin-1) and analysis of its binding properties through molecular docking and dynamics simulations. Steroids 73:708–719
Roux C, Wolf C, Mulliez N, Gaoua W, Cormier V, Chevy F, Citadelle D (2000) Role of cholesterol in embryonic development. Am J Clin Nutr 71:1270S–1279S
Yu H, Patel SB (2005) Recent insights into the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Clin Genet 68:383–391
Hastings PJ, Ira G, Lupski JR (2009) A microhomology-mediated break-induced replication model for the origin of human copy number variation. PLoS Genet 5(1):e1000327
Nelms BE, Maser RS, MacKay JF, Lagally MG, Petrini JH (1998) In situ visualization of DNA double-strand break repair in human fibroblasts. Science 280:590–592
Nikiforova MN, Stringer JR, Blough R, Medvedovic M, Fagin JA, Nikiforov YE (2000) Proximity of chromosomal loci that participate in radiation-induced rearrangements in human cells. Science 290:138–141
Rossi E, Verri AP, Patricelli MG, Destefani V, Ricca I, Vetro A, Ciccone R, Giorda R, Toniolo D, Maraschio P, Zuffardi O (2008) A 12 Mb deletion at 7q33-q35 associated with autism spectrum disorders and primary amenorrhea. Eur J Med Genet 51:631–638
Strauss KA, Puffenberger EG, Huentelman MJ, Gottlieb S, Dobrin SE, Parod JM, Stephan DA, Morton DH (2006) Recessive symptomatic focal epilepsy and mutant contactin-associated protein-like 2. N Engl J Med 354:1370–1377
Bakkaloglu B, O'Roak BJ, Louvi A, Gupta AR, Abelson JF, Morgan TM, Chawarska K, Klin A, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Stillman AA, Tanriover G, Abrahams BS, Duvall JA, Robbins EM, Geschwind DH, Biederer T, Gunel M, Lifton RP, State MW (2008) Molecular cytogenetic analysis and resequencing of contactin associated protein-like 2 in autism spectrum disorders. Am J Hum Genet 82:165–173
Kalscheuer VM, FitzPatrick D, Tommerup N, Bugge M, Niebuhr E, Neumann LM, Tzschach A, Shoichet SA, Menzel C, Erdogan F, Arkesteijn G, Ropers HH, Ullmann R (2007) Mutations in autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2) in patients with mental retardation. Hum Genet 121:501–509
Henrichsen CN, Vinckenbosch N, Zöllner S, Chaignat E, Pradervand S, Schütz F, Ruedi M, Kaessmann H, Reymond A (2009) Segmental copy number variation shapes tissue transcriptomes. Nat Genet 41:424–429
Cook EH Jr, Scherer SW (2008) Copy-number variations associated with neuropsychiatric conditions. Nature 455:919–923
Badano JL, Mitsuma N, Beales PL, Katsanis N (2006) The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:125–148
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the kind cooperation of patient and his parents and their giving consent to publish these data. We are also indebted to Dr. S. W. Scherer (Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada) for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Netherlands Foundation for Brain Research (grant no. 2008(1).34 to M. Poot) and the German Research Foundation (grant no. HA1374/7-2 to T. Haaf).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poot, M., Beyer, V., Schwaab, I. et al. Disruption of CNTNAP2 and additional structural genome changes in a boy with speech delay and autism spectrum disorder. Neurogenetics 11, 81–89 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0205-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0205-1