Abstract
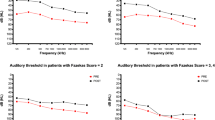
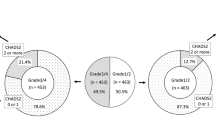
Epidemiological evidence suggests a strict correlation between sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) and cerebrovascular disorders. Leukoaraiosis represents a diffuse alteration of the periventricular and subcortical white matter. The aim of our study was to verify if the presence of white matter hyperintensity (WMH) was higher in patients affected by SSNHL compared to controls and evaluate the correlation between WMH and the cardiovascular risk factors, hearing level, and the response to therapy in SSNHL patients. The study group included 36 subjects affected by unilateral SSNHL. Thirty-six age- and sex-matched normal subjects with a negative history of SSNHL were used as controls. All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (1.5 Tesla GE Signa) and the extent of leukoaraiosis was assessed with the Fazekas scale. The results of the present study demonstrate a high prevalence of WMH in SSNHL patients compared to controls confirming the hypothesis of a vascular impairment in SSNHL patients. The higher recovery rate in patients with greater periventricular white matter hyperintensity (PWMH) may suggest a vascular etiology that is still responsive to medical treatment. We aim to expand both the number of patients and the controls to avoid the limitation of the still small number to warrant solid scientific conclusions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Georgopoulos RA, Schessel DA (2013) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. In: Kountakis SE (ed) Encyclopedia of otolaryngology, head and neck surgery. Springer, Berlin
Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Pinto M, Di Teo C, Fornarelli F, Gesualdo M et al (2012) Endothelial function and cardiovascular risk in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Atherosclerosis 225(2):511–516
Wilson WR, Veltri RW, Laird N, Sprinkle PM (1983) Viral and epidemiologic studies of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 91:653–658
Byl FM Jr (1984) Sudden hearing loss: eight years’ experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope 94(5 Pt 1):647–661
Fetterman BL, Saunders JE, Luxford WM (1996) Prognosis and treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol 17(4):529–536
Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME (1996) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 29(3):393–405
Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Arlinger S, Hultcrantz E (2007) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: results drawn from the Swedish national database. Acta Otolaryngol 127(11):1168–1175
Shaia FT, Sheehy JL (1976) Sudden sensori-neural hearing impairment: a report of 1,220 cases. Laryngoscope 86(3):389–398
Huy PT, Sauvaget E (2005) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is not an otologic emergency. Otol Neurotol 26(5):896–902
Tucci DL, Farmer JC Jr, Kitch RD, Witsell DL (2002) Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with systemic steroids and valacyclovir. Otol Neurotol 23(3):301–308
Plontke SK (2018) Diagnostics and therapy of sudden hearing loss. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:Doc05
El Sabbagh NG, Sewitch MJ, Bezdjian A, Daniel SJ (2017) Intratympanic dexamethasone in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 127(8):1897–1908
Kim JY, Hong JY, Kim DK (2018) JAMA association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with risk of cardiocerebrovascular disease: a study using data from the Korea National Health Insurance Service. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144(2):129–135. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2017.2569
Lin HC, Chao PZ, Lee HC (2008) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss increases the risk of stroke: a 5-year follow-up study. Stroke 39(10):2744–2748
Kuo CL, Shiao AS, Wang SJ, Chang WP, Lin YY (2016) Risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in stroke patients: a 5-year nationwide investigation of 44,460 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(36):e4841
Suchy Y, Eastvold A (2018) Leukoaraiosis. In: Kreutzer JS, DeLuca J, Caplan B (eds) Encyclopedia of clinical neuropsychology. Springer, Cham
Hachinski VC, Potter P, Merskey H (1986) Leuko-araiosis: an ancient term for a new problem. Can J Neurol Sci 13(4 Suppl):533–534
Hassan A, Hunt BJ, O’Sullivan M, Parmar K, Bamford JM, Briley D et al (2003) Markers of endothelial dysfunction in lacunar infarction and ischaemic leukoaraiosis. Brain 126:424–432
Murray A, Staff RT, Shenkin SD, Deary IJ, Starr JM, Whalley LJ (2005) Brain white matter hyperintensities: relative importance of vascular risk factors in nondemented elderly people. Radiology 237:251–257
Debette S, Markus HS (2010) The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 341:c3666. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c3666
Shiraishi T, Kubo T, Okumura S, Naramura H, Nishimur M, Okusa M, Matsunaga T (1993) Hearing recovery in sudden deafness patients using a modified defibrinogenation therapy. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 501:46–50
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Offenbacher H, Schmidt R, Kleinert G, Payer F (1993) Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Neurology 43(9):1683–1689
Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA (1987) MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer ‘s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:351–356
Schmidt R, Fazekas F, Kleinert G, Offenbacher H, Gindl K, Payer F et al (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging signal hyperintensities in the deep and subcortical white matter. A comparative study between stroke patients and normal volunteers. Arch Neurol 49:825–827
Koc A, Sanisoglu O (2003) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: literature survey on recent studies. J Otolaryngol 32:308–313
Quaranta N, De Ceglie V, D'Elia A (2016) Endothelial dysfunction in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a review. Audiol Res 6(1):151
Wardlaw JM, Valdés Hernández MC, Muñoz-Maniega S (2015) What are white matter hyperintensities made of? Relevance to vascular cognitive impairment. J Am Heart Assoc 4(6):001140. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.114.001140 Review
Eckert MA, Kuchinsky SE, Vaden KI, Cute SL, Spampinato MV, Dubno JR (2013) White matter hyperintensities predict low frequency hearing in older adults. JARO 14:425–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-013-0381-4
De Laat KF, Tuladhar AM, van Norden AGW, Norris DG, Zwiers MP, de Leeuw F-E (2011) Loss of white matter integrity is associated with gait disorders in cerebral small vessel disease. Brain 134:73–83
Baezner H, Blahak C, Poggesi A, Pantoni L, Inzitari D, Chabriat H, Erkinjuntti T, Fazekas F, Ferro JM, Langhorne P, O'Brien J, Scheltens P, Visser MC, Wahlund LO, Waldemar G, Wallin A, Hennerici MG, On behalf of the LADIS Study Group (2008) Association of gait and balance disorders with age-related white matter changes: the LADIS study. Neurology 70:935–942
Cerchiai N, Mancuso M, Navari E, Giannini N, Casani AP (2017) Aging with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Dizziness: The importance of undiagnosed peripheral vestibular disorders. Front Neurol 8:241
Gouw AA, Seewann A, Van Der Flier WM, Barkhof F, Rozemuller AM, Scheltens P, Geurts JJ (2011) Heterogeneity of small vessel disease: a systematic review of MRI and histopathology correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82(2):126–135
Uchida Y, Sugiura S, Nakashima T, Ando F, Shimokata H (2017) Contribution of 1425G/A polymorphism in protein kinase C-Eta (PRKCH) gene and brain white matter lesions to the risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in a Japanese nested case-control study. J Neurogenet 25(3):82–87
Fazekas F (2014) Incidental periventricular white matter hyperintensities revisited: what detailed morphological image analyses can tell us. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35(1):63–64
Pascucci M, Loacono C, Tortorelli D’Ambrosio MG et al (2010) La leucoaraiosi cerebrale (classificazione, eziologia, correlati funzionali ed istopatologici). Geriatria XXI(13–18) XXII n. 1 Jan/Feb 2010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dicuonzo, F., Purciariello, S., De Marco, A. et al. MR evaluation of encephalic leukoaraiosis in sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) patients. Neurol Sci 40, 357–362 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3647-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3647-0