Abstract
Objective
To investigate the pattern and severity of hippocampal subfield volume loss in patients with left and right mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (mTLE) using quantitative MRI volumetric analysis.
Methods
A total of 21 left and 14 right mTLE subjects, as well as 15 healthy controls, were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. A publically available magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain volumetry system (volBrain) was used for volumetric analysis of hippocampal subfields. The T1-weighted images were processed with a HIPS pipeline.
Results
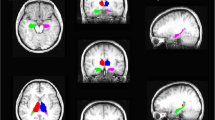
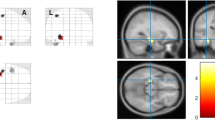
A distinct pattern of hippocampal subfield atrophy was found between left and right mTLE patients when compared with controls. Patients with left mTLE exhibited ipsilateral hippocampal atrophy and segmental volume depletion of the Cornu Ammonis (CA) 2/CA3, CA4/dentate gyrus (DG), and strata radiatum-lacunosum-moleculare (SR-SL-SM). Those with right mTLE exhibited similar ipsilateral hippocampal atrophy but with additional segmental CA1 volume depletion. More extensive bilateral subfield volume loss was apparent with right mTLE patients.
Conclusion
We demonstrate that left and right mTLE patients show a dissimilar pattern of hippocampal subfield atrophy, suggesting the pathophysiology of epileptogenesis in left and right mTLE to be different.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Boling WW (2018) Surgical considerations of intractable mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Sci 8(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8020035
Thom M (2014) Review: hippocampal sclerosis in epilepsy: a neuropathology review. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 40(5):520–543. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12150
Kemmotsu N, Girard HM, Bernhardt BC, Bonilha L, Lin JJ, Tecoma ES, Iragui VJ, Hagler DJ Jr, Halgren E, McDonald CR (2011) MRI analysis in temporal lobe epilepsy: cortical thinning and white matter disruptions are related to side of seizure onset. Epilepsia 52(12):2257–2266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03278.x
Garcia-Finana M, Denby CE, Keller SS, Wieshmann UC, Roberts N (2006) Degree of hippocampal atrophy is related to side of seizure onset in temporal lobe epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(5):1046–1052
Pail M, Brazdil M, Marecek R, Mikl M (2010) An optimized voxel-based morphometric study of gray matter changes in patients with left-sided and right-sided mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE/HS). Epilepsia 51(4):511–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02324.x
Whelan CD, Altmann A, Botía JA, Jahanshad N, Hibar DP, Absil J, Alhusaini S, Alvim MKM, Auvinen P, Bartolini E, Bergo FPG, Bernardes T, Blackmon K, Braga B, Caligiuri ME, Calvo A, Carr SJ, Chen J, Chen S, Cherubini A, David P, Domin M, Foley S, França W, Haaker G, Isaev D, Keller SS, Kotikalapudi R, Kowalczyk MA, Kuzniecky R, Langner S, Lenge M, Leyden KM, Liu M, Loi RQ, Martin P, Mascalchi M, Morita ME, Pariente JC, Rodríguez-Cruces R, Rummel C, Saavalainen T, Semmelroch MK, Severino M, Thomas RH, Tondelli M, Tortora D, Vaudano AE, Vivash L, von Podewils F, Wagner J, Weber B, Yao Y, Yasuda CL, Zhang G, Bargalló N, Bender B, Bernasconi N, Bernasconi A, Bernhardt BC, Blümcke I, Carlson C, Cavalleri GL, Cendes F, Concha L, Delanty N, Depondt C, Devinsky O, Doherty CP, Focke NK, Gambardella A, Guerrini R, Hamandi K, Jackson GD, Kälviäinen R, Kochunov P, Kwan P, Labate A, McDonald CR, Meletti S, O’Brien TJ, Ourselin S, Richardson MP, Striano P, Thesen T, Wiest R, Zhang J, Vezzani A, Ryten M, Thompson PM, Sisodiya SM (2018) Structural brain abnormalities in the common epilepsies assessed in a worldwide ENIGMA study. Brain 141(2):391–408. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx341
Hunsaker MR, Lee B, Kesner RP (2008) Evaluating the temporal context of episodic memory: the role of CA3 and CA1. Behav Brain Res 188(2):310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.11.015
Yassa MA, Stark CE (2011) Pattern separation in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 34(10):515–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2011.06.006
Rossler M, Zarski R, Bohl J, Ohm TG (2002) Stage-dependent and sector-specific neuronal loss in hippocampus during Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 103(4):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-001-0475-7
Schonheit B, Zarski R, Ohm TG (2004) Spatial and temporal relationships between plaques and tangles in Alzheimer-pathology. Neurobiol Aging 25(6):697–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.09.009
Mueller SG, Laxer KD, Scanlon C, Garcia P, McMullen WJ, Loring DW, Meador KJ, Weiner MW (2012) Different structural correlates for verbal memory impairment in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal lobe sclerosis. Hum Brain Mapp 33(2):489–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21226
Comper SM, Jardim AP, Corso JT, Gaca LB, Noffs MHS, Lancellotti CLP, Cavalheiro EA, Centeno RS, Yacubian EMT (2017) Impact of hippocampal subfield histopathology in episodic memory impairment in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsy Behav 75:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.08.013
Winterburn J, Pruessner JC, Sofia C, Schira MM, Lobaugh NJ, Voineskos AN, Chakravarty MM (2015) High-resolution in vivo manual segmentation protocol for human hippocampal subfields using 3T magnetic resonance imaging. J Vis Exp 105:e51861. https://doi.org/10.3791/51861
Kreilkamp BAK, Weber B, Elkommos SB, Richardson MP, Keller SS (2018) Hippocampal subfield segmentation in temporal lobe epilepsy: relation to outcomes. Acta Neurol Scand 137(6):598–608. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12926
Kim JB, Suh SI, Kim JH (2015) Volumetric and shape analysis of hippocampal subfields in unilateral mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal atrophy. Epilepsy Res 117:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2015.09.004
Manjon JV, Coupe P (2016) volBrain: an online MRI brain volumetry system. Front Neuroinform 10:30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2016.00030
Næss-Schmidt E, Tietze A, Blicher JU, Petersen M, Mikkelsen IK, Coupé P, Manjón JV, Eskildsen SF (2016) Automatic thalamus and hippocampus segmentation from MP2RAGE: comparison of publicly available methods and implications for DTI quantification. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(11):1979–1991
Kwan P, Arzimanoglou A, Berg AT, Brodie MJ, Allen Hauser W, Mathern G, Moshe SL, Perucca E, Wiebe S, French J (2010) Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 51(6):1069–1077. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02397.x
Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Elisevich KV, Schwalb JM, Bagher-Ebadian H, Mahmoudi F, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2014) Lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy by multimodal multinomial hippocampal response-driven models. J Neurol Sci 347(1):107–118
Hosseini M-P, Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Pompili D, Jafari-Khouzani K, Elisevich K, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2016) Comparative performance evaluation of automated segmentation methods of hippocampus from magnetic resonance images of temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Med Phys 43(1):538–538. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4938411
Nazem-Zadeh M-R, Schwalb JM, Elisevich KV, Bagher-Ebadian H, Hamidian H, Akhondi-Asl A-R, Jafari-Khouzani K, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2014) Lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy using a novel uncertainty analysis of MR diffusion in hippocampus, cingulum, and fornix, and hippocampal volume and FLAIR intensity. J Neurol Sci 342(1):152–161
Nazem-Zadeh MR, Chapman CH, Lawrence TS, Tsien CI, Cao Y (2013) Uncertainty in assessment of radiation-induced diffusion index changes in individual patients. Phys Med Biol 58:1–20
Avants BB, Tustison NJ, Song G, Cook PA, Klein A, Gee JC (2011) A reproducible evaluation of ANTs similarity metric performance in brain image registration. NeuroImage 54(3):2033–2044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.025
Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, Gee JC (2010) N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(6):1310–1320. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2010.2046908
Nyul LG, Udupa JK (1999) On standardizing the MR image intensity scale. Magn Reson Med 42(6):1072–1081
Romero JE, Coupe P, Manjón JV High resolution hippocampus subfield segmentation using multispectral multiatlas patch-based label fusion. In: Wu G, Coupé P, Zhan Y, Munsell BC, Rueckert D (eds) Patch-based techniques in medical imaging, Cham, 2016// 2016. Springer International Publishing, pp 117–124
Romero JE, Coupé P, Manjón JV (2017) HIPS: a new hippocampus subfield segmentation method. NeuroImage 163:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.049
Winterburn JL, Pruessner JC, Chavez S, Schira MM, Lobaugh NJ, Voineskos AN, Chakravarty MM (2013) A novel in vivo atlas of human hippocampal subfields using high-resolution 3 T magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 74:254–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.02.003
Yushkevich PA, Amaral RS, Augustinack JC, Bender AR, Bernstein JD, Boccardi M, Bocchetta M, Burggren AC, Carr VA, Chakravarty MM, Chetelat G, Daugherty AM, Davachi L, Ding SL, Ekstrom A, Geerlings MI, Hassan A, Huang Y, Iglesias JE, La Joie R, Kerchner GA, LaRocque KF, Libby LA, Malykhin N, Mueller SG, Olsen RK, Palombo DJ, Parekh MB, Pluta JB, Preston AR, Pruessner JC, Ranganath C, Raz N, Schlichting ML, Schoemaker D, Singh S, Stark CE, Suthana N, Tompary A, Turowski MM, Van Leemput K, Wagner AD, Wang L, Winterburn JL, Wisse LE, Yassa MA, Zeineh MM (2015) Quantitative comparison of 21 protocols for labeling hippocampal subfields and parahippocampal subregions in in vivo MRI: towards a harmonized segmentation protocol. NeuroImage 111:526–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.01.004
Coupe P, Manjon JV, Chamberland M, Descoteaux M, Hiba B (2013) Collaborative patch-based superresolution for diffusion-weighted images. NeuroImage 83:245–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.06.030
Steve TA, Jirsch JD, Gross DW (2014) Quantification of subfield pathology in hippocampal sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res 108(8):1279–1285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.07.003
Ahmadi ME, Hagler DJ Jr, McDonald CR, Tecoma ES, Iragui VJ, Dale AM, Halgren E (2009) Side matters: diffusion tensor imaging tractography in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(9):1740–1747. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1650
Keller SS, Schoene-Bake JC, Gerdes JS, Weber B, Deppe M (2012) Concomitant fractional anisotropy and volumetric abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy: cross-sectional evidence for progressive neurologic injury. PLoS One 7(10):e46791. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046791
Sanjari Moghaddam H, Rahmani F, Aarabi MH, Nazem-Zadeh MR, Davoodi-Bojd E, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2019) White matter microstructural differences between right and left mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neurol Belg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-019-01074-x
Coan AC, Appenzeller S, Bonilha L, Li LM, Cendes F (2009) Seizure frequency and lateralization affect progression of atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 73(11):834–842. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181b783dd
Liu M, Bernhardt BC, Bernasconi A, Bernasconi N (2016) Gray matter structural compromise is equally distributed in left and right temporal lobe epilepsy. Hum Brain Mapp 37(2):515–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23046
Ji J, Maren S Differential roles for hippocampal areas CA1 and CA3 in the contextual encoding and retrieval of extinguished fear. Learn Mem 15(4):244–251. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.794808
Bartsch T, Döhring J, Rohr A, Jansen O, Deuschl G (2011) CA1 neurons in the human hippocampus are critical for autobiographical memory, mental time travel, and autonoetic consciousness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(42):17562–17567. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1110266108
Barrientos SA, Tiznado V (2016) Hippocampal CA1 subregion as a context decoder. 36 (25):6602-6604. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1107-16.2016 The Journal of Neuroscience
Abdel Razek AAK, Talaat M, El-Serougy L, Gaballa G, Abdelsalam M (2019) Clinical applications of arterial spin labeling in brain tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr 43(4):525–532. https://doi.org/10.1097/rct.0000000000000873
Razek A, Taman SE, El Regal ME, Megahed A, Elzeny S, El Tantawi N (2020) Diffusion tensor imaging of microstructural changes in the gray and white matter in patients with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I. J Comput Assist Tomogr 44(3):393–398. https://doi.org/10.1097/rct.0000000000001008
Oner AY, Eryurt B, Ucar M, Capraz I, Kurt G, Bilir E, Tali T (2015) pASL versus DSC perfusion MRI in lateralizing temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden : 1987) 56(4):477–481. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185114531128
Nazem-Zadeh MR, Bowyer SM, Moran JE, Davoodi-Bojd E, Zillgitt A, Weiland BJ, Bagher-Ebadian H, Mahmoudi F, Elisevich KV, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2016) MEG coherence and DTI connectivity in mTLE. Brain Topogr 29(4):598–622
Acknowledgments
The authors recognize and are grateful for the contributions of the Iranian National Brain Mapping Laboratory (NBML), Tehran, Iran, for their data acquisition service.
Funding
This work was partially funded and supported by Iran’s National Elites Foundation, National Institute for Medical Research Development, and Cognitive Sciences & Technologies Council, in 2017 to 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical University.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghaddam, H.S., Aarabi, M.H., Mehvari-Habibabadi, J. et al. Distinct patterns of hippocampal subfield volume loss in left and right mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurol Sci 42, 1411–1421 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04653-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04653-6