Abstract
Purpose
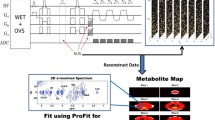
Today’s available chemical shift imaging (CSI) analysis tools are based on Fourier transform of the entire data set prior to interactive display. This strategy is associated with limitations particularly when arbitrary voxel positions within a 3D spatial volume are needed by the user. In this work, we propose and demonstrate a processing-resource-efficient alternative strategy for both interactive and automated CSI data processing up to three spatial dimensions.
Methods
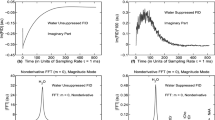
This approach uses real-time voxel-shift by first-order phase manipulation as a basis and therefore allows grid-free voxel positioning within the 3D volume. The corresponding spectrum is extracted from the 4D data (3D spatial/1D spectral) at each time a voxel position is selected. The spatial response function and hence the exact voxel size and shape are calculated in parallel including the same processing parameters. Using this mechanism sequentially along with AMARES time-domain modeling, we also implemented automated quantitative and B 0-insensitive metabolite mapping.
Results
Metabolite maps of N-acetyl aspartate, choline and creatine were generated using 1H-CSI data from the brain of healthy volunteers and patients with tumor and epilepsy. 31P-3D-CSI of the heart of a healthy volunteer is also shown.
Conclusion
The calculated metabolite maps demonstrate good stability and accuracy of the algorithm in all situations tested. The suggested algorithm constitutes therefore an attractive alternative to existing CSI processing strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiru F, Burian M, Hajek M, Bjelke B (2002) LCModel for spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Mater Phy 1(15 Suppl): 368
Ebel A, Maudsley AA (2003) Improved spectral quality for 3D MR spectroscopic imaging using a high spatial resolution acquisition strategy. Magn Reson Imaging 21(2): 113–120
Soher BJ, Young K, Govindaraju V, Maudsley AA (1998) Automated spectral analysis III: application to in vivo proton MR spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 40(6): 822–831
Maudsley AA, Darkazanli A, Alger JR, Hall LO, Schuff N, Studholme C, Yu Y, Ebel A, Frew A, Goldgof D, Gu Y, Pagare R, Rousseau F, Sivasankaran K, Soher BJ, Weber P, Young K, Zhu X (2006) Comprehensive processing, display and analysis for in vivo MR spectroscopic imaging. NMR Biomed 19(4): 492–503
Otazo R, Tsai SY, Lin FH, Posse S (2007) Accelerated short-TE 3D proton echo-planar spectroscopic imaging using 2D-SENSE with a 32-channel array coil. Magn Reson Med 58(6): 1107–1116
Stefan D, Di Cesare F, Andrasescu A, Popa E, Lazariev A, Vescovo E, Strback O, Williams S, Starcuk Z, Cabanas M, Van Ordmondr D, Graveron-Demilly D (2009) Quantitation of magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals: the jMRUI software package. Meas Sci Technol 20(10). doi:10.1088/0957-0233/20/10/104035
Vigneron DB, Nelson SJ, Murphy-Boesch J, Kelley DA, Kessler HB, Brown TR, Taylor JS (1990) Chemical shift imaging of human brain: axial, sagittal, and coronal P-31 metabolite images. Radiology 177(3): 643–649
Nelson SJ (2001) Analysis of volume MRI and MR spectroscopic imaging data for the evaluation of patients with brain tumors. Magn Reson Med 46(2): 228–239
Nicoli F, Le Fur Y, Denis B, Ranjeva JP, Confort-Gouny S, Cozzone PJ (2003) Metabolic counterpart of decreased apparent diffusion coefficient during hyperacute ischemic stroke: a brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study. Stroke 34(7): e82–e87
Galanaud D, Le Fur Y, Nicoli F, Denis B, Confort-Gouny S, Ranjeva JP, Viout P, Pelletier J, Cozzone PJ (2001) Regional metabolite levels of the normal posterior fossa studied by proton chemical shift imaging. Magn Reson Mater Phy 13(2): 127–133
Guye M, Le Fur Y, Confort-Gouny S, Ranjeva JP, Bartolomei F, Regis J, Raybaud CA, Chauvel P, Cozzone PJ (2002) Metabolic and electrophysiological alterations in subtypes of temporal lobe epilepsy: a combined proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging and depth electrodes study. Epilepsia 43(10): 1197–1209
Caus T, Kober F, Marin P, Mouly-Bandini A, Quilici J, Metras D, Cozzone PJ, Bernard M (2006) Non-invasive diagnostic of cardiac allograft vasculopathy by 31P magnetic resonance chemical shift imaging. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 29(1): 45–49
Hofmann L, Slotboom J, Jung B, Maloca P, Boesch C, Kreis R (2002) Quantitative 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain: influence of composition and parameterization of the basis set in linear combination model-fitting. Magn Reson Med 48(3): 440–453
McLean MA, Woermann FG, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2000) Quantitative analysis of short echo time (1)H-MRSI of cerebral gray and white matter. Magn Reson Med 44(3): 401–411
Kuzniecky R, Palmer C, Hugg J, Martin R, Sawrie S, Morawetz R, Faught E, Knowlton R (2001) Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy: neuronal dysfunction or cell loss. Arch Neurol 58(12): 2048–2053
Guye M, Ranjeva JP, Le Fur Y, Bartolomei F, Confort-Gouny S, Regis J, Chauvel P, Cozzone PJ (2005) 1H-MRS imaging in intractable frontal lobe epilepsies characterized by depth electrode recording. Neuroimage 26(4): 1174–1183
Mason GF, Pan JW, Ponder SL, Twieg DB, Pohost GM, Hetherington HP (1994) Detection of brain glutamate and glutamine in spectroscopic images at 4.1 T. Magn Reson Med 32(1): 142–145
Dreher W, Kuhn B, Gyngell ML, Busch E, Niendorf T, Hossmann KA, Leibfritz D (1998) Temporal and regional changes during focal ischemia in rat brain studied by proton spectroscopic imaging and quantitative diffusion NMR imaging. Magn Reson Med 39(6): 878–888
Maudsley AA, Lin E, Weiner MW (1992) Spectroscopic imaging display and analysis. Magn Reson Imaging 10(3): 471–485
Kienlin M, Rösch C, Le Fur Y, Behr W, Roder F, Haase A, Horn M, Illing B, Hu K, Ertl G, Neubauer S (1998) Three-dimensional 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of regional high-energy phosphate metabolism in injured rat heart. Magn reson Med 39: 731–741
Li BS, Babb JS, Soher BJ, Maudsley AA, Gonen O (2002) Reproducibility of 3D proton spectroscopy in the human brain. Magn Reson Med 47(3): 439–446
Maudsley AA, Hilal SK (1985) Field inhomogeneity correction and data processing for spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 2(3): 218–233
Maudsley AA, Wu Z, Meyerhoff DJ, Weiner MW (1994) Automated processing for proton spectroscopic imaging using water reference deconvolution. Magn Reson Med 31(6): 589–595
Klose U (1990) In vivo proton spectroscopy in presence of eddy currents. Magn Reson Med 14(1): 26–30
Spielman D, Webb P, Macovski A (1989) Water referencing for spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 12(1): 38–49
Ebel A, Maudsley AA (2005) Detection and correction of frequency instabilities for volumetric 1H echo-planar spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(2): 465–469
Bhattacharyya PK, Lowe MJ, Phillips MD (2007) Spectral quality control in motion-corrupted single-voxel J-difference editing scans: an interleaved navigator approach. Magn Reson Med 58(4): 808–812
van Der Veen JW, Weinberger DR, Tedeschi G, Frank JA, Duyn JH (2000) Proton MR spectroscopic imaging without water suppression. Radiology 217(1): 296–300
Brown TR, Stoyanova R (1996) NMR spectral quantitation by principal-component analysis. II. Determination of frequency and phase shifts. J Magn Reson B 112(1): 32–43
Soher BJ, van Zijl PC, Duyn JH, Barker PB (1996) Quantitative proton MR spectroscopic imaging of the human brain. Magn Reson Med 35(3): 356–363
Ratiney H, Sdika M, Coenradie Y, Cavassila S, van Ormondt D, Graveron-Demilly D (2005) Time-domain semi-parametric estimation based on a metabolite basis set. NMR Biomed 18(1): 1–13
Kreis R, Slotboom J, Hofmann L, Boesch C (2005) Integrated data acquisition and processing to determine metabolite contents, relaxation times, and macromolecule baseline in single examinations of individual subjects. Magn Reson Med 54(4): 761–768
Cavassila S, Deval S, Huegen C, van Ormondt D, Graveron-Demilly D (2001) Cramer-Rao bounds: an evaluation tool for quantitation. NMR Biomed 14(4): 278–283
Jiru F, Skoch A, Klose U, Grodd W, Hajek M (2006) Error images for spectroscopic imaging by LC model using Cramer-Rao bounds. Magn Reson Mater Phy 19(1): 1–14
Pijnappel W, Van den Boogaart A, De Beer R, Van Ormondt D (1992) SVD-based quantification of magnetic resonance signals. J Magn Reson 97: 97–122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Grant Support: This work was sponsored by Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS UMR No 6612), Université de la Méditerranée and Institut Universitaire de France.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10334-010-0210-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Fur, Y., Nicoli, F., Guye, M. et al. Grid-free interactive and automated data processing for MR chemical shift imaging data. Magn Reson Mater Phy 23, 23–30 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-009-0186-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-009-0186-y