Abstract
Object
To present an algorithm for optimization of background suppression pulse timing for arterial spin labeling (ASL) perfusion imaging.
Materials and methods
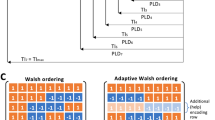
An algorithm for optimization of background suppression pulse timing is proposed. Numerical optimization of timing of the background suppression pulses is investigated in both constrained and unconstrained ASL sequences. The performance of the parameters from the algorithm is evaluated in phantom and also in vivo in five human subjects.
Results
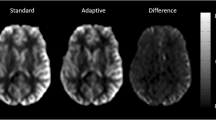
The background signal is suppressed to less than 1% across a broad range of T1s with a modest number of inversion pulses using the timings acquired from the numerical optimization algorithm proposed in this study. The performance of the parameters from the algorithm is also confirmed in vivo.
Conclusion
Successful background suppression over a broad range of tissues is achievable. Values for optimal pulse timing in both pulsed and continuous ASL studies are reported to facilitate sequence design with different labeling parameters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsop D, Detre J (1999) Background suppressed 3D RARE ASL perfusion imaging. In: International society for magnetic resonance in medicine 7th scientific meeting, Philadelphia, p 601
Ye FQ, Frank JA, Weinberger DR, McLaughlin AC (2000) Noise reduction in 3D perfusion imaging by attenuating the static signal in arterial spin tagging (ASSIST). Magn Reson Med 44(1):92–100
Dixon WT, Sardashti M, Castillo M, Stomp GP (1991) Multiple inversion recovery reduces static tissue signal in angiograms. Magn Reson Med 18(2):257–268
Mani S, Pauly J, Conolly S, Meyer C, Nishimura D (1997) Background suppression with multiple inversion recovery nulling: applications to projective angiography. Magn Reson Med 37(6):898–905
Dai W, Robson PM, Shankaranarayanan A, Alsop DC (2011) Reduced resolution transit delay prescan for quantitative continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med (in press)
Shor NZ (1985) Minimization methods for non-differentiable functions. Springer, New York
Garcia DM, Duhamel G, Alsop DC (2005) Efficiency of inversion pulses for background suppressed arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 54(2):366–372
de Bazelaire CM, Duhamel GD, Rofsky NM, Alsop DC (2004) MR imaging relaxation times of abdominal and pelvic tissues measured in vivo at 3.0 T: preliminary results. Radiology 230(3):652–659
Dai W, Garcia D, de Bazelaire C, Alsop DC (2008) Continuous flow-driven inversion for arterial spin labeling using pulsed radio frequency and gradient fields. Magn Reson Med 60(6):1488–1497
Garcia DM, de Bazelaire C, Alsop DC (2005) Pseudo-continuous flow driven adiabatic inversion for arterial spin labeling. in: international society for magnetic resonance in medicine 13th scientific meeting, Miami, Florida, USA, p 9
Kunz D (1987) Frequency-modulated radiofrequency pulses in spin-echo and stimulated-echo experiments. Magn Reson Med 4(2):129–136
Ordidge RJ, Wylezinska M, Hugg JW, Butterworth E, Franconi F (1996) Frequency offset corrected inversion (FOCI) pulses for use in localized spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 36(4):562–566
O’Dell LA, Harris KJ, Schurko RW (2010) Optimized excitation pulses for the acquisition of static NMR powder patterns from half-integer quadrupolar nuclei. J Magn Reson 203(1):156–166
Bydder M, Larkman DJ, Hajnal JV (2002) Combination of signals from array coils using image-based estimation of coil sensitivity profiles. Magn Reson Med 47(3):539–548
Maleki N, Dai W, Alsop DC (2011) Blood flow quantification of the human retina with MRI. NMR Biomed 24(1):104–111
Duhamel G, Alsop D (2004) Single-shot susceptibility insensitive whole brain 3D perfusion imaging with ASL. In: International society for magnetic resonance in medicine 12th scientific meeting, Kyoto, Japan, p 518
Fernandez-Seara MA, Wang Z, Wang J, Rao HY, Guenther M, Feinberg DA, Detre JA (2005) Continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion measurements using single shot 3D GRASE at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 54(5):1241–1247
Gunther M, Oshio K, Feinberg DA (2005) Single-shot 3D imaging techniques improve arterial spin labeling perfusion measurements. Magn Reson Med 54(2):491–498
St Lawrence KS, Frank JA, Bandettini PA, Ye FQ (2005) Noise reduction in multi-slice arterial spin tagging imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(3):735–738
Blamire AM, Styles P (2000) Spin echo entrapped perfusion image (SEEPAGE). A nonsubtraction method for direct imaging of perfusion. Magn Reson Med 43(5):701–704
Duyn JH, Tan CX, van Gelderen P, Yongbi MN (2001) High-sensitivity single-shot perfusion-weighted fMRI. Magn Reson Med 46(1):88–94
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health through grant MH80729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maleki, N., Dai, W. & Alsop, D.C. Optimization of background suppression for arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Mater Phy 25, 127–133 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0286-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0286-3