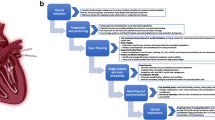
Abstract
The correlation of hemodynamic events with clinical or pathological observations is represented by a variety of applications reflecting the broad range of this theme. The position paper describes several cases in which benefits of combining imaging information with transport models of contrast material, can cause a gain in hemodynamic information. What appears to be lack of cohesiveness among the cases illustrates the variety in the application of hemodynamic research to the practice of medicine. Some of the contributions presented at the symposium do not directly apply to clinical medicine, but instead described mathematical models or applications to animal physiology or technical advancements in measuring blood rheology. Although related to this theme topic they fall somewhat outside the main scope. The topics summarized below demonstrate four examples in which translation of the research to the clinical arena can be realized in a short period of time. Overall recommendations for priority objectives related to this topic are provided at the end of this position paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Back, L. H., and D. W. Crawford. Wall shear stress estimates in coronary artery constrictions. J. Biomech. Eng. 114:515–520, 1992.
Back, L. H., J. R. Radbill, and Y. I. Cho. Measurement and prediction of flow through a replica segment of a mildly atherosclerotic coronary artery of man. J. Biomech. 19:1–17, 1986.
Banerjee, R., L. H. Back, M. R. Back, and Y. I. Cho. Physiological flow analysis in significant human coronary artery stenoses. Biorheology 40:451–476, 2003.
Bleasdale, R. A., K. H. Parker, and C. J. H. Jones. Chasing the wave. Unfashionable but important new concepts in arterial wave travel. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284:H1879–1885, 2003.
Chandran, K. B., M. J. Vonesh, A. Roy, S. Greenfield, B. Kane, R. Greene, and D. D. McPherson. Computation of vascular flow dynamics from intravascular ultrasound images. Med. Eng. Phys. 18:295–304, 1996.
Di Mario, C., R. Gil, P. J. de Feyter, J. C. H. Schuurbiers, and P. W. Serruys. Utilization of translesional hemodynamics: Comparison of pressure and flow methods in stenosis assessment in patients with coronary artery disease. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 38:189–201, 1996.
Doucette, J. W., P. D. Corl, H. M. Payne, A. E. Flynn, M. Goto, Nassi, M, and J. Segal. Validation of a Doppler guide wire for intravascular measurement of coronary artery flow velocity. Circulation 85:1899–1911, 1992.
Emanuelsson, H., M. Dohnal, C. Lamm, and L. Tenerz. Initial experiences with a miniaturized pressure transducer during coronary angioplasty. Cathet. Cardiovasc. Diagn. 24:137–143, 1991.
Gould, K. L. Pressure-flow characteristics of coronary stenoses in unsedated dogs at rest and during coronary vasodilation. Circ. Res. 43:242–253, 1978.
Gould, K. L. Quantification of coronary artery stenosis in vivo. Circ. Res. 57:341–353, 1985.
Gould, K. L., R. L. Kirkeeide, and M. Buchi. Coronary flow reserve as a physiologic measure of stenosis severity. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 15:459–474, 1990.
Hoffman, J. I. E. Problems of coronary flow reserve. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 28:884–896, 2000.
Holdsworth, D. W., M. Drangova, and A. Fenster. Quantitative angiographic blood-flow measurement using pulsed intra-arterial injection. Med. Phys. 26(10):2168–2175, 1999.
Hong, H., S. Aksenov, X. Guan, J. T. Fallon, D. Waters, and C. Chen. Remodeling of small intramyocardial coronary arteries distal to a severe epicardial coronary artery stenosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22:2059–2065, 2002.
Kern, M. J. Coronary physiology revisited: Practical insights from the cardiac catheterization laboratory. Circulation 101:1344–1351, 2000.
Komaru, T., H. Kanatsuka, and K. Shirato. Coronary microcirculation: Physiology and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Ther. 86:217–261, 2000.
Krams, R., J. J. Wentzel, J. A. Oomen, R. Vinke, J. C. Schuurbiers, P. J. de Feyter, P. W. Serruys, and C. J. Slager. Evaluation of endothelial shear stress and 3d geometry as factors determining the development of atherosclerosis and remodeling in human coronary arteries in vivo. Combining 3d reconstruction from angiography and ivus (angus) with computational fluid dynamics. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 17:2061–2065, 1997.
Ku, D. N. Blood flow in arteries. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 29:399–434, 1997.
Lieber, B. B., C. Sadasivan, M. J. Gounis, J. Seong, L. Miskolczi, and A. K. Wakhloo. Functional Angiography. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 33:1–102, 2005.
Marques, K. M. J., H. J. Spruijt, C. Boer, N. Westerhof, C. A. Visser, and F. C. Visser. The diastolic flow-pressure gradient relation in coronary stenoses in humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 39:1630–1636, 2002.
Marzilli, M., G. Sambuceti, R. Testa, and S. Fedele. Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blockade and coronary resistance in unstable angina. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 40:2102–2109, 2002.
Mates, R. E., R. L. Gupta, A. C. Bell, and F. J. Klocke. Fluid dynamics of coronary artery stenosis. Circ Res 42:152–162, 1978.
Meuwissen, M., M. Siebes, J. A. E. Spaan, and J. J. Piek. Rationale of combined intracoronary pressure and flow velocity measurements. Z. Kardiol. 91(Suppl 3):108–112, 2002.
Meuwissen, M., M. Siebes, S. A. Chamuleau, J. G. Tijssen, J. A. E. Spaan, and J. J. Piek. Intracoronary pressure and flow velocity for hemodynamic evaluation of coronary stenoses. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 1:471–479, 2003.
Meuwissen, M., M. Siebes, S. A. J. Chamuleau, B. L. F. van Eck-Smit, K. T. Koch, R. J. de Winter, J. G. P. Tijssen, J. A. E. Spaan, and J. J. Piek. Hyperemic stenosis resistance index for evaluation of functional coronary lesion severity. Circulation 106:441–446, 2002.
Meuwissen, M., S. A. J. Chamuleau, M. Siebes, C. E. Schotborgh, K. T. Koch, R. J. de Winter, M. Bax, A. de Jong, J. A. E. Spaan, and J. J. Piek. Role of variability in microvascular resistance on fractional flow reserve and coronary blood flow velocity reserve in intermediate coronary lesions. Circulation 103:184–187, 2001.
Pijls, N. H. J., J. A. van Son, R. L. Kirkeeide, B. De Bruyne, and K. L. Gould. Experimental basis of determining maximum coronary, myocardial, and collateral blood flow by pressure measurements for assessing functional stenosis severity before and after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 87:1354–1367, 1993.
Reichle, F. A., M. Sovak, R. L. Soulen, and G. P. Rosemond. Portal vein blood flow determination in the unanesthetized human by umbilicoportal cannulation. J. Surg. Res. 12(3):146–50, 1972.
Sadasivan, C., B. B. Lieber, M. J. Gounis, D. K. Lopes, and L. N. Hopkins. Angiographic quantification of contrast medium washout from cerebral aneurysms after stent placement. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 23(7):1214–1221, 2002.
Serruys, P. W., C. Di Mario, N. Meneveau, P. de Jaegere, S. Strikwerda, P. J. de Feyter, and H. Emanuelsson. Intracoronary pressure and flow velocity with sensor-tip guidewires: A new methodologic approach for assessment of coronary hemodynamics before and after coronary interventions. Am. J. Cardiol. 71:41D–53D, 1993.
Siebes, M., B.-J. Verhoeff, M. Meuwissen, R. J. de Winter, J. A. E. Spaan, and J. J. Piek. Single-wire pressure and flow velocity measurement to quantify coronary stenosis hemodynamics and effects of percutaneous interventions. Circulation 109:756–762, 2004.
Siebes, M., S. A. J. Chamuleau, M. Meuwissen, J. J. Piek and J. A. E. Spaan. Influence of hemodynamic conditions on fractional flow reserve: Parametric analysis of underlying model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 283:H1462–H1470, 2002.
Slager, C. J., J. J. Wentzel, J. C. Schuurbiers, J. A. Oomen, J. Kloet, R. Krams, C. von Birgelen, W. J. van der Giessen, P. W. Serruys and P. J. de Feyter. True 3-dimensional reconstruction of coronary arteries in patients by fusion of angiography and ivus (angus) and its quantitative validation. Circulation 102:511–516, 2000.
Stone, P. H., A. U. Coskun, S. Kinlay, M. E. Clark, M. Sonka, A. Wahle, O. J. Ilegbusi, Y. Yeghiazarians, J. J. Popma, J. Orav, R. E. Kuntz, and C. L. Feldman. Effect of endothelial shear stress on the progression of coronary artery disease, vascular remodeling, and in-stent restenosis in humans: In vivo 6-month follow-up study. Circulation 108:438–444, 2003.
Sun, Y.-H., T. J. Anderson, K. H. Parker, and J. V. Tyberg. Wave-intensity analysis: A new approach to coronary hemodynamics. J. Appl. Physiol. 89:1636–1644, 2000.
Taylor, G. I. Dispersion of soluble matter in solvent flowing slowly through a tube. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 219(1137):186–203, 1953.
Taylor, G. I. The dispersion of matter in turbulent flow through a pipe. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 223(1155):446–68, 1954.
Topol, E. J., and S. E. Nissen. Our preoccupation with coronary luminology: The dissociation between clinical and angiographic findings in ischemic heart disease. Circulation 92:2333–2342, 1995.
Wahle, A., G. P. M. Prause, S. C. DeJong, and M. Sonka. Geometrically correct 3-d reconstruction of intravascular ultrasound images by fusion with biplane angiography-methods and validation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 18:686–699, 1999.
Wakhloo, A. K., B. B. Lieber, S. Rudin, M. D. Fronckowiak, R. A. Mericle, and L. N. Hopkins. A novel approach to flow quantification in brain arteriovenous malformations prior to enbucrilate embolization: Use of insoluble contrast (Ethiodol droplet) angiography. J. Neurosurg. 89(3):395–404, 1998.
Wentzel J. J., D. M. Whelan, W. J. van der Giessen, H. M. van Beusekom, I. Andhyiswara, P. W. Serruys, C. J. Slager, and R. Krams. Coronary stent implantation changes 3-d vessel geometry and 3-d shear stress distribution. J. Biomech. 33:1287–1295, 2000.
Wentzel, J. J., E. Janssen, J. Vos, J. C. Schuurbiers, R. Krams, P. W. Serruys, P. J. de Feyter, and C. J. Slager. Extension of increased atherosclerotic wall thickness into high shear stress regions is associated with loss of compensatory remodeling. Circulation 108:17–23, 2003.
Wentzel, J. J., F. J. Gijsen, N. Stergiopulos, P. W. Serruys, C. J. Slager, and R. Krams. Shear stress, vascular remodeling and neointimal formation. J. Biomech. 36:681–688, 2003.
Yamaguchi, T. Clinical Application of Computational Mechanics to the Cardiovascular System. Tokyo, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2000.
Yamaguchi, T., T. Hayasaka, D. Mori, H. Hayashi, K. Yano, F. Mizuno, and M. Harazawa. Towards Computational Biomechanics Based Cardiovascular Medical Practice. In: Computational Fluid Dynamics 2002, edited by S. W. Armfeld, P. Morgan, and K. Srinivas. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2003, pp. 46–61.
Young D. F. Fluid mechanics of arterial stenoses. J. Biomech. Eng. 101:157–175, 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lieber, B.B., Siebes, M. & Yamaguchi, T. Correlation of Hemodynamic Events with Clinical and Pathological Observations. Ann Biomed Eng 33, 1695–1703 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-8760-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-8760-6