Abstract
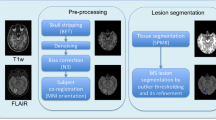
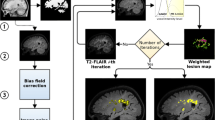
The presence of large number of false lesion classification on segmented brain MR images is a major problem in the accurate determination of lesion volumes in multiple sclerosis (MS) brains. In order to minimize the false lesion classifications, a strategy that combines parametric and nonparametric techniques is developed and implemented. This approach uses the information from the proton density (PD)- and T2-weighted and fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR) images. This strategy involves CSF and lesion classification using the Parzen window classifier. Image processing, morphological operations, and ratio maps of PD- and T2-weighted images are used for minimizing false positives. Contextual information is exploited for minimizing the false negative lesion classifications using hidden Markov random field-expectation maximization (HMRF-EM) algorithm. Lesions are delineated using fuzzy connectivity. The performance of this algorithm is quantitatively evaluated on 23 MS patients. Similarity index, percentages of over, under, and correct estimations of lesions are computed by spatially comparing the results of present procedure with expert manual segmentation. The automated processing scheme detected 80% of the manually segmented lesions in the case of low lesion load and 93% of the lesions in those cases with high lesion load.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSF :
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- EDSS :
-
Expanded disability status scale
- EM :
-
Expectation maximization
- FLAIR :
-
Fluid attenuation inversion recovery
- FNM :
-
False negative minimization
- FPM :
-
False positive minimization
- FSE :
-
Fast spin echo
- GM :
-
Gray matter
- HMRF :
-
Hidden Markov random field
- HMRF-EM :
-
Hidden Markov random field-expectation maximization
- IDL :
-
Interactive data language
- MR :
-
Magnetic resonance
- MRF :
-
Markov random field
- MRI :
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MS :
-
Multiple sclerosis
- PCE :
-
Percentage of correct estimation
- PD :
-
Proton density
- POE :
-
Percentage of overestimation
- PUE :
-
Percentage of underestimation
- SI :
-
Similarity index
- SPM :
-
Statistical parametric mapping
- WM :
-
White matter
REFERENCES
Anbeek, P., K. L. Vincken, M. J. van Osch, R. H. Bisschops, and J. van der Grond. Probabilistic segmentation of white matter lesions in MR imaging. NeuroImage 21:1037–1044, 2004.
Ashburner, J., and K. Friston. MRI sensitivity correction and tissue classification. NeuroImage 7:S706, 1998.
Ballard, D. H., and C. M. Brown. Computer Vision. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 1982.
Bedell, B. J., P. A. Narayana, and J. S. Wolinsky. A dual approach for minimizing false lesion classifications on magnetic resonance images. Magn. Reson. Med. 37:94–102, 1997.
Bland, J. M., and D. G. Altman. Comparing methods of measurement: Why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet 346:1085–1087, 1995.
Duda, R. O., P. E. Hart, and D. G. Stork. Pattern Classification. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2001.
Gerig, G., O. Kubler, R. Kikinis, and F. A. Jolesz. Nonlinear anisotropic filtering of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 11:221–232, 1992.
Geurts, J. J. G., L. Bö, P. J. W. Pouwels, J. A. Castelijns, C. H. Polman, and F. Barkhof. Cortical lesions in multiple sclerois: Combined postmortem MR imaging and histopathology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 26:572–577, 2005.
He, R., and P. A. Narayana. Global optimization of mutual information: Application of three-dimensional retrospective registration of magnetic resonance images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 26:277–292, 2002.
Krishnan, K., and M. S. Atkins. Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in MRI—An image analysis approach. Proc. SPIE Med. Imaging 3338:1106–1116, 1998.
Leemput, K. V., F. Maes, D. Vandermeulen, A. Colchester, and P. Suetens. Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions by model outlier detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 20:677–688, 2001.
Miller, D. H., M. Filippi, F. Fazekas, J. L. Frederiksen, P. M. Matthews, X. Montalban, and C. H. Polman. Role of magnetic resonance imaging within diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 56:273–278, 2004.
Narayana, P. A., and A. Borthakur. Effect of radio frequency inhomogeneity correction on the reproducibility of intra-cranial volumes using MR image data. Magn. Reson. Med. 33:396–400, 1995.
Nyul, L. G., J. K. Udupa, and X. Zhang. New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 19:143–150, 2000.
Perona, P., and J. Malik. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 12:629–639, 1990.
Udupa, J. K., L. Wei, S. Samarasekera, Y. Miki, M. A. van Buchem, and R. I. Grossman. Multiple sclerosis lesion quantitation using fuzzy-connectedness principles. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 16:598–609, 1997.
Wells, W. M., III, and W. E. L. Grimson. Adaptive segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 15:429–442, 1996.
Wolinsky, J. S., P. A. Narayana, and K. P. Johnson. Multiple Sclerosis Study Group and the MRI Analysis Center. United States open-label glatiramer acetate extension trial for relapsing multiple sclerosis: MRI and clinical correlates. Mult. Scler. 7:33–41, 2001.
Zhang, Y., M. Brady, and S. Smith. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 20:45–57, 2001.
Zijdenbos, A. P., R. Forghani, and A. C. Evans. Automatic “pipeline” analysis of 3-D MRI data for clinical trials: application to multiple sclerosis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21:1280–1291, 2002.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work is supported by National Institutes of Health Grant EB002095 to PAN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajja, B.R., Datta, S., He, R. et al. Unified Approach for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation on Brain MRI. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 142–151 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-9009-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-9009-0