Abstract
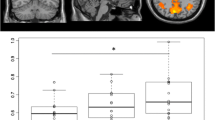
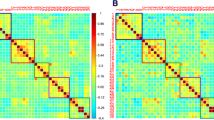
HIV causes neural dysfunction in infected individuals. This dysfunction often manifests as cognitive symptoms and can be detected using neuroimaging. Highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART), in addition to providing virologic control, has reduced the number of profoundly impaired individuals but more mild forms of neurocognitive disorders remains prevalent. A potential confound in previous studies of HIV-associated cognitive dysfunction is that HAART may be neurotoxic. Thus, observed effects, attributed to HIV, may be in part due to HAART. It is unclear whether and to what extent current medications contribute to observed brain dysfunction. We studied changes in functional connectivity and cerebral blood flow in HIV uninfected (HIV–) individuals before and after being given two common antiretroviral medications: efavirenz and ritonavir. Neither drug was associated with significant changes in functional connectivity or cerebral blood flow. Our results suggests that previous changes in functional connectivity and cerebral blood flow in HIV infected individuals receiving HAART may largely due to the virus and remaining reservoirs and less due to toxic action of these anti-retroviral medications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsop DC et al. (2014) Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine/Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.1002/mrm.25197
Ances BM et al. (2009) Resting cerebral blood flow: a potential biomarker of the effects of HIV in the brain. Neurology 73:702–708. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181b59a97
Antinori A et al. (2007) Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology 69:1789–1799. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000287431.88658.8b
Biswal B, Yetkin Z, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34:537–541
Brier MR, Mitra A, McCarthy JE, Ances BM, Snyder AZ (2015) Partial covariance based functional connectivity computation using Ledoit-Wolf covariance regularization. NeuroImage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.07.039
Brier MR et al. (2012) Loss of intranetwork and internetwork resting state functional connections with Alzheimer's disease progression. J Neurosci 32:8890–8899. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5698-11.2012
Brier MR et al. (2014) Unrecognized preclinical Alzheimer disease confounds rs-fcMRI studies of normal aging. Neurology 83:1613–1619. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000939
Chen Y, Wang DJ, Detre JA (2011) Test-retest reliability of arterial spin labeling with common labeling strategies. JMRI 33:940–949. doi:10.1002/jmri.22345
Committee UKCHCSS et al. (2011) HIV-associated central nervous system diseases in the recent combination antiretroviral therapy era. Eur J Neurol Off J Eur Fed Neurol Soc 18:527–534. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03291.x
Dai W, Garcia D, de Bazelaire C, Alsop DC (2008) Continuous flow-driven inversion for arterial spin labeling using pulsed radio frequency and gradient fields. Magn Reson Med: Off J Soc Magn Reson Med/Soc Magn Reson Med 60:1488–1497. doi:10.1002/mrm.21790
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9673–9678. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504136102
Fox MD, Zhang D, Snyder AZ, Raichle ME (2009) The global signal and observed anticorrelated resting state brain networks. J Neurophysiol 101:3270–3283. doi:10.1152/jn.90777.2008
Gonzalez-Scarano F, Martin-Garcia J (2005) The neuropathogenesis of AIDS. Nat Rev Immunol 5:69–81. doi:10.1038/nri1527
Herscovitch P, Raichle ME (1985) What is the correct value for the brain-blood partition coefficient for water. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol: Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 5:65–69
Holt JL, Kraft-Terry SD, Chang L (2012) Neuroimaging studies of the aging HIV-1-infected brain. J Neurobiol 18:291–302. doi:10.1007/s13365-012-0114-1
Kaul M, Garden GA, Lipton SA (2001) Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature 410:988–994. doi:10.1038/35073667
Kharasch ED, Bedynek PS, Walker A, Whittington D, Hoffer C (2008) Mechanism of ritonavir changes in methadone pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: II. Ritonavir effects on CYP3A and P-glycoprotein activities. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:506–512
Kharasch ED et al. (2012) Mechanism of efavirenz influence on methadone pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 91:673–684. doi:10.1038/clpt.2011.276
Lu H, Clingman C, Golay X, van Zijl PC (2004) Determining the longitudinal relaxation time (T1) of blood at 3.0 tesla. Magn Reson Med: Off J Soc Magn Reson Med/Soc Magn Reson Med 52:679–682. doi:10.1002/mrm.20178
Masters MC, Ances BM (2014) Role of neuroimaging in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Semin Neurol 34:89–102. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1372346
Ogawa S, Menon RS, Tank DW, Kim SG, Merkle H, Ellermann JM, Ugurbil K (1993) Functional brain mapping by blood oxygenation level-dependent contrast magnetic resonance imaging. A comparison of signal characteristics with a biophysical model. Biophys J 64:803–812. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81441-3
Power JD, Barnes KA, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2012) Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage 59:2142–2154. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.018
Robertson K, Liner J, Meeker RB (2012) Antiretroviral neurotoxicity. J Neurobiol 18:388–399. doi:10.1007/s13365-012-0120-3
Robertson KR et al. (2010) Neurocognitive effects of treatment interruption in stable HIV-positive patients in an observational cohort. Neurology 74:1260–1266. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d9ed09
Schweinsburg BC et al. (2005) Brain mitochondrial injury in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive (HIV+) individuals taking nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Neurobiol 11:356–364. doi:10.1080/13550280591002342
Smyser CD, Inder TE, Shimony JS, Hill JE, Degnan AJ, Snyder AZ, Neil JJ (2010) Longitudinal analysis of neural network development in preterm infants. Cereb Cortex 20:2852–2862. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq035
Tanenbaum AB, Snyder AZ, Brier MR, Ances BM (2015) A method for reducing the effects of motion contamination in arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol: Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metabol. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2015.124
Thomas JB, Brier MR, Ortega M, Benzinger TL, Ances BM (2015) Weighted brain networks in disease: centrality and entropy in human immunodeficiency virus and aging. Neurobiol Aging 36:401–412. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.06.019
Thomas JB, Brier MR, Snyder AZ, Vaida FF, Ances BM (2013) Pathways to neurodegeneration: effects of HIV and aging on resting-state functional connectivity. Neurology 80:1186–1193. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318288792b
Wright EJ (2009) Neurological disease: the effects of HIV and antiretroviral therapy and the implications for early antiretroviral therapy initiation. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 4:447–452. doi:10.1097/COH.0b013e32832dd0c2
Acknowledgments
Supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01DA14211 (EK), R01DA25931 (EK), K24-DA00417 (EK), R01NR012657 (BMA), R01NR012907 (BMA), R01NR014449 (BMA), and R21MH099979 (BMA). Funding was also provided by the Alzheimer’s Association NIRP-12-257747 (BMA). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brier, M.R., Wu, Q., Tanenbaum, A.B. et al. Effect of HAART on Brain Organization and Function in HIV-Negative Subjects. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 10, 517–521 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9634-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9634-9