Abstract
Purpose
We sought to optimize scanning parameters for MR elastography at 3.0 T clinical unit.
Materials and methods
10 volunteers were scanned with various magnetization encoding gradient (MEG) frequencies from 60 to 120 Hz at every 10 Hz, with otherwise fixed parameters (external driver frequency/amplitude = 60 Hz/50 %, 10 mm slice thickness, etc.). Images were qualitatively assessed for the degree of image defects, and also quantitatively for the areas without cross-hatching. After determining optimal MEG frequency, external driver amplitudes of 70 % (vs 50 %) and slice thickness of 8 mm (vs 10 mm) were also tested. With the optimized parameters, scans were repeated 1 week after the initial scan, and the repeatability of the liver stiffness measurement was validated.
Results
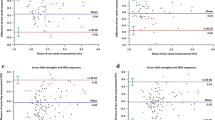
80 or 90 Hz was shown to be the best MEG frequency. There were no significant differences in the qualitative and quantitative assessment between the two amplitudes and two slice thicknesses; however, 70 % amplitude resulted in discomfort at the chest wall beneath the external acoustic driver. Thus, MEG 80 (or 90) Hz, amplitude 50 %, and thickness 10 (or 8) mm were considered optimal. Repeatability of the liver stiffness measurement was ±10 % (95 % confidence interval).
Conclusions
With the optimized parameters, repeatability of ±10 % in liver stiffness measurement was obtained.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rouviere O, Yin M, Dresner MA, et al. MR elastography of the liver: preliminary results. Radiology. 2006;240:440–8.
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Salameh N, et al. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology. 2007;245:458–66.
Klatt D, Asbach P, Rump J, et al. In vivo determination of hepatic stiffness using steady-state free precession magnetic resonance elastography. Invest Radiol. 2006;41:841–8.
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:32–40.
Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver: preliminary results and estimation of interrater reliability. Jpn J Radiol. 2010;28:623–7.
Asbach P, Klatt D, Schlosser B, et al. Viscoelasticity-based staging of hepatic fibrosis with multifrequency MR elastography. Radiology. 2010;257:80–6.
Shire NJ, Yi M, Chen J, et al. Test–retest repeatability of MR elastography for noninvasive liver fibrosis assessment in hepatitis C. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:947–55.
Hines CDG, Bley TA, Lindstrom MJ, Reeder SB. Repeatability of magnetic resonance elastography for quantification of hepatic stiffness. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31:725–31.
Kim BH, Lee JM, Lee YJ, et al. MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: experience from a tertiary center in Asia. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34:1110–6.
Lee DH, Lee JM, Han JK, and Choi BI. MR elastography of healthy liver parenchyma: normal value and reliability of the liver stiffness value measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38:1215–23.
Yin M, Talwalker JA, Glaser KJ, et al. A preliminary assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:1207–13.
Wang Y, Ganger DR, Levitsky J, et al. Assessment of chronic hepatitis and fibrosis: comparison of MR elastography and diffusion-weighted imaging. Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196:553–61.
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2012;11:291–7.
Mitsufuji T, Shinagawa Y, Fujimitsu R, et al. Measurement repeatability of MR elastogaphy at 3.0T: comparison among three different region-of-interest placement methods. Jpn. J Radiol. 2013;31:336–41.
Acknowledgments
We greatly thank Dr. Richard C. Ehman, Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, for his invaluable advice and comments on our discussion, and also Mr. Kazuyuki Uchiumi and Mr. Hiroyuki Kabasawa, GE Health Care Japan, for their expertise.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shinagawa, Y., Mitsufuji, T., Morimoto, S. et al. Optimization of scanning parameters for MR elastography at 3.0 T clinical unit: volunteer study. Jpn J Radiol 32, 441–446 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-014-0320-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-014-0320-2