Abstract
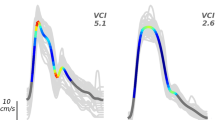
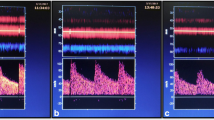
To determine the optimal velocity values in diagnosing unilateral middle cerebral artery (MCA) stenosis by Transcranial Doppler (TCD), and improve the diagnostic accuracy using magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), a total of 302 unilateral MCA stenosis patients undergoing TCD also consented to a MRA of the intracranial arteries. The peak systolic velocity (PSV) and each MCA spectrum for each patient were recorded. Using the MRA to confirm, the degree of middle cerebral artery stenosis was categorized into four groups: normal (normal caliber and signal), mild (<50 %), moderate (50–69 %), severe (70–99 %, or no flow detected). The velocity difference among these four groups was significant (P < 0.001). The optimal PSV values for normal and stenosis were 160 cm/s. For mild and moderate were 200 cm/s, for moderate and severe were 280 cm/s. Using PSV as the diagnostic criteria, the Kappa number was >0.668. The optimal PSV differential value for mild and moderate was 70 cm/s, for moderate and severe at 120 cm/s. Optimal combined criteria for moderate stenosis were PSV >200 cm/s and PSV differential value >70 cm/s (specificity 87.2 %), for severe stenosis were PSV >280 cm/s and PSV differential value >120 cm/s (sensibility 81.6 %). Transcranial Doppler distinguishes normal and MCA stenosis with a reduced lumen diameter of less than 50 %. Using the PSV criteria, TCD has a high coincidence rate with MRA in the diagnosis of MCA stenosis. Combined PSV differential value and the abnormal spectrum may improve the accuracy of TCD in diagnosing moderate or severe stenosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nishimaru, K., McHenry, L. C., & Toole, J. F. (1984). Cerebral angiographic and clinical differences in carotid system transient ischemic attacks between American Caucasian and Japanese patients. Stroke, 15, 56–59.
Feldmann, E., Daneault, N., Kwan, E., et al. (1990). Chinese-white differences in the distribution of occlusive cerebrovascular disease. Neurology, 40, 1541–1545.
Wityk, R. J., Lehman, D., Klag, M., et al. (1996). Race and sex differences in the distribution of cerebral atherosclerosis. Stroke, 27, 1974–1980.
Huang, Y. N., Gao, S., Li, S. W., et al. (1997). Vascular lesions in Chinese patients with transient ischemic attacks. Neurology, 48, 524–525.
Mazighi, M., Tanasescu, R., Ducrocq, X., et al. (2006). Prospective study of symptomatic atherothrombotic intracranial stenoses: the GESICA study. Neurology, 66, 1187–1191.
Samuels, O. B., Joseph, G. J., Lynn, M. J., et al. (2000). A standardized method for measuring intracranial arterial stenosis. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 21, 643–646.
Hua, Yang. (2002). The practical ultrasound diagnostics of carotid aretery and brain vasculature (pp. 47–51). Beijing: Science Press.
Gao, S., & Huang, J. (2004). The diagnostic technologies and clinical applications of Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (pp. 51–54). Beijing: Chinese Peking Union Medical College Press.
de Bray, J. M., Joseph, P. A., Jeanvoine, H., et al. (1998). Transcranial Doppler evaluation of middle cerebral artery stenosis. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 7, 611–616.
Suwanwela, N. C., Phanthumchinda, K., & Suwanwela, N. (2002). Transcranial Doppler sonography and CT angiography in patients with atherothrombotic middle cerebral artery stroke. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23(8), 1352–1355.
Gao, S., Lam, W. W., Chan, Y. L., et al. (2002). Optimal values of flow velocity on Transcranial Doppler in grading middle cerebral artery stenosis in comparison with magnetic resonance angiography. Journal of Neuroimaging, 12, 213–218.
Felberg, R. A., Christou, I., Demchuk, A. M., et al. (2002). Screening for intracranial stenosis with Transcranial Doppler: the accuracy of mean flow velocity thresholds. Journal of Neuroimaging, 12, 9–14.
Hao, Q., Gao, S., Leung, T. W., et al. (2010). Pilot study of new diagnostic criteria for middle cerebral artery stenosis by Transcranial Doppler. Journal of Neuroimaging, 20, 122–129.
Alexandrov, A. V. (2007). The Spencer’s Curve: clinical implications of a classic hemodynamic model. Journal of Neuroimaging, 17, 6–10.
Stock, K. W., Radue, E. W., Jacob, A. L., et al. (1995). Intracranial arteries: prospective blinded comparative study of MR angiography and DSA in 50 patients. Radiology, 195, 451–456.
Spencer, M. P., & Reid, J. M. (1979). Quantitation of carotid stenosis with continuous-wave (C-W) Doppler ultrasound. Stroke, 10, 326–330.
Rorick, M. B., Nichols, F. T., & Adams, R. J. (1994). Transcranial Doppler correlation with angiography in detection of intracranial stenosis. Stroke, 25, 1931–1934.
Demirkaya, S., Uluc, K., Bek, S., et al. (2008). Normal blood flow velocities of basal cerebral arteries decrease with advancing age: a Transcranial Doppler sonography study. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, 214, 145–149.
Xing, Y. Q., Han, K., Bai, Z., et al. (2008). The diagnostic value of Transcranial Doppler sonography of hemodynamic changes of intracranial circulation in the patients with chronic middle cerebral artery occlusion. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 28, 1906–1909.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yingqi Xing and Lin Wang contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Xing, Y., Li, Y. et al. Evaluation of Flow Velocity in Unilateral Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis by Transcranial Doppler. Cell Biochem Biophys 70, 823–830 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9986-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9986-4