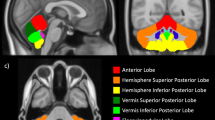
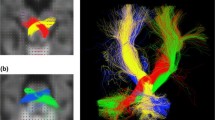
Abstract
The objective of this study was to correlate neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm-born children and their perinatal clinical and imaging characteristics with diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures of the three cerebellar peduncles at age 7. Included in this prospective longitudinal study were 140 preterm-born children (<30 weeks gestation) who underwent neurodevelopmental assessment (IQ, motor, language, working memory) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) at age 7 years. White matter tracts in the superior, middle, and inferior cerebellar peduncles were delineated using regions of interest drawn on T2-weighted images and fractional anisotropy (FA) maps. Diffusion measures (mean diffusivity (MD) and FA) and tract volumes were calculated. Linear regression was used to assess relationships with outcome. The severity of white matter injury in the neonatal period was associated with lower FA in the right superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP) and lower tract volumes of both SCPs and middle cerebellar peduncles (MCPs). In the MCP, higher IQ was associated with lower MD in the whole group and higher FA in right-handed children. In the SCP, lower motor scores were associated with higher MD and higher language scores were associated with higher FA. These associations remained significant in multivariable models. This study adds to the body of literature detailing the importance of cerebellar involvement in cognitive function related to reciprocal connections with supratentorial structures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manto M. The cerebellum, cerebellar disorders, and cerebellar research—two centuries of discoveries. Cerebellum. 2008;7:505–16.
Salmi J, Pallesen KJ, Neuvonen T, Brattico E, Korvenoja A, Salonen O, et al. Cognitive and motor loops of the human cerebro-cerebellar system. J Cogn Neurosci. 2010;22:2663–76.
Thach WT. On the mechanism of cerebellar contributions to cognition. Cerebellum. 2007;6:163–7.
Holmes G. The cerebellum of man. Brain. 1939;62:1–30.
Glickstein M, Doron K. Cerebellum: connections and functions. Cerebellum. 2008;7:589–94.
Strick PL, Dum RP, Fiez JA. Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2009;32:413–34.
Ghez C, Thach WT, The Cerebellum. In: Principles of Neural sciences, 4th Ed. Editors: Kandel RK, Swartz JH, Jessel TM. Mc Graw Hill. 2000: 832–852.
Dobbing J, Sands J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch Dis Child. 1973;48:757–67.
Xue R, van Zijl PC, Crain BJ, Solaiyappan M, Mori S. In vivo three-dimensional reconstruction of rat brain axonal projections by diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42:1123–7.
Tam EW, Miller SP, Studholme C, Chau V, Glidden D, Poskitt KJ, et al. Differential effects of intraventricular hemorrhage and white matter injury on preterm cerebellar growth. J Pediatr. 2011;158:366–71.
Tam EW, Ferriero DM, Xu D, Berman JI, Vigneron DB, Barkovich AJ, et al. Cerebellar development in the preterm neonate: effect of supratentorial brain injury. Pediatr Res. 2009;66:102–6.
Limperopoulos C, Bassan H, Gauvreau K, Robertson Jr RL, Sullivan NR, Benson CB, et al. Does cerebellar injury in premature infants contribute to the high prevalence of long-term cognitive, learning, and behavioral disability in survivors? Pediatrics. 2007;120:584–93.
Limperopoulos C, Chilingaryan G, Guizard N, Robertson RL, Du Plessis AJ. Cerebellar injury in the premature infant is associated with impaired growth of specific cerebral regions. Pediatr Res. 2010;68:145–50.
Limperopoulos C, Chilingaryan G, Sullivan N, Guizard N, Robertson RL, du Plessis AJ. Injury to the premature cerebellum: outcome is related to remote cortical development. Cereb Cortex. 2014;24:728–36.
Mori S, Zhang J. Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron. 2006;51:527–39.
Mukherjee P, Miller JH, Shimony JS, Conturo TE, Lee BC, Almli CR, et al. Normal brain maturation during childhood: developmental trends characterized with diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology. 2001;221:349–58.
Hüppi PS, Dubois J. Diffusion tensor imaging of brain development. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006;11:489–97.
Lebel C, Gee M, Camicioli R, Wieler M, Martin W, Beaulieu C. Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter tract evolution over the lifespan. Neuroimage. 2012;60:340–52.
Hüppi PS, Murphy B, Maier SE, Zientara GP, Inder TE, Barnes PD, et al. Microstructural brain development after perinatal cerebral white matter injury assessed by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatrics. 2001;107:455–60.
Murakami A, Morimoto M, Yamada K, Kizu O, Nishimura A, Nishimura T, et al. Fiber-tracking techniques can predict the degree of neurologic impairment for periventricular leukomalacia. Pediatrics. 2008;122:500–6.
Eluvathingal TJ, Chugani HT, Behen ME, Juhász C, Muzik O, Maqbool M, et al. Abnormal brain connectivity in children after early severe socioemotional deprivation: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Pediatrics. 2006;117:2093–100.
Nagel BJ, Bathula D, Herting M, Schmitt C, Kroenke CD, Fair D, et al. Altered white matter microstructure in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011;50:283–92.
Bechtel N, Kobel M, Penner IK, Klarhöfer M, Scheffler K, Opwis K, et al. Decreased fractional anisotropy in the middle cerebellar peduncle in children with epilepsy and/or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a preliminary study. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;15:294–8.
Anderson P, Doyle LW, Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group. Neurobehavioral outcomes of school-age children born extremely low birth weight or very preterm in the 1990s. JAMA. 2003;289:3264–72.
Larroque B, Ancel PY, Marret S, Marchand L, André M, Arnaud C, et al. Neurodevelopmental disabilities and special care of 5-year-old children born before 33 weeks of gestation (the EPIPAGE study): a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371:813–20.
Aarnoudse-Moens CS, Weisglas-Kuperus N, van Goudoever JB, Oosterlaan J. Meta-analysis of neurobehavioral outcomes in very preterm and/or very low birth weight children. Pediatrics. 2009;124:717–28.
Steggerda SJ, Leijser LM, Wiggers-de Bruïne FT, van der Grond J, Walther FJ, van Wezel-Meijler G. Cerebellar injury in preterm infants: incidence and findings on US and MR images. Radiology. 2009;252(1):190–9.
Thompson DK, Warfield SK, Carlin JB, Pavlovic M, Wang HX, Bear M, et al. Perinatal risk factors altering regional brain structure in the preterm infant. Brain. 2007;130:667–77.
Mathur AM, Neil JJ, McKinstry RC, Inder TE. Transport, monitoring, and successful brain MR imaging in unsedated neonates. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38:260–4.
Kidokoro H, Neil JJ, Inder TE. New MR imaging assessment tool to define brain abnormalities in very preterm infants at term. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:2208–14.
Wechsler D. Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI). 1999; The Psychological Corporation.
Henderson SE, Sugden DA, Barnett AL. Movement Assessment Battery for Children e Second Edition (Movement ABC-2). London: The Psychological Corporation; 2007.
Semel E, Wiig EH, Secord WA. Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals, Fourth Edition (CELF-4). Toronto: The Psychological Corporation/A Harcourt Assessment Company; 2003.
Baddeley AD, Hitch G. Working memory. In G. Bower (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 8, pp. 47–90). 1974; New York: Academic Press.
Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell D, Wood E, Galuppi B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1997;39:214–23.
Treyvaud K, Ure A, Doyle LW, Lee KJ, Rogers CE, Kidokoro H, et al. Psychiatric outcomes at age seven for very preterm children: rates and predictors. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2013;54:772–9.
Goodman R, Ford T, Richards H, Gatward R, Meltzer H. The development and well-being assessment: description and initial validation of an integrated assessment of child and adolescent psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2000;41:645–55.
Roberts G, Howard K, Spittle AJ, Brown NC, Anderson PJ, Doyle LW. J Rates of early intervention services in very preterm children with developmental disabilities at age 2 years. Paediatr Child Health. 2008;44:276–80.
Estep ME, Smyser CD, Anderson PJ, Ortinau CM, Wallendorf M, Katzman CS, et al. Diffusion tractography and neuromotor outcome in very preterm children with white matter abnormalities. Pediatr Res. 2014;76:86–92.
Shimony JS, Burton H, Epstein AA, McLaren DG, Sun SW, Snyder AZ. Diffusion tensor imaging reveals white matter reorganization in early blind humans. Cereb Cortex. 2006;16:1653–61.
Conturo TE, Lori NF, Cull TS, Akbudak E, Snyder AZ, Shimony JS, et al. Tracking neuronal fiber pathways in the living human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:10422–7.
Bender R, Lange S. Adjusting for multiple testing—when and how? J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54:343–9.
Allin M, Matsumoto H, Santhouse AM, Nosarti C, AlAsady MH, Stewart AL, et al. Cognitive and motor function and the size of the cerebellum in adolescents born very pre-term. Brain. 2001;124:60–6.
van Kooij BJ, Benders MJ, Anbeek P, Van Haastert IC, De Vries LS, Groenendaal F. Cerebellar volume and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy at term, and neurodevelopment at 2 years of age in preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2012;54:260–6.
Constable RT, Ment LR, Vohr BR, Kesler SR, Fulbright RK, Lacadie C, et al. Prematurely born children demonstrate white matter microstructural differences at 12 years of age, relative to term control subjects: an investigation of group and gender effects. Pediatrics. 2008;121:306–16.
van Kooij BJ, van Pul C, Benders MJ, van Haastert IC, de Vries LS, Groenendaal F. Fiber tracking at term displays gender differences regarding cognitive and motor outcome at 2 years of age in preterm infants. Pediatr Res. 2011;70:626–32.
Allin MP, Kontis D, Walshe M, Wyatt J, Barker GJ, Kanaan RA, et al. White matter and cognition in adults who were born preterm. PLoS One. 2011;6, e24525.
Counsell SJ, Edwards AD, Chew AT, Anjari M, Dyet LE, Srinivasan L, et al. Specific relations between neurodevelopmental abilities and white matter microstructure in children born preterm. Brain. 2008;131:3201–8.
Hanaie R, Mohri I, Kagitani-Shimono K, Tachibana M, Azuma J, Matsuzaki J, et al. Altered microstructural connectivity of the superior cerebellar peduncle is related to motor dysfunction in children with autistic spectrum disorders. Cerebellum. 2013;12:645–56.
Gelinas JN, Fitzpatrick KP, Kim HC, Bjornson BH. Cerebellar language mapping and cerebral language dominance in pediatric epilepsy surgery patients. Neuroimage Clin. 2014;12:296–306.
Beaulieu C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002;15:435–55.
Szaflarski JP, Rajagopal A, Altaye M, Byars AW, Jacola L, Schmithorst VJ, et al. Left-handedness and language lateralization in children. Brain Res. 2012;1433:85–97.
Johnson RT, Yeatman JD, Wandell BA, Buonocore MH, Amaral DG, Nordahl CW. Diffusion properties of major white matter tracts in young, typically developing children. NeuroImage. 2014;88:143–54.
Trivedi R, Agarwal S, Rathore RK, Saksena S, Tripathi RP, Malik GK, et al. Understanding development and lateralization of major cerebral fiber bundles in pediatric population through quantitative diffusion tensor tractography. Pediatr Res. 2009;66:636–41.
Sivaswamy L, Kumar A, Rajan D, Behen M, Muzik O, Chugani D, et al. A diffusion tensor imaging study of the cerebellar pathways in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Child Neurol. 2010;25:1223–31.
Parker J, Mitchell A, Kalpakidou A, Walshe M, Jung HY, Nosarti C, et al. Cerebellar growth and behavioural & neuropsychological outcome in preterm adolescents. Brain. 2008;131:1344–51.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Australia’s National Health and Medical Research Council (Centre for Clinical Research Excellence 546519 to LD, PA, TI; Centre for Research Excellence 1060733 to LD, PA; Project grants 237117 to LD, 491209 to PA; Senior Research Fellowships 628371 & 1081288 to PA), United Cerebral Palsy Foundation (USA), Leila Y. Mathers Charitable Foundation (USA), the Brown Foundation (USA), the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program, The Royal Children’s Hospital Foundation, National Institute of Health R01HD058056, UL1 TR000448 and K02NS089852, and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. We would like to thank Dr Deanne Thompson for reviewing the manuscript and Dr Lena Novack for statistical guidance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 11 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shany, E., Inder, T.E., Goshen, S. et al. Diffusion Tensor Tractography of the Cerebellar Peduncles in Prematurely Born 7-Year-Old Children. Cerebellum 16, 314–325 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-016-0796-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-016-0796-7