Abstract
Objective
To report the incidence of trigeminal neuropathy seen among new patients in a referral center within a period of 1 year (2013). The cause of damage, method of management and treatment outcome was assessed after 1-year follow-up.
Materials and Methods
The records of all new patients visiting the oral and maxillofacial unit of the University hospital of Leuven in 2013 were screened for a history of damage to branches of the trigeminal nerve. The selected records were examined and the duration of nerve damage, received treatment as well as the outcome of the neuropathy after treatment was noted after 1-year follow-up.
Results
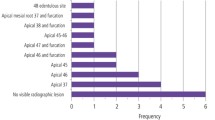
56 patients (21 males, 35 females) from 7602 new patients had symptoms of damage to the trigeminal nerve branch. These symptoms persist in more than one-third of the patients [21/56 (37.5 %)] after 1-year follow-up. The least recovery is seen from oral surgery, implant placement, orthognathic surgery and tooth extraction. After 1 year 85 % (12/14) of neuropathic pain cases still have their symptoms as compared to 19 % (5/26) of patients with hypoesthesia.
Conclusion
This study shows a low incidence of nerve damage among the new patients presenting in oral and maxillofacial surgery clinic (<1 %); however, one-third of patients who sustain nerve damage never recover fully. Early diagnosis of the cause of neuropathy is essential. There is a need to objectively assess all patients with symptoms of trigeminal nerve damage before, during and after treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jerjes W, Upile T, Shah P, Nhembe F, Gudka D, Kafas P, McCarthy E, Abbas S, Patel S, Hamdoon Z, Abiola J, Vourvachis M, Kalkani M, Al-Khawalde M, Leeson R, Banu B, Rob J, El-Maaytah M, Hopper C (2010) Risk factors associated with injury to the inferior alveolar and lingual nerves following third molar surgery-revisited. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 109:335–345
Pogrel MA, Kaban LB (1993) Injuries to the inferior alveolar and lingual nerves. J Calif Dent Assoc 21:50–54
Robert RC, Bacchetti P, Pogrel MA (2005) Frequency of trigeminal nerve injuries following third molar removal. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:732–735
Andrabi SM, Alam S, Zia A, Khan MH, Kumar A (2014) Mental nerve paresthesia secondary to initiation of endodontic therapy: a case report. Restor Dent Endod 39:215–219
Pogrel MA (2007) Damage to the inferior alveolar nerve as the result of root canal therapy. J Am Dent Assoc 138:65–69
Wijbenga JG, Verlinden CR, Jansma J, Becking AG, Stegenga B (2009) Long-lasting neurosensory disturbance following advancement of the retrognathic mandible: distraction osteogenesis versus bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:719–725
Yoshioka I, Tanaka T, Khanal A, Habu M, Kito S, Kodama M, Oda M, Wakasugi-Sato N, Matsumoto-Takeda S, Fukai Y, Tokitsu T, Tomikawa M, Seta Y, Tominaga K, Morimoto Y (2010) Relationship between inferior alveolar nerve canal position at mandibular second molar in patients with prognathism and possible occurrence of neurosensory disturbance after sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:3022–3027
Yamauchi K, Takahashi T, Kaneuji T, Nogami S, Yamamoto N, Miyamoto I, Yamashita Y (2011) Risk factors for neurosensory disturbance after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy based on position of mandibular canal and morphology of mandibular angle. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:401–406
Bagheri SC, Meyer RA, Khan HA, Steed MB (2009) Microsurgical repair of peripheral trigeminal nerve injuries from maxillofacial trauma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1791–1799
Politis C, Lambrichts I, Agbaje JO (2014) Neuropathic pain after orthognathic surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 117:e102–e107
Politis C, Sun Y, Lambrichts I, Agbaje JO (2013) Self-reported hypoesthesia of the lower lip after sagittal split osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:823–829
D’Agostino A, Trevisiol L, Gugole F, Bondi V, Nocini PF (2010) Complications of orthognathic surgery: the inferior alveolar nerve. J Craniofac Surg 21:1189–1195
Agbaje JO, Salem AS, Jacobs R, Politis C (2015) Systematic review of the incidence of inferior alveolar nerve injury in bilateral sagittal split osteotomy and the assessment of neurosensory disturbances. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:447–451
Westermark A, Bystedt H, von Konow KL (1998) Inferior alveolar nerve function after mandibular osteotomies. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 36:425–428
Monnazzi MS, Real-Gabrielli MF, Passeri LA, Gabrielli MA (2012) Cutaneous sensibility impairment after mandibular sagittal split osteotomy: a prospective clinical study of the spontaneous recovery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:696–702
Cespedes-Sanchez JM, Ayuso-Montero R, Mari-Roig A, Arranz-Obispo C, Lopez-Lopez J (2014) The importance of a good evaluation in order to prevent oral nerve injuries: a review. Acta Odontol Scand 72:161–167
Cheung LK, Leung YY, Chow LK, Wong MC, Chan EK, Fok YH (2010) Incidence of neurosensory deficits and recovery after lower third molar surgery: a prospective clinical study of 4338 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39:320–326
Hillerup S (2007) Iatrogenic injury to oral branches of the trigeminal nerve: records of 449 cases. Clin Oral Investig 11:133–142
Penarrocha MA, Penarrocha D, Bagan JV, Penarrocha M (2012) Post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy. A study of 63 cases. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 17:e297–e300
Bagheri SC, Meyer RA, Khan HA, Wallace J, Steed MB (2010) Microsurgical repair of the peripheral trigeminal nerve after mandibular sagittal split ramus osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:2770–2782
Degala S, Shetty SK, Bhanumathi M (2015) Evaluation of neurosensory disturbance following orthognathic surgery: a prospective study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 14:24–31
Scarano A, Di CF, Quaranta A, Piattelli A (2007) Injury of the inferior alveolar nerve after overfilling of the root canal with endodontic cement: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 104:e56–e59
Silbert BI, Kolm S, Silbert PL (2013) Postprocedural inflammatory inferior alveolar neuropathy: an important differential diagnosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 115:e1–e3
Moon S, Lee SJ, Kim E, Lee CY (2012) Hypoesthesia after IAN block anesthesia with lidocaine: management of mild to moderate nerve injury. Restor Dent Endod 37:232–235
Wijbenga JG, Verlinden CR, Jansma J, Becking AG, Stegenga B (2009) Long-lasting neurosensory disturbance following advancement of the retrognathic mandible: distraction osteogenesis versus bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:719–725
Al-Sabbagh M, Okeson JP, Khalaf MW, Bhavsar I (2015) Persistent pain and neurosensory disturbance after dental implant surgery: pathophysiology, etiology, and diagnosis. Dent Clin N Am 59:131–142
Tay AB, Zuniga JR (2007) Clinical characteristics of trigeminal nerve injury referrals to a university centre. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 36:922–927
Ziccardi VB, Assael LA (2001) Mechanisms of trigeminal nerve injuries. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin N Am 9:1–11
Westermark A, Englesson L, Bongenhielm U (1999) Neurosensory function after sagittal split osteotomy of the mandible: a comparison between subjective evaluation and objective assessment. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg 14:268–275
Essick GK, Phillips C, Turvey TA, Tucker M (2007) Facial altered sensation and sensory impairment after orthognathic surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 36:577–582
Spencer CJ, Gremillion HA (2007) Neuropathic orofacial pain: proposed mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment considerations. Dent Clin N Am 51:209–224
Eisenberg E, River Y, Shifrin A, Krivoy N (2007) Antiepileptic drugs in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Drugs 67:1265–1289
Eliav E, Gracely RH, Nahlieli O, Benoliel R (2004) Quantitative sensory testing in trigeminal nerve damage assessment. J Orofac Pain 18:339–344
Svensson P, Baad-Hansen L, Thygesen T, Juhl GI, Jensen TS (2004) Overview on tools and methods to assess neuropathic trigeminal pain. J Orofac Pain 18:332–338
Baad-Hansen L, Pigg M, Ivanovic SE, Faris H, List T, Drangsholt M, Svensson P (2013) Intraoral somatosensory abnormalities in patients with atypical odontalgia—a controlled multicenter quantitative sensory testing study. Pain 154:1287–1294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest related to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agbaje, J.O., Van de Casteele, E., Hiel, M. et al. Neuropathy of Trigeminal Nerve Branches After Oral and Maxillofacial Treatment. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 15, 321–327 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-015-0843-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-015-0843-9