Abstract
1. Transient forebrain ischemia in adult rats, induced by 10 min of bilateral carotid occlusion and an arterial hypotension of 40 mmHg, caused substantial damage not only to CA-1 neurons in hippocampus but also to epithelial cells in lateral ventricle choroid plexus.
2. When transient forebrain ischemia was followed by reperfusion (recovery) intervals of 0 to 12 hr, there was moderate to severe damage to many frond regions of the choroidal epithelium. In some areas, epithelial debris was sloughed into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Although some epithelial cells were disrupted and necrotic, their neighbors exhibited normal morphology. This patchy response to ischemia was probably due to regional differences in reperfusion or cellular metabolism.
3. Between 12 and 24 hr postischemia, there was marked restoration of the Na+, K+, water content, and ultrastructure of the choroid plexus epithelium. Since there was no microscopical evidence for mitosis, we postulate that healthy epithelial cells either were compressed together on the villus or migrated from the choroid plexus stalk to more distal regions, in order to “fill in gaps” along the basal lamina caused by necrotic epithelial cell disintegration.
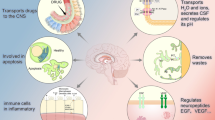
4. Epithelial cells of mammalian choroid plexus synthesize and secrete many growth factors and other peptides that are of trophic benefit following injury to regions of the cerebroventricular system. For example, several growth factors are upregulated in choroid plexus after ischemic and traumatic insults to the central nervous system.
5. The presence of numerous types of growth factor receptors in choroid plexus allows growth factor mediation of recovery processes by autocrine and paracrine mechanisms.
6. The capability of choroid plexus after acute ischemia to recover its barrier and CSF formation functions is an important factor in stabilizing brain fluid balance.
7. Moreover, growth factors secreted by choroid plexus into CSF are distributed by diffusion and convection into brain tissue near the ventricular system, e.g., hippocampus. By this endocrine-like mechanism, growth factors are conveyed throughout the choroid plexus–CSF–brain nexus and can consequently promote repair of ischemia-damaged tissue in the ventricular wall and underlying brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Baird, A., and Bohlen, P. (1990). Fibroblast growth factors. In Sporn, M. B., and Roberts, A. B. (eds.), Peptide Growth Factors and Their Receptors, Springer, Berlin, pp. 369-418.
Baskin, D. G., Wilcox, B. J., Figlewicz, D. P., and Dorsa, D. M. (1988). Insulin and insulin-like growth factors in the CNS. TINS 11:107-111.
Bloch, B., Normand, E., Kovesdi, I., and Bohlen, P. (1992). Expression of the HBNF (heparin-binding neurite-promoting factor) gene in the brain of fetal, neonatal and adult rat: an in situ hybridization study. Dev. Brain Res. 70:267-278.
Bohannon, N. J., Corp, E. S., Wilcox, B. J., Figlewicz, D. P., Dorsa, D. M., and Baskin, D. G. (1988). Localization of binding sites for insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in the rat brain by quantitative autoradiography. Brain Res. 444:205-213.
Chalazonitis, A., Kalberg, J., Twardzik, D. R., Morrison, R. S., and Kessler, J. A. (1992). Transforming growth factor-β has neurotrophic actions on sensory neurons in vitro and is synergistic with nerve growth factor. Dev. Biol. 152:121-132.
Chodobski, A., Szmydynger-Chodobska, J., Vannorsdall, M. D., Epstein, M. H., and Johanson, C. E. (1994). AT1 receptor subtype mediates the inhibitory effect of central angiotensin II on cerebrospinal fluid formation in the rat. Reg. Peptides 53:123-129.
Chodobski, A., Loh, Y. P., Corsetti, S., Szmydynger-Chodobska, J., Johanson, C. E., Lim, Y.-P., and Monfils, P. R. (1997). The presence of arginine vasopressin and its mRNA in rat choroid plexus epithelium. Mol. Brain Res. 48:67-72.
Cortez, S., Johanson, C., Kuo-LeBlanc, V., Rodriguez-Wolf, M., Baird, A., Gonzalez, A. M., Seddon, A., and Stopa, E. G. (1995). Heparin-binding growth factors in control and Alzheimer choroids plexus. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 21:741.
Cuevas, P., Cercellar, F., Reimers, D., Xiaobing, F., and Gimenez-Gallego, G. (1994). Immunohistochemical localization of basic fibroblast growth factor in choroid plexus of the rat. Neurol. Res. 16:310-312.
Diaz-Ruiz, C., Perez-Thomas, R., Domingo, J., and Ferrer, I. (1993). Immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor-α in choroid plexus of the rat and chicken. Neurosci. Lett. 164:44-46.
Endoh, M., Pulsinelli, W. A., and Wagner, J. A. (1994). Transient global ischemia induces dynamic changes in the expression of bFGF and the FGF receptor. Mol. Brain Res. 22:76-88.
Esser, S., Wolburg, K., Wolburg, H., Breier, G., Kurzchalia, T., and Risau, W. (1998). Vascular endothelial growth factor induces endothelial fenestrations in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 140:947-959.
Finch, C. E., Laping, N. J., Morgan, T. E., Nichols, N. R., and Pasinetti, G. M. (1993). TGF-β1 is an organizer of responses to neurodegeneration. J. Cell Biochem. 53:314-322.
Finklestein, S. P., Apostolides, P. J., Caday, C. G., Prosser, J., Philips, M. F., and Klagsbrun, M. (1988). Increased basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity at the site of focal brain wounds. Brain Res. 460:253-259.
Flanders, K. C., Ren, R. F., and Lippa, C. F. (1998). Transforming growth factor-βs in neurodegenerative diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. 54:71-85.
Garner, C., and Brown P. D. (1992). Two types of chloride channel in the apical membrane of rat choroid plexus epithelial cells. Brain Res. 591:137-145.
Gillardon, F., Lenz, C., Kuschinsky, W., and Zimmerman, M. (1996). Evidence for apoptotic cell death in the choroid plexus following focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 207:113-116.
Glaumann, B., Glaumann, H., Berezersky, I., and Trump, B. (1977). Studies on cellular recovery from injury. II. Ultrastructural studies on the recovery of the pars convoluta of the proximal tubule of the rat kidney from temporary ischemia. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. 24:1-18.
Gospodarowicz, D., and Moran, J. S. (1975). Mitogenic effect of fibroblast growth factor on early passage cultures of human and murine fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 66:451-457.
Holloway, L. S., Jr., and Cassin, S. (1972). Cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in the newborn dog during normoxia and hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. 223:499-502.
Hynes, M. A., Brooks, P. J., Van Wyk, J. J., and Lund, P. K. (1988). Insulin-like growth factor II messenger ribonucleic acids are synthesized in the choroid plexus of the rat brain. Mol. Endocrinol. 2:47-54.
Ikeda, J., Mies, G., Nowak, T. S., Jr., Joo, F., and Klatzo, I. (1992). Evidence for increased calcium influx across the choroid plexus following brief ischemia of gerbil brain. Neurosci. Lett. 142:257-259.
Johanson, C. E. (1989a). Ontogeny of the blood-brain barrier. In Neuwelt, E. (ed.), Implications of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Its Manipulation, Vol. 1. Basic Science Aspects, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 101-129.
Johanson, C. E. (1989b). Potential for pharmacological manipulation of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. In Neuwelt, E. (ed.), Implications of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Its Manipulation, Vol. 1. Basic Sci. Aspects, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 223-260.
Johanson, C. E. (1993). Tissue Barriers: Diffusion, bulk flow and volume transmission of proteins and peptides within the brain. In Audus, K. L., and Raub, T. J. (eds.), Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 5: Biological Barriers to Protein Delivery, Plenum, New York, pp. 467-486.
Johanson, C. E. (1995). Ventricles and cerebrospinal fluid. In Michael Conn, P. (ed.), Neuroscience in Medicine, J. B. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp. 171-196.
Johanson, C. E. (1998). Arachnoid membrane, subarachnoid CSF and pia-glia. In Pardridge, W. M. (ed.), Introduction to the Blood-Brain Barrier: Methodology, Biology and Pathology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 259-269.
Johanson, C. E., and Murphy, V. A. (1990). Acetazolamide and insulin alter choroid plexus epithelial cell [Na+], pH, and volume. Am. J. Physiol. 258:F1538-F1546.
Johanson, C. E., and Woodbury, D. M. (1978). Uptake of C-14 urea by the in vivo choroid plexus cerebrospinal fluid-brain system: Identification of sites of molecular sieving by the choroid plexus of the rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 275:167-176.
Johanson, C. E., Reed, D. J., and Woodbury, D. M. (1974). Active transport of sodium and potassium by the choroid plexus of the rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 241:359-372.
Johnson, N. F., and Foulds, W. S. (1978). The effects of total acute ischemia on the structure of the rabbit retina. Exp. Eye Res. 27:45-59.
Jung, W., Castren, E., Odenthal, M., Vande Woude, G. F., Ishii, T., Dienes, H.-P., Lindholm, D., and Schirmacher, P. (1994). Expression and functional interaction of hepatocyte growth factor-scatter factor and its receptor c-met in mammalian brain. J. Cell Biol. 126:485-494.
Kawamata, T., Dietrich, W. D., Schaller, T., Gotts, J. E., Cocke, R. R., Benowitz, L. I., and Finklestein, S. P. (1997). Intracisternal basic fibroblast growth factor enhances functional recovery and upregulates the expression of a molecular marker of neuronal sprouting following focal cerebral infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:8179-8184.
Klein, R., Martin-Zanca, D., Barbacid, M., and Parada, L. F. (1990). Expression of the tyrosine kinase receptor gene trkB is confined to the murine embryonic and adult nervous system. Development 109:845-850.
Klempt, N. D., Sirimanne, E., Gunn, A. J., Klempt, M., Singh, K., Williams, C., and Gluckman, P. D. (1992). Hypoxia-ischemia induces transforming growth factor β1 mRNA in the infant rat brain. Mol. Brain Res. 13:93-101.
Knuckey, N. W., Preston, J., Palm, D., Epstein, M. H., and Johanson, C. E. (1993). Hydrocephalus decreases chloride efflux from the choroid plexus epithelium. Brain Res. 618:313-317.
Knuckey, N. W., Palm, D., Primiano, M., Epstein, M. H., and Johanson, C. E. (1995). N-Acetylcysteine enhances hippocampal neuronal survival after transient brain ischemia in rats. Stroke 26:305-311.
Knuckey, N. W., Finch, P., Palm, D. E., Primiano, M. J., Johanson, C. E., Flanders, K. C., and Thompson, N. L. (1996). Differential neuronal and astrocytic expression of transforming growth factor beta isoforms in rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Mol. Brain Res. 40:1-14.
Kozlowski, G. P. (1982). Ventricular route hypothesis and peptide-containing structures of the cerebroventricular system. In Rodriguez, E. M., and van Wimersma Greidanus, Ti. B. (eds.), Frontiers of Hormone Research, Vol. 9. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) and Peptide Hormones, S. Karger, Basel, pp. 105-118.
Lafond, R. E., Giammalvo, J. T., and Norkin, L. C. (1995). Relationship between expression of epidermal growth factor and simian virus 40 T antigen in a line of transgenic mice. Transgenic Res. 4:306-314.
Lee, B. C. P., and Zimmer, J. (1978). Ventricular opacification after intravascular injections of contrast material. Radiology 128:647-649.
Levine, S. (1987). Choroid plexus: Target for systemic disease and pathway to the brain. Lab. Invest. 56:231-233.
Logan, A., Frautschy, S. A., Gonzalez, A.-M., and Baird, A. (1992a). A time course for the focal elevation of synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor and one of its high-affinity receptors (flg) following a localized cortical brain injury. J. Neurosci. 12:3828-3837.
Logan, A., Frautschy, S. A., Gonzalez, A.-M., Sporn, M. B., and Baird, A. (1992b). Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor β1 in the rat brain after a localized cerebral injury. Brain Res. 587:216-225.
Maktabi, M. A., and Faraci, F. M. (1994). Endogenous angiotensin II inhibits production of cerebrospinal fluid during posthypoxemic reoxygenation in the rabbit. Stroke 25:1489-1494.
Marmor, M., and Dalal, R. (1993). Irregular retinal and RPE damage after pressure-induced ischemia in the rabbit. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 34:2570-2575.
Michael, D. K., and Heisey, S. R. (1973). Effects of brain ventricular perfusion and hypoxia on CSF formation and absorption. Exp. Neurol. 41:769-772.
Murphy, V. A., and Johanson, C. E. (1985). Adrenergic-induced enhancement of brain barrier system permeability to small nonelectrolytes: Choroid plexus versus cerebral capillaries. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 5:401-412.
Nagahiro, S., Goto, S., Korematsu, K., Sumi, M., Takahashi, M., and Ushio, Y. (1994). Disruption of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier by transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 633:305-311.
Nilsson, C., Lindvall-Axelsson, M., and Owman, C. (1992). Neuroendocrine regulatory mechanisms in the choroid plexus-cerebrospinal fluid system. Brain Res. Rev. 17:109-138.
Nozaki, K., Finklestein, S. P., and Beal, M. F. (1993). Basic fibroblast growth factor protects against hypoxia-ischemia and NMDA neurotoxicity in neonatal rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 13:221-228.
Ohta, S., Gido, G., and Siesjo, B. K. (1992). Influence of ischemia on blood-brain and blood-CSF calcium transport. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 12:525-528.
Palm, D., Knuckey, N., Guglielmo, M., Watson, P., Primiano, M., and Johanson, C. (1995a). Choroid plexus electrolytes and ultrastructure following transient forebrain ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. 269:R73-R79.
Palm, D. E., Knuckey, N. W., Primiano, M. J., Spangenberger, A. G., and Johanson, C. E. (1995b). Cystatin C, a protease inhibitor, in degenerating rat hippocampal neurons following transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res. 691:1-8.
Pollay, M. (1974). Transport mechanisms in the choroid plexus. Fed. Proc. 33:2064-2069.
Pollay, M., Hisey, B., Reynolds, E., Tomkins, P., Stevens, F. A., and Smith, R. (1985). Choroid plexus Na+/K+-activated adenosine triphosphatase and cerebrospinal fluid formation. Neurosurgery 17:768-772.
Preston, J. E., Sutherland, G., and Finsten, A. (1993). Three openings of the blood-brain barrier produced by forebrain ischemia in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 149:75-78.
Pulsinelli, W. A., Brierly, J. B., and Plum, F. (1982). Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann. Neurol. 11:491-498.
Riegler, M., Sedivy, R., Sogukoglu, T., Cosentini, E., Bischof, G., Teleky, B., Feil, W., Schiessel, R., Hamilton, G., and Wenzl, E. (1997). Effect of growth factors on epithelial restitution of human colonic mucosa in vitro. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 32:925-932.
Schreiber, G., and Aldred, A. (1990). Pathophysiological aspects of plasma protein formation in the choroid plexus. In Johansson, B., Owman, C., and Widner, H. (eds.), Pathophysiology of the Blood-Brain Barrier, Elsevier, New York, pp. 89-102.
Smith, Q. R., and Johanson, C. E. (1980). Effect of ouabain and potassium on ion concentrations in the choroidal epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. 238:F399-F406.
Smith, Q. R., and Johanson, C. E. (1991). Chloride efflux from isolated choroid plexus. Brain Res. 562:306-310.
Solem, M., Rawson, C., Lindburg, K., and Barnes, D. (1990). Transforming growth factor beta regulates cystatin C in serum-free mouse embryo (SFME) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 172:945-951.
Spector, R., and Johanson, C. E. (1989). The mammalian choroid plexus. Sci. Am. 261:68-74.
Stopa, E. G., Gonzalez, A. M., Chorsky, R., Corona, R. J., Alvarez, J., Bird, E. D., and Baird, A. (1990). Aneurotrophic role for basic fibroblast growth factor in Alzheimer' disease. In Igbal, K., McLachlan, D. R. C., Winblad, B., and Wisniewski, H. M. (eds.), Alzheimer' Disease: Basic Mechanism, Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies, John Wiley and Sons, New York, Chap. 37.
Takami, K., Iwane, M., Kiyota, Y., Miyamoto, M., Tsukuda, R., and Shiosaka, S. (1992). Increase of basic fibroblast growth factor immunoreactivity and its mRNA level in rat brain following transient forebrain ischemia Exp. Brain Res. 90:1-10.
Valentino, K. L., Pham, H., Ocrant, I., and Rosenfeld, R. G. (1988). Distribution of insulin-like growth factor II receptor immunoreactivity in rat tissues. Endocrinology 122:2753-2763.
Vega, J. A., Del Valle, M. E., Calzada, B., Bengoechea, M. E., and Perez-Casas, A. (1992). Expression of nerve growth factor receptor immunoreactivity in the rat choroid plexus. Cell. Mol Biol. 38:145-149.
Wanaka, A., Johnson, E. M., Jr., and Milbrandt, J. (1990). Localization of FGF receptor mRNA in the adult rat central nervous system by in situ hybridization. Neuron 5:267-281.
Yanaka, A., Muto, H., Fukutomi, H., Ito, S., and Silen, W. (1996). Role of transforming growth factor-β in the restitution of injured guinea pig gastric mucosa in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 271:G75-G85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johanson, C.E., Palm, D.E., Primiano, M.J. et al. Choroid Plexus Recovery After Transient Forebrain Ischemia: Role of Growth Factors and Other Repair Mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 197–216 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007097622590
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007097622590